Fleas, Lice and Scabies - Management of Patients. Ref IPC v1.1. Status: Approved Document type: Approved document
|
|
|
- Shanna Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fleas, Lice and Scabies - Management of Patients Ref IPC v1.1 Status: Approved Document type: Approved document
2 Contents 1. Purpose Related documents Fleas What do fleas look like? How do fleas affect people? Fleas of particular importance Housekeeping and control measures - fleas Lice What do lice look like? Head lice Pubic lice Body lice How do lice affect people? Head lice Pubic lice Body lice Housekeeping and control measures - lice Head lice Pubic lice Body lice Dealing with clothing and linen Why deal with clothing and linen How to deal with clothing For pubic lice and head lice normal washing of patients clothing is sufficient How to deal with linen Hair disinfection Why carry out hair disinfection? Hair disinfection equipment checklist How to carry out hair disinfection Scabies (sarcoptes scabiei) What are scabies? How do scabies affect people? Lesions caused by scabies Topical preparations for treating scabies Managing and treating scabies Individual treatment IPC v1.1 Page 2 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
3 Group treatment Treating crusted scabies Additional information Definitions References and further reading Document control Examples of fleas and lice IPC v1.1 Page 3 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
4 1. Purpose This procedure describes what to do when managing patients with human infestation, from scabies, lice and fleas. 2. Related documents This procedure describes what you need to do to implement the Fleas, Lice and Scabies section of the Infection Prevention and Control Policy The Standard (Universal) Precautions for Infection Prevention and Control defines the universal standards for IPC which you must read, understand and be trained in before carrying out the procedures described in this document. This procedure also refers to:- Laundering and safe handling of linen and clothing Protective clothing and equipment Disposal of Clinical Waste Policy IPC v1.1 Page 4 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
5 3. Fleas 3.1. What do fleas look like? Adult fleas are between 1-3mm long, brownish-red in colour and are wingless. Their bodies are compressed from side to side, helping them move easily through fur and hair. They have well-developed hind legs for running and jumping. Flea eggs are pearl white in colour, oval shaped and approximately 0.5mm long How do fleas affect people? UK fleas do not usually transmit disease. Flea bites are identified as a small dark red spot surrounded by a reddened area. Flea bites last 2-3 days and can be intensely itchy. Some people can become immune to flea bites. Others can become hypersensitive to flea bites. Fleas are normally host specific e.g. a dog flea will only reproduce on a dog, but they will feed on an alternative host Fleas of particular importance Cephalides Canis - dog flea. Ctenocephalides Felis - cat flea. Pulex Irritans - the human flea (this is now uncommon). IPC v1.1 Page 5 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
6 3.4. Housekeeping and control measures - fleas Remove all bedding and seal in a water soluble bag. Send to laundry facility:- Place into a water soluble bag and secure Place into a laundry bag and secure Label "Infected clothes" and ward name Send to laundry facility For clothing, see Laundering and safe handling of linen and clothing. There is not specific treatment for the patient other than bathing and clean clothes. Contact Hotel Services on , mobile or fax to arrange for a Pest Control contractor to advise or carry out an eradication programme if environmental contamination is suspected. Vacuum floors, carpets, upholstery etc and treat with a residual insecticide if necessary. The Pest Control Contractor will arrange to treat inaccessible areas, i.e. ducting, under fixtures etc with residual insecticide if necessary. Members of the family or close contacts of the home environment should seek advice from their General Practitioner. IPC v1.1 Page 6 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
7 4. Lice Lice are parasitic insects that feed on human blood. Humans can host 3 different types of louse:- Pediculus Humanus - Capitis - (head louse). Pediculus Humanus - Corporis - (body/clothing louse). Phthirius Pubis - (pubic louse) What do lice look like? Head lice 2-3mm long, grey white in colour, wingless, elongated body. Mainly found near the scalp but may occur in armpits, beards, eyelashes and eyebrows. Eggs (nits) are pinhead size, oval in shape and take 5-10 days to hatch. Transmitted by head-to-head contact Pubic lice Crablike in appearance. White to brownish in colour and oval shaped. Found in the pubic hair and may be detected by the presence of black powder in under clothes and severe skin irritation. May infect body hair e.g. beards, eyebrows and sparse hair on the head of elderly men. Transmitted by close direct contact usually sexual contact Body lice Larger than head and pubic lice. Can be found anywhere on the body, especially around the waist and under the armpits. Lay eggs in clothing. Transmitted by person-to-person contact. IPC v1.1 Page 7 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
8 4.2. How do lice affect people? Head lice Head lice feel like a tickling sensation along the scalp, with the feeling that something is moving around in the hair. As the head louse bites the scalp, there is itching. This is an allergic reaction to the saliva. Sores can develop from constantly scratching the head. Bacteria can spread from fingers to scalp causing an infection Pubic lice Some people can have pubic lice without any symptoms. Most people complain of intense itching that becomes worse at night. The bites of pubic lice can cause blue-gray marks on the inner thighs and pubic area Body lice Symptoms include:- o constant and intense itching o a rash that looks like small welts. Itching is most intense around the waist, groin, and thighs. If a patient has had body lice for a long time, infection can darken and thicken the skin. IPC v1.1 Page 8 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
9 4.3. Housekeeping and control measures - lice Head lice Affected area Action required Patient Hair disinfection (see section 6). Clothing Bedding Environment Routine laundering Routing laundering Routine cleaning Pubic lice Affected area Action required Patient Hair disinfection (see section 6). Apply the appropriate lotion directly to the pubic hair, between the legs and around the anus, according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Aqueous solutions are recommended as other types may be painful. Clothing Bedding Environment Partner Routine laundering Routing laundering Routine cleaning Advise sexual partner to attend GP for advice if appropriate Patient s consent given Body lice Affected area Patient Clothing Action required No specific treatment except bathing and putting on clean clothes See Laundering and safe handling of linen and clothing Bedding Place into a water soluble bag and secure. Place into a laundry bag and secure. Label "Infected Linen" and ward name. Send to laundry facility. Environment No specific action needed Family and close contacts It may be necessary to advise them to seek advice from their GP. If appropriate patient s consent given IPC v1.1 Page 9 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
10 5. Dealing with clothing and linen 5.1. Why deal with clothing and linen To prevent the spread of ectoparasites to other patients and health care workers How to deal with clothing For Body Lice only Event Action required When removing the patient s clothing. Wear gloves and aprons.(body lice only). Destroying clothing. Check clothes as valuables may be sewn into linings. It is rarely necessary to destroy patient s clothing. If destruction is advised, obtain the patient's or relative's written permission. If the patient/resident refuses permission to destroy the clothes Seal the clothes in a plastic bag and return to relatives; Advise them how to clean the clothes to effectively kill lice and eggs: o Wash at a temperature of 60 o C for longer than 15 minutes. o Or turn dry clothes inside out and tumble dry for at least 45 minutes on a hot setting, then wash as normal. o Or turn clothes inside out and dry clean. When sending clothing to the laundry Notify the laundry and make arrangements for delivery: Place into a water soluble bag and secure; Place into a laundry bag and secure; Label "Infected clothes" and ward name; Send to laundry facility. Heat labile clothes may be damaged during the heat process in the laundry. Make patients aware of this and obtain written permission to cover the event of clothes being damaged. For pubic lice and head lice normal washing of patients clothing is sufficient. IPC v1.1 Page 10 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
11 5.3. How to deal with linen Bedding: o Place bedding into a water soluble bag and secure; o Place into a laundry bag and secure; o Label "Infected Linen" and ward name; o Send to laundry facility. 6. Hair disinfection 6.1. Why carry out hair disinfection? To remove lice and nits from the scalp and hair To prevent secondary infections from scratching and skin conditions such as impetigo etc. To prevent infection to other patients and health care workers Hair disinfection equipment checklist Apron and gloves (for nurse) Towels Disposable polythene sheet (to protect patient and bed if patient is bed-ridden) Prescribed lotion Lice detection comb 6.3. How to carry out hair disinfection Tactfully explain to the patient the procedure and the reason for it. Ensure the patient is comfortable and privacy provided (the bathroom is preferable). Ensure the area is well ventilated. Apply lotion and leave on the hair as per the manufacturer's instructions (do not dry with a hair dryer and keep away from heat) After the recommended time comb the hair to remove dead lice, then shampoo. The patient may feel more comfortable having clean night clothes and bedding. Treatment must be repeated after 7 days using the same preparation. IPC v1.1 Page 11 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
12 For children under 6 months of age, or children with allergic conditions, asthma etc. contact Phamarcy for advice. The Pharmacist will recommend the current treatment as outlined within Clinical Knowledge Summaries headlice and scabies. The same preparations may be used for pubic lice. Ensure contact tracing is completed thoroughly to identify any close contacts that may require treatment (this is usually over a 4-8 week period). 7. Scabies (sarcoptes scabiei) 7.1. What are scabies? The "itch" mite responsible for scabies is mm and only just visible as a white spot with a chestnut-coloured head. The female mite tunnels into the skin and deposits eggs. The tunnels may occur anywhere but most commonly affect arms, wrists, hands, particularly in the finger webs, underarms, nipples and genitals. The mite does not fly or jump and it is blind. It will not survive for long away from the host. Scabies is a common public health problem with an estimated global prevalence of 300 million. The incidence of Scabies varies over time. Epidemics occur at approximately 30 year intervals and persist for about 15 years How do scabies affect people? Symptoms Intense itching (especially at night) caused by an allergy to chemicals found in the excrement of the scabies mite; Eczematous rash; Itching does not start immediately but usually within 1-8 weeks after infection occurs. Transmission Contact through care by nurses and other carers (these staff may not always show classical signs); Skin to skin contact e.g., sleeping together, holding hands, sexual contact. The mite does not jump from person to person. IPC v1.1 Page 12 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
13 Identification 70% of mites are found on the hands, usually between the fingers, the wrists, but may be found on other areas of the body; Sometimes in children under two years, they can be found on the soles of the feet; If there is difficulty in diagnosis, skin scrapings can help confirm the presence of mites. This should only be carried out by a trained, experienced dermatologist or public health staff Lesions caused by scabies Type of lesion Identification Primary lesion These are the burrows followed by the Scabies rash which is a follicular, papular rash on body areas such as upper arms, middle trunk, inner upper thigh and anterior aspect of the wrist. May also be found in other less-common areas. The rash can be very dense around the axilla, abdomen and on penile areas blister like spots can form. Intense itching may occur particularly at night when warm in bed. This is due to the mite sensitising the skin of the person. Diagnosis is confirmed by finding the mites or their eggs at the end of their threadlike tunnel or burrow. Secondary lesion Can take the form of excoriation, eczematous areas and secondary infections. Crusted scabies Can be seen in immunosuppressed clients, learning disability homes and in the elderly population. Usually presents in the form of crusted lesions found mainly around the wrist areas but can also affect other parts of the body. An erythematous rash is usually found covering the body. Thousands of mites can be present, capable of disseminating into the immediate environment. Can live for 1-2 days in warm conditions. A confirmed diagnosis from a Dermatologist is essential to ensure that clients are not being treated for other skin conditions, as this can lead to much distress for the client and the carer. For example, steroid treatment may make scabies unrecognisable and does not improve the eczematous response. There is a small risk of infection through upholstered furniture, particularly in communal areas, e.g. in nursing and residential homes. IPC v1.1 Page 13 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
14 7.3. Topical preparations for treating scabies Name Lyclear Dermal Cream (permethrin 5%) Description Low toxicity. 8 hour treatment. Babies and children under 2 years to be treated under medical supervision. From 2 months to 2 years only use 1/8 th of a tube. Repeat treatment after 7 days Derbac M (Malathion) 24 hour treatment. Children under 2 years to be treated under medical supervision. Repeat treatment after 7 days. Benzyl Benzoate 24 hour treatment. Not recommended for children. It is an irritant and is therefore to be used with care under medical supervision. Itching can persist for some time after treatment. An anti-pruritic cream is helpful on intense areas of itching (e.g. Eurax) Managing and treating scabies Individual treatment After diagnosis and prescribing of treatment, cream or lotion is best applied in the evening before retiring to bed. Cream or lotion must be applied to cool dry skin to be most effective. All body areas from the neck down, including the palms of the hands and soles of the feet must have the cream/lotion applied. Cream/lotion must be re-applied to any parts of the body which have been washed off (e.g. hands). Clients under 2 years or over 65 years need the scalp and behind the ear lobes treated. Mites can harbour themselves under the nails. Ensure nails are cut and clean. After treatment (8 or 24 hours - check manufacturer s guidance) shower or bath as normal. After washing off treatment provide clean clothes and clean bed linen. Clothes can be washed as normal. All close family contacts of scabies to be treated whether a rash is present or not. In health care situations it is important to perform an assessment before others are given treatment. A hot shower or bath before application is not recommended. Do not put the same clothes back on Group treatment It is important that an outbreak is managed by treating all clients, staff and close relatives at the same time. IPC v1.1 Page 14 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
15 When an outbreak is confirmed (2 or more cases) arrangements must be made for treatment to take place at a specified time and date. It is reasonable and advisable to delay treatment until plans have been properly made. Symptomatic relief can be given to clients, if required. Treat individuals as previously described (7.4.1). Remove slippers from clients and wash if appropriate. Where this is not possible, place the slippers in a tied bag for 24 hours. They can then be used as normal. Remove any pots of cream from the client s room which are used on a day-to-day basis and destroy (e.g. creams for dry skin). Treat all close contacts of infected clients. This would normally include family, staff, visitors and agency staff. This will be determined by IPCNs and OHD staff. After treatment, follow as per individual cases. A second treatment may be required in some cases but this requires assessment Treating crusted scabies Three treatments are required 24 hours apart for all cases of crusted scabies. This also includes scalp treatment. Clean the client s room thoroughly (good vacuum and use of detergent and water), paying particular attention to all upholstered areas such as chairs, bed heads and curtains. Communal areas such as the sitting room and dining areas must also be cleaned thoroughly. All bed linen must be washed at the highest temperature possible for the articles. If linen is not laundered on site, it should be placed in a red dissolvable bag, into an outer linen bag and despatched to the laundry. Follow up is essential after one week to ensure that no further treatment is required Additional information Apart from crusted scabies laundry can be washed in the normal way. Identical mites can be found on domestic and stray animals. It is vital to advise on general health associated with diet, and to ensure adequate intake of minerals and vitamins (particularly vitamin A). Education is an important element for clients, staff and their relatives and friends. Keep fingernails smooth, rounded and short to prevent traumatising the skin when scratching. IPC v1.1 Page 15 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
16 8. Definitions Term Ectoparasites Ectoparasitosis Definition A parasite that lives on or in the skin but not within the body. Fleas and lice are ectoparasites. Infestation with an ectoparasite 9. References and further reading WILLIS, J. (1990) Common Pests. Community Outlook. Sept. pp UNIVERSITY OF YORK (1999) Treating Head Lice and Scabies Foundation, Effectiveness Matters, Vol. 4, Issue1. MAUNDER, J. Headlice - Recognising The Signs. Reprinted from the Chemist and Druggist (Personal copy). MAUNDER, J. (1989) Refractory Pseudo-Scabies. The Practitioner. Vol.233, pp MAUNDER, J. (1995) Scabies Update. Medical Entomology Centre. Cambridge. NHS Library CKS 2008 Treatment Guidelines Headlice JENKINS, M. (2001) Scabies. Nursing Times Plus. Vol. 97, No. 22. LAWRENCE J & MAY D (2003) Infection Prevention and Control in the Community (Chapter 13 pp Churchill/Livingston. London & Edinburgh WALKER J. A. & JOHNSTONE P.W. (2000) Interventions for Treating Scabies. Cochrane Library issue 3 Department of Health (2006) The Health Act 2006 Code of Practice for the Prevention and Control of Health Care Associated Infection London DH IPC v1.1 Page 16 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
17 10. Document control Next review date: 7 March 2016 This document replaces: Lead: Name Title IC/0012/v4 Management of Patients with Human Infestations (Fleas, Lice and Scabies) Angela Ridley Members of working party: Name Title This document has been agreed and accepted by: (Director) This document was approved by: Angela Ridley Alexia Hardy Andrea Brodie David Elders Julie Southern Name Chris Stanbury Date Senior Nurse IPC and Physical Health and Back Care Senior Nurse IPC and Physical Health and Back Care Senior Nurse Information Mapping and Policy Development Manager Policy Project Facilitators Title 7 March 2013 QuAC Director of Nursing and Governance Name of committee/group An equality analysis was completed on this document on: Amendment details: 27 May 2011 Change record Version Date Amendment details Status Mar 2013 New document Ratified Nov 2015 Hotel services contact details amended Minor amendment IPC v1.1 Page 17 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
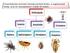
18 11. Examples of fleas and lice Lifecycle of a louse Head louse Body louse Egg (nit) Flea Scabie Mite Pubic louse IPC v1.1 Page 18 of 18 Ratified date: 7 March 2013
Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care
 Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Scabies Version 1.01 May 2015 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Scabies May 2015 Version 1.01 Page 1 of 10 Please
Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Scabies Version 1.01 May 2015 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Scabies May 2015 Version 1.01 Page 1 of 10 Please
ECTOPARASITIC INFESTATIONS / INFECTIONS: FLEAS, LICE AND MITES (SCABIES) PROCEDURE
 Reference Number: UHB 275 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: 23 rd June 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: 141 ECTOPARASITIC INFESTATIONS / INFECTIONS: FLEAS, LICE AND MITES (SCABIES) PROCEDURE
Reference Number: UHB 275 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: 23 rd June 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: 141 ECTOPARASITIC INFESTATIONS / INFECTIONS: FLEAS, LICE AND MITES (SCABIES) PROCEDURE
There are three types of lice: Body lice (Pediculus humanus corporis) Larger in size than head or pubic lice Live in seams of clothing
 Lice (head, body, pubic) and Scabies What are they? Lice are small parasites that live entirely on humans. Pediculosis is the term for an infestation of lice. The female lice hold on to skin or hairs and
Lice (head, body, pubic) and Scabies What are they? Lice are small parasites that live entirely on humans. Pediculosis is the term for an infestation of lice. The female lice hold on to skin or hairs and
Scabies Identification, Treatment and Environmental Cleaning
 Scabies Identification, Treatment and Environmental Cleaning Level III Purpose The purpose of this procedure is to treat residents infected with and sensitized to Sarcoptes scabiei and to prevent the spread
Scabies Identification, Treatment and Environmental Cleaning Level III Purpose The purpose of this procedure is to treat residents infected with and sensitized to Sarcoptes scabiei and to prevent the spread
SCABIES. Signs and symptoms
 SCABIES Scabies is caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which burrows into the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Scabies is a contagious skin infection that spreads rapidly in crowded conditions
SCABIES Scabies is caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which burrows into the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Scabies is a contagious skin infection that spreads rapidly in crowded conditions
IPC-PGN-13.5 Part of NTW(C)23 Infection, Prevention and Control Policy
 Infection Prevention and Control Practice Guidance Note Scabies V03 Date issued Issue 1 Apr 15 Planned review April 2018 IPC-PGN-13.5 Part of NTW(C)23 Infection, Prevention and Control Policy Author/Designation
Infection Prevention and Control Practice Guidance Note Scabies V03 Date issued Issue 1 Apr 15 Planned review April 2018 IPC-PGN-13.5 Part of NTW(C)23 Infection, Prevention and Control Policy Author/Designation
Replacement. Status: Replacing: Policy for the Management of Parasitic Infestations Version: V 1.0 Date: August 2015
 Clinical Parasitic Infestations, SOP Document Control Summary Replacement. Status: Replacing: Policy for the Management of Parasitic Infestations Version: V 1.0 Date: August 2015 Author/Owner: Judy Carr
Clinical Parasitic Infestations, SOP Document Control Summary Replacement. Status: Replacing: Policy for the Management of Parasitic Infestations Version: V 1.0 Date: August 2015 Author/Owner: Judy Carr
The most up-to-date version of this policy can be viewed at the following website:
 Page 1 of 9 Review SOP Objective To ensure that patients with head lice are cared for appropriately and actions are taken to minimise the risk of cross-infection. This SOP applies to all staff employed
Page 1 of 9 Review SOP Objective To ensure that patients with head lice are cared for appropriately and actions are taken to minimise the risk of cross-infection. This SOP applies to all staff employed
HEAD LICE. The most up-to-date version of this policy can be viewed at the following website:
 Page Page 1 of 9 Policy Objective To ensure that patients with head lice are cared for appropriately and actions are taken to minimise the risk of cross-infection. This policy applies to all staff employed
Page Page 1 of 9 Policy Objective To ensure that patients with head lice are cared for appropriately and actions are taken to minimise the risk of cross-infection. This policy applies to all staff employed
Frequently asked questions about. Scabies. From the Branch-Hillsdale-St. Joseph Community Health Agency
 Frequently asked questions about Scabies From the Branch-Hillsdale-St. Joseph Community Health Agency What is scabies? Scabies is an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var.
Frequently asked questions about Scabies From the Branch-Hillsdale-St. Joseph Community Health Agency What is scabies? Scabies is an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var.
Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: TREATMENT OF PEDICULOSIS (LICE) AND SCABIES
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 412 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: TREATMENT OF PEDICULOSIS (LICE) AND SCABIES 1. PURPOSE: This
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 412 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: TREATMENT OF PEDICULOSIS (LICE) AND SCABIES 1. PURPOSE: This
OAK HILL ACADEMY Policy on Lice
 1 OAK HILL ACADEMY Policy on Lice If a child is suspected to have nits or lice during the school day, the child will be checked by the nurse. If it is determined that the child has nits or lice, they will
1 OAK HILL ACADEMY Policy on Lice If a child is suspected to have nits or lice during the school day, the child will be checked by the nurse. If it is determined that the child has nits or lice, they will
Policy Document Control Page. Designation: Infection Prevention & Control Specialist
 Policy Document Control Page Title Title: Management of Head, Body and Pubic Lice Policy Version: 6 Reference Number: CL74 Supersedes Supersedes: V5 Amendments: Specific treatment medications removed Originator
Policy Document Control Page Title Title: Management of Head, Body and Pubic Lice Policy Version: 6 Reference Number: CL74 Supersedes Supersedes: V5 Amendments: Specific treatment medications removed Originator
HEAD LICE. What are head lice? Who is at risk for getting head lice?
 HEAD LICE What are head lice? The head louse, or Pediculus humanus capitis, is a parasitic insect that can be found on the head, eyebrows, and eyelashes of people. Head lice feed on human blood several
HEAD LICE What are head lice? The head louse, or Pediculus humanus capitis, is a parasitic insect that can be found on the head, eyebrows, and eyelashes of people. Head lice feed on human blood several
NITS AND ITCHY BITS. (Table 1)
 NITS AND ITCHY BITS Head Lice(Pediculosis Cipitis): Children are often brought to the surgery complaining of itchy scalps. Parents will usually have already thought of Head Lice and applied a number of
NITS AND ITCHY BITS Head Lice(Pediculosis Cipitis): Children are often brought to the surgery complaining of itchy scalps. Parents will usually have already thought of Head Lice and applied a number of
Policy Document Control Page
 Policy Document Control Page Title Title: Management of Scabies Policy Version: 6 Reference Number: CL80 Supersedes Supersedes: Version 5 Alterations Specific treatment/medications removed Updated references
Policy Document Control Page Title Title: Management of Scabies Policy Version: 6 Reference Number: CL80 Supersedes Supersedes: Version 5 Alterations Specific treatment/medications removed Updated references
SECTION 10.3 SCABIES
 SECTION 10.3 SCABIES Scabies: General Information Scabies: How is it Treated? Scabies: Diagnosis and Treatment for Health Professionals Scabies: Management of Scabies in Health and Social Care Settings
SECTION 10.3 SCABIES Scabies: General Information Scabies: How is it Treated? Scabies: Diagnosis and Treatment for Health Professionals Scabies: Management of Scabies in Health and Social Care Settings
What Is Scabies? Learning how to manage the spread of the human itch mite Sarcoptes scabiei
 What Is Scabies? Learning how to manage the spread of the human itch mite Sarcoptes scabiei IMPORTANT Scabies is a human itch mite infection that causes a rash and itching. It can vary in how long it lasts
What Is Scabies? Learning how to manage the spread of the human itch mite Sarcoptes scabiei IMPORTANT Scabies is a human itch mite infection that causes a rash and itching. It can vary in how long it lasts
Scabies is a very common skin condition caused by an infestation of mites.
 Scabies is a very common skin condition caused by an infestation of mites. The most common symptom is a very itchy rash, which may increase in severity if left untreated. Prescription topical creams and
Scabies is a very common skin condition caused by an infestation of mites. The most common symptom is a very itchy rash, which may increase in severity if left untreated. Prescription topical creams and
Scabies. Dr. Ghassan Salah
 Scabies Dr. Ghassan Salah Scabies Scabies is a skin infestation caused by a mite Causes: The female scabies mite (Sarcoptes scabei ) burrows through the stratum corneum of the skin and lays its eggs just
Scabies Dr. Ghassan Salah Scabies Scabies is a skin infestation caused by a mite Causes: The female scabies mite (Sarcoptes scabei ) burrows through the stratum corneum of the skin and lays its eggs just
Occupational Health and Safety Unit. Preventing, treating and controlling head lice in the community
 Originator : OHSU/cmm Date: January 2010 Occupational Health and Safety Unit Working with you for a safer, healthier future Preventing, treating and controlling head lice in the community Contents Page
Originator : OHSU/cmm Date: January 2010 Occupational Health and Safety Unit Working with you for a safer, healthier future Preventing, treating and controlling head lice in the community Contents Page
Public Schools Branch
 Public Schools Branch Pediculosis (Head Lice) Management Protocol General Information Head lice are tiny insects that live only on the scalp of human beings and are the size of a pinhead. They do not have
Public Schools Branch Pediculosis (Head Lice) Management Protocol General Information Head lice are tiny insects that live only on the scalp of human beings and are the size of a pinhead. They do not have
Main Title. Head Lice 101. Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities
 Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
Main Title. Head Lice 101. An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities. Description
 Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
Balhousie School Presentation
 Balhousie School Presentation Presented by: Paula Muir Subject leader Hairdressing www.perth.uhi.ac.uk Perth College is a registered Scottish charity, number SC021209. Head Lice Aims Our aim today is to
Balhousie School Presentation Presented by: Paula Muir Subject leader Hairdressing www.perth.uhi.ac.uk Perth College is a registered Scottish charity, number SC021209. Head Lice Aims Our aim today is to
Main Title. Head Lice 101 Description. An Overview for Parents, Teachers and Communities
 Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers and Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers and Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
W - WHO IS THE PATIENT H HOW LONG HAS THIS BEEN OCCURRING. Self Care
 HEAD LICE Possible head lice infestation Head lice are acquired from other infected people, mainly by direct head-to-head contact. Empty egg sacs are white and shiny and may be found further along the
HEAD LICE Possible head lice infestation Head lice are acquired from other infected people, mainly by direct head-to-head contact. Empty egg sacs are white and shiny and may be found further along the
Severe itching (pruritus), especially at night; a pimple-like (papular) itchy (pruritic) is also common
 Typical Scabies vs Crusted Scabies Human scabies is caused by an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis). The adult female scabies mites burrow into the upper layer
Typical Scabies vs Crusted Scabies Human scabies is caused by an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis). The adult female scabies mites burrow into the upper layer
Protocol for the Management and Control of Infestations
 Protocol for the Management and Control of Infestations Policy Number: Version: V2.0 Authorisation Committee: Clin.2.0 Appendix D Date of Authorisation: 03/03/2011 Name and Job Title of Authors: Name of
Protocol for the Management and Control of Infestations Policy Number: Version: V2.0 Authorisation Committee: Clin.2.0 Appendix D Date of Authorisation: 03/03/2011 Name and Job Title of Authors: Name of
Once a Week, Take a Peek! (Head Lice Advice)
 Once a Week, Take a Peek! (Head Lice Advice) Within most schools at any one time, there will be a small number of children infected with head lice. Infection levels remain fairly constant so we need your
Once a Week, Take a Peek! (Head Lice Advice) Within most schools at any one time, there will be a small number of children infected with head lice. Infection levels remain fairly constant so we need your
What Are Lice, Scabies, and Bed Bugs?
 A collaborative effort of Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC and The Pennsylvania Child Welfare Resource Center What Are Lice, Scabies, and Bed Bugs? Lice, scabies, and bed bugs affect people all
A collaborative effort of Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC and The Pennsylvania Child Welfare Resource Center What Are Lice, Scabies, and Bed Bugs? Lice, scabies, and bed bugs affect people all
The school nurse has 4 goals
 Head Lice The school nurse has 4 goals Prevent / contain the spread of lice in the school setting Educate parents to prevent, recognize and treat head lice Minimize school absence Prevent children from
Head Lice The school nurse has 4 goals Prevent / contain the spread of lice in the school setting Educate parents to prevent, recognize and treat head lice Minimize school absence Prevent children from
Once a Week, Take a Peek! (Head Lice Advice)
 Once a Week, Take a Peek! (Head Lice Advice) Within most schools at any one time, there will be a small number of children infected with head lice. Infection levels remain fairly constant so we need your
Once a Week, Take a Peek! (Head Lice Advice) Within most schools at any one time, there will be a small number of children infected with head lice. Infection levels remain fairly constant so we need your
Nits (Eggs) Smaller than lice but easier to detect. Each nit is attached firmly to a single hair strand with a gluelike
 HEAD LICE (PEDICULOSIS)........ KEEP ON TRACK Head lice are tiny insects that are about one to two mm (one-eighth of an in.) long. They have special mouth parts for piercing the human scalp. The scalp
HEAD LICE (PEDICULOSIS)........ KEEP ON TRACK Head lice are tiny insects that are about one to two mm (one-eighth of an in.) long. They have special mouth parts for piercing the human scalp. The scalp
Rawmarsh Sandhill Primary School. Headlice Policy
 Rawmarsh Sandhill Primary School Headlice Policy Updated January 2018 Aim of this policy. Rawmarsh Sandhill Primary School is aware of the national problem of headlice and how it can sometimes affect children
Rawmarsh Sandhill Primary School Headlice Policy Updated January 2018 Aim of this policy. Rawmarsh Sandhill Primary School is aware of the national problem of headlice and how it can sometimes affect children
The Facts. about. Head Lice
 The Facts about Head Lice Further copies of this leaflet are available FREE from: Publications Centre The National Assembly for Wales Cathays Park Cardiff CF10 3NQ Tel: (029) 2082 3683 Fax: (029) 2082
The Facts about Head Lice Further copies of this leaflet are available FREE from: Publications Centre The National Assembly for Wales Cathays Park Cardiff CF10 3NQ Tel: (029) 2082 3683 Fax: (029) 2082
BEDBUGS, SCABIES AND HEAD LICE OH MY! Dermatologists address the growing incidence of parasitic infestations linked to skin and hair problems
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE BEDBUGS, SCABIES AND HEAD LICE OH MY! Dermatologists address the growing incidence of parasitic infestations linked to skin and hair problems MIAMI (March 4, 2010) If simply the thought
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE BEDBUGS, SCABIES AND HEAD LICE OH MY! Dermatologists address the growing incidence of parasitic infestations linked to skin and hair problems MIAMI (March 4, 2010) If simply the thought
SCOTT COUNTY AREA SCHOOLS & COMMUNITY HEAD LICE MANAGEMENT PLAN
 SCOTT COUNTY AREA SCHOOLS & COMMUNITY HEAD LICE MANAGEMENT PLAN DEVELOPED BY SCOTT COUNTY KIDS HEALTH COMMITTEE With representatives from Bettendorf Community School District Davenport Community School
SCOTT COUNTY AREA SCHOOLS & COMMUNITY HEAD LICE MANAGEMENT PLAN DEVELOPED BY SCOTT COUNTY KIDS HEALTH COMMITTEE With representatives from Bettendorf Community School District Davenport Community School
Panic Pests - Head Lice. Shujuan (Lucy) Li University of Arizona
 Panic Pests - Head Lice Shujuan (Lucy) Li University of Arizona Head Lice Blood feeding ectoparasites associated with the scalp. More commonly found in school age students (3-11 years old) and girls. Transfer
Panic Pests - Head Lice Shujuan (Lucy) Li University of Arizona Head Lice Blood feeding ectoparasites associated with the scalp. More commonly found in school age students (3-11 years old) and girls. Transfer
ADMINISTRATIVE PROCEDURE
 ADMINISTRATIVE PROCEDURE B1:4 School Operations Safety and Security Pediculosis in Schools Page 1 of 9 1. Purpose: To ensure that issues and procedures related to pediculosis (head lice) are dealt with
ADMINISTRATIVE PROCEDURE B1:4 School Operations Safety and Security Pediculosis in Schools Page 1 of 9 1. Purpose: To ensure that issues and procedures related to pediculosis (head lice) are dealt with
Pest Control Policy. Policy PROV 55 July 2010
 Pest Control Policy Policy PROV 55 July 2010 Document Management Title of document Pest Control Policy Type of document Policy PROV 55 Description Target audience Author Department Directorate Approved
Pest Control Policy Policy PROV 55 July 2010 Document Management Title of document Pest Control Policy Type of document Policy PROV 55 Description Target audience Author Department Directorate Approved
Pediculosis Procedures & Resources Guidebook
 Attachment 2 RES Item 7.4 January 12, 2012 KAWARTHA PINE RIDGE DISTRICT SCHOOL BOARD Pediculosis Procedures & Resources Guidebook (To Support Board Policy No. ES-1.2, Pediculosis in Schools) Head Lice
Attachment 2 RES Item 7.4 January 12, 2012 KAWARTHA PINE RIDGE DISTRICT SCHOOL BOARD Pediculosis Procedures & Resources Guidebook (To Support Board Policy No. ES-1.2, Pediculosis in Schools) Head Lice
Chapter 18. Grooming. All items and derived items 2015, 2011 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 18 Grooming Grooming Hair care, shaving, and nail and foot care: Prevent infection and promote comfort Affect love, belonging, and self-esteem needs 2 Hair Care You assist with hair care whenever
Chapter 18 Grooming Grooming Hair care, shaving, and nail and foot care: Prevent infection and promote comfort Affect love, belonging, and self-esteem needs 2 Hair Care You assist with hair care whenever
HEAD LICE (Pediculus Humanus Capitis)
 What are head lice and some facts? HEAD LICE (Pediculus Humanus Capitis) Head lice are annoying parasitic insects that live in the hair and on the scalp of humans. They are about the size of a sesame seed
What are head lice and some facts? HEAD LICE (Pediculus Humanus Capitis) Head lice are annoying parasitic insects that live in the hair and on the scalp of humans. They are about the size of a sesame seed
Handbook regarding Lice Management
 Handbook regarding Lice Management 2009-2010 School Year Information provided by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention http://www.cdc.gov/ 1 P a g e This Package Contains the Following: Fact Sheet
Handbook regarding Lice Management 2009-2010 School Year Information provided by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention http://www.cdc.gov/ 1 P a g e This Package Contains the Following: Fact Sheet
FACTS & MYTHS ABOUT HEAD LICE
 FACTS & MYTHS ABOUT HEAD LICE Head lice are generally misunderstood. Below are facts and myths about lice. FACTS Head lice do not fly (they have no wings), jump or hop About half of all infested individuals
FACTS & MYTHS ABOUT HEAD LICE Head lice are generally misunderstood. Below are facts and myths about lice. FACTS Head lice do not fly (they have no wings), jump or hop About half of all infested individuals
ST. NINIAN S RC PRIMARY SCHOOL
 ST. NINIAN S RC PRIMARY SCHOOL NAOINEAN NAOMH: D AR N IUIL POLICY ON MANAGING HEAD LICE INFECTION IN CHILDREN Advice and Practice in line with National Guidelines April, 2003 National Guidelines on Managing
ST. NINIAN S RC PRIMARY SCHOOL NAOINEAN NAOMH: D AR N IUIL POLICY ON MANAGING HEAD LICE INFECTION IN CHILDREN Advice and Practice in line with National Guidelines April, 2003 National Guidelines on Managing
Head Lice Information
 Head Lice Information The adult head louse is 2 to 3 mm long (the size of a sesame seed), has 6 legs, and is usually tan to grayish-white in color. The female lives up to 3 to 4 weeks and, once mature,
Head Lice Information The adult head louse is 2 to 3 mm long (the size of a sesame seed), has 6 legs, and is usually tan to grayish-white in color. The female lives up to 3 to 4 weeks and, once mature,
A GUIDE TO HEAD LICE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
 A GUIDE TO HEAD LICE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT May 2018 What are Head Lice? Head lice are very small, tan-colored insects about the size of a sesame seed which live only on human heads. They live and lay
A GUIDE TO HEAD LICE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT May 2018 What are Head Lice? Head lice are very small, tan-colored insects about the size of a sesame seed which live only on human heads. They live and lay
Head Lice. KidsHealth.org. Signs of Head Lice. The most-visited site devoted to children's health and development
 KidsHealth.org The most-visited site devoted to children's health and development Head Lice The head louse is a tiny, wingless parasitic insect that lives among human hairs and feeds on tiny amounts of
KidsHealth.org The most-visited site devoted to children's health and development Head Lice The head louse is a tiny, wingless parasitic insect that lives among human hairs and feeds on tiny amounts of
LOUSEOLOGY 101. Parent Information Reed School February 9, :30 a.m.-9:30 a.m.
 LOUSEOLOGY 101 Parent Information Reed School February 9, 2011 8:30 a.m.-9:30 a.m. This program provides general information only. Consult your pediatrician with any specific questions or concerns about
LOUSEOLOGY 101 Parent Information Reed School February 9, 2011 8:30 a.m.-9:30 a.m. This program provides general information only. Consult your pediatrician with any specific questions or concerns about
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PARASITES LICE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : PARASITES LICE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 parasites lice parasites lice pdf parasites lice Head lice infestation, or pediculosis, is spread most commonly by close person-to-person
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PARASITES LICE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 parasites lice parasites lice pdf parasites lice Head lice infestation, or pediculosis, is spread most commonly by close person-to-person
Managing Head Lice in the School Setting AN OUNCE OF PREVENTION IS WORTH A POUND OF CURE
 Managing Head Lice in the School Setting AN OUNCE OF PREVENTION IS WORTH A POUND OF CURE What is Head Lice A small parasitic insect that lives on the scalp and neck hairs of a human host Originated and
Managing Head Lice in the School Setting AN OUNCE OF PREVENTION IS WORTH A POUND OF CURE What is Head Lice A small parasitic insect that lives on the scalp and neck hairs of a human host Originated and
Head lice. What they are, how to spot them and how to treat them. Facts about head lice.
 Facts about head lice. Head lice are tiny insects, which live on the hair close to the scalp. They feed from the human scalp by sucking blood from the skin. Both adults and children can get head lice.
Facts about head lice. Head lice are tiny insects, which live on the hair close to the scalp. They feed from the human scalp by sucking blood from the skin. Both adults and children can get head lice.
GRAND FORKS PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT HEAD LICE POLICY AND PROCEDURE
 GRAND FORKS PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT HEAD LICE POLICY AND PROCEDURE MEDICAL IMPACT OF HEAD LICE Pediculosis is an infestation of head lice, not an infection. It does not pose a significant health hazard
GRAND FORKS PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT HEAD LICE POLICY AND PROCEDURE MEDICAL IMPACT OF HEAD LICE Pediculosis is an infestation of head lice, not an infection. It does not pose a significant health hazard
MOIRA HOUSE GIRLS SCHOOL HEAD LICE
 Head Lice Introduction The aim of this Policy is to ensure a consistent, coordinated and cooperative approach to managing head lice in the school community. Roles and Responsibilities The Parents responsibilities
Head Lice Introduction The aim of this Policy is to ensure a consistent, coordinated and cooperative approach to managing head lice in the school community. Roles and Responsibilities The Parents responsibilities
Head lice Information for parents
 Head lice Information for parents tips Head louse eggs take up to 10 days to hatch. Baby lice take 6 14 days to become fully grown, and it is after this that they will take the opportunity to move from
Head lice Information for parents tips Head louse eggs take up to 10 days to hatch. Baby lice take 6 14 days to become fully grown, and it is after this that they will take the opportunity to move from
NOTES FOR FAMILIES. Head lice: The Truth and the Myths
 NOTES FOR FAMILIES Head lice: The Truth and the Myths The lice Head lice are small insects with six legs. They are often said to be "as large as a match head". In fact, they are often not much bigger than
NOTES FOR FAMILIES Head lice: The Truth and the Myths The lice Head lice are small insects with six legs. They are often said to be "as large as a match head". In fact, they are often not much bigger than
Having lice is embarrassing! It's associated with poor hygiene. If my kids get lice, I'm not going to tell anyone.
 LICE INFORMATION The head louse is an insect that lives and breeds on the human head. It is found worldwide and as many as 6 to 12 million people get head lice per year. Head lice do not live on pets or
LICE INFORMATION The head louse is an insect that lives and breeds on the human head. It is found worldwide and as many as 6 to 12 million people get head lice per year. Head lice do not live on pets or
Estill County 76 Golden Court Irvine, KY (606) Fax: (606)
 Estill County 76 Golden Court Irvine, KY 40336-6917 (606) 723-4557 Fax: (606) 723-5912 http://extension.ca.uky.edu When & Where: Friday, June 15 Monday, June 18 at J.M. Feltner 4-H Camp in London, KY.
Estill County 76 Golden Court Irvine, KY 40336-6917 (606) 723-4557 Fax: (606) 723-5912 http://extension.ca.uky.edu When & Where: Friday, June 15 Monday, June 18 at J.M. Feltner 4-H Camp in London, KY.
head lice Facts Detection Treatment
 head lice Facts Detection Treatment 1 Facts Head lice are six-legged wingless insects that live on the hair close to the scalp. They are the size of a pin head when they hatch and smaller than a match
head lice Facts Detection Treatment 1 Facts Head lice are six-legged wingless insects that live on the hair close to the scalp. They are the size of a pin head when they hatch and smaller than a match
headlice the facts and myths everyone s essential guide
 headlice the facts and myths everyone s essential guide The lice u Head lice are small insects with six legs. They are often said to be as large as a match head ; in fact, they are not much bigger than
headlice the facts and myths everyone s essential guide The lice u Head lice are small insects with six legs. They are often said to be as large as a match head ; in fact, they are not much bigger than
Creating the space s. St Nicholas C of E Primary School Head Lice Policy
 Headteacher: Mrs Alison Shearer B.Ed Hons, M.A, NPQH Creating the space s for your child to grow. St Nicholas C of E Primary School Head Lice Policy Rationale St Nicholas C of E Primary School is aware
Headteacher: Mrs Alison Shearer B.Ed Hons, M.A, NPQH Creating the space s for your child to grow. St Nicholas C of E Primary School Head Lice Policy Rationale St Nicholas C of E Primary School is aware
HEAD LICE INFORMATION
 HEAD LICE INFORMATION HOW DO I KNOW IF MY CHILD HAS HEAD LICE? Many head lice infections cause no symptoms, and probably less than half cause itch. So you have to LOOK to find out if your child has head
HEAD LICE INFORMATION HOW DO I KNOW IF MY CHILD HAS HEAD LICE? Many head lice infections cause no symptoms, and probably less than half cause itch. So you have to LOOK to find out if your child has head
Head Lice 101 What You Should Know About Head Lice
 Head Lice 101 What You Should Know About Head Lice Overview Head lice are a common community problem. An estimated 6 to 12 million infestations occur each year in the United States, most commonly among
Head Lice 101 What You Should Know About Head Lice Overview Head lice are a common community problem. An estimated 6 to 12 million infestations occur each year in the United States, most commonly among
Head Lice Information. Mahomet-Seymour Head Lice Policy FAQ s Helpful information if someone in your home has head lice.
 Head Lice Information Mahomet-Seymour Head Lice Policy FAQ s Helpful information if someone in your home has head lice. MAHOMET-SEYMOUR SCHOOLS UPDATED HEADLICE POLICY April 2, 2018 Evidence based practices
Head Lice Information Mahomet-Seymour Head Lice Policy FAQ s Helpful information if someone in your home has head lice. MAHOMET-SEYMOUR SCHOOLS UPDATED HEADLICE POLICY April 2, 2018 Evidence based practices
HEAD LICE. Your Questions Answered. don tbugme
 HEAD LICE Your Questions Answered don tbugme truth&lice WHAT ARE HEAD LICE? They are grey/brown insects, from pin-head to match-head in size (1 to 3 mm long) that live close to the scalp on humans. Each
HEAD LICE Your Questions Answered don tbugme truth&lice WHAT ARE HEAD LICE? They are grey/brown insects, from pin-head to match-head in size (1 to 3 mm long) that live close to the scalp on humans. Each
Head Lice Information for Parents from CDC
 Head Lice Information for Parents from CDC You should examine your child's head, especially behind the ears and at the nape of the neck, for crawling lice and nits if your child exhibits symptoms of a
Head Lice Information for Parents from CDC You should examine your child's head, especially behind the ears and at the nape of the neck, for crawling lice and nits if your child exhibits symptoms of a
By treatments.net
 Natural Scabies Treatments FFiinndd R Reelliieeff tthhee N Naattuurraall W Waayy By www.scabies- treatments.net Introduction If you have downloaded this report, you have no doubt been suffering with scabies
Natural Scabies Treatments FFiinndd R Reelliieeff tthhee N Naattuurraall W Waayy By www.scabies- treatments.net Introduction If you have downloaded this report, you have no doubt been suffering with scabies
- F - PEDICULOSIS (HEAD LICE)
 - F - PEDICULOSIS (HEAD LICE) What are they? Head lice are tiny gray insects (about 1/16 long) that live in human hair and feed on human blood. Head lice do not spread any disease. The head louse crawls
- F - PEDICULOSIS (HEAD LICE) What are they? Head lice are tiny gray insects (about 1/16 long) that live in human hair and feed on human blood. Head lice do not spread any disease. The head louse crawls
Treat the infested person(s): Requires using an Over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription medication.
 Pursuant to Texas Education Code, Section 38.031, this notice regarding head lice is being provided to parents. CDC Head Lice Treatment General Guidelines Treatment for head lice is recommended for persons
Pursuant to Texas Education Code, Section 38.031, this notice regarding head lice is being provided to parents. CDC Head Lice Treatment General Guidelines Treatment for head lice is recommended for persons
What they are, how to spot them and how to treat them Working together for a safer healthcare environment
 Head Lice What they are, how to spot them and how to treat them Working together for a safer healthcare environment What are head lice? Source: www.en.wikipedia.org What are nits? Head lice are small wingless
Head Lice What they are, how to spot them and how to treat them Working together for a safer healthcare environment What are head lice? Source: www.en.wikipedia.org What are nits? Head lice are small wingless
Head Lice Presentation. Patricia Guenther RN, BSN Aviano Elementary School
 Head Lice Presentation Patricia Guenther RN, BSN Aviano Elementary School What are Head Lice? Head Lice are a tiny, wingless parasitic insect that live among human hair and feeds on tiny amounts of blood
Head Lice Presentation Patricia Guenther RN, BSN Aviano Elementary School What are Head Lice? Head Lice are a tiny, wingless parasitic insect that live among human hair and feeds on tiny amounts of blood
SCABIES Medical Author: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD Medical Editor: William C. Shiel Jr., MD, FACP, FACR
 SCABIES Medical Author: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD Medical Editor: William C. Shiel Jr., MD, FACP, FACR 1) Scabies Facts Scabies is an itchy, highly contagious skin condition caused by an infestation
SCABIES Medical Author: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD Medical Editor: William C. Shiel Jr., MD, FACP, FACR 1) Scabies Facts Scabies is an itchy, highly contagious skin condition caused by an infestation
Managing Head Lice at Home
 Managing Head Lice at Home Please keep this booklet for Future Reference Contents Introduction 3 Head Lice Life Cycle 4 The Facts about Head Lice 5 Preventing the Spread of Head Lice 5 How to Find Head
Managing Head Lice at Home Please keep this booklet for Future Reference Contents Introduction 3 Head Lice Life Cycle 4 The Facts about Head Lice 5 Preventing the Spread of Head Lice 5 How to Find Head
Procedure/ Care Plan for Domiciliary Care Workers/ Support Workers - Application of Prescribed Creams/ Ointments/ Lotions (Adult)
 Application of Prescribed Creams/ Ointments/ Lotions (Adult) CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Medicines Management Specific Title: Procedure: Application of prescribed Creams/ Ointments/ Lotions (Adult) Author:
Application of Prescribed Creams/ Ointments/ Lotions (Adult) CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Medicines Management Specific Title: Procedure: Application of prescribed Creams/ Ointments/ Lotions (Adult) Author:
Guideline for Managing Scabies in Aged Residential Care Facilitator: Julie Daltrey NZRN Clinical Nurse Specialist Gerontology
 Document JD01 for Managing Scabies in Aged Residential Facilitator: Julie Daltrey NZRN145770 Clinical Nurse Specialist Gerontology Clinical reviewer: Associate Professor Amanda M M Oakley MBChB FRACP DipHealInf
Document JD01 for Managing Scabies in Aged Residential Facilitator: Julie Daltrey NZRN145770 Clinical Nurse Specialist Gerontology Clinical reviewer: Associate Professor Amanda M M Oakley MBChB FRACP DipHealInf
Head Lice. Prevention and Treatment. Ruth-Anne Morris Public Health Nurse. September 2013
 Head Lice Prevention and Treatment Ruth-Anne Morris Public Health Nurse September 2013 How Is Head Lice Spread? Head lice spread through direct contact among children (head-to-head),or indirectly on items
Head Lice Prevention and Treatment Ruth-Anne Morris Public Health Nurse September 2013 How Is Head Lice Spread? Head lice spread through direct contact among children (head-to-head),or indirectly on items
Head Lice Management. By Askari A. Kazmi Consultant Chemist / CEO. KazmisBioscienceLabs
 Head Lice Management By Askari A. Kazmi Consultant Chemist / CEO KazmisBioscienceLabs Types of lice Three Types Louse What are head lice, and how do they differ from other lice? Head lice (Pediculus capitis)
Head Lice Management By Askari A. Kazmi Consultant Chemist / CEO KazmisBioscienceLabs Types of lice Three Types Louse What are head lice, and how do they differ from other lice? Head lice (Pediculus capitis)
All There Is to Know about Head Lice
 New version All There Is to Know about Head Lice Lice have been around for a long time and they are not about to disappear any time soon. They are not dangerous, although they can be annoying. Did You
New version All There Is to Know about Head Lice Lice have been around for a long time and they are not about to disappear any time soon. They are not dangerous, although they can be annoying. Did You
Head Lice Guidelines. A Saginaw Township Community School District guide to identify, treat, manage and prevent head lice
 Head Lice Guidelines A Saginaw Township Community School District guide to identify, treat, manage and prevent head lice Table of Contents Guidelines & Procedures.3 Prevention & Cleaning Tips.4 Head Lice
Head Lice Guidelines A Saginaw Township Community School District guide to identify, treat, manage and prevent head lice Table of Contents Guidelines & Procedures.3 Prevention & Cleaning Tips.4 Head Lice
Self-care information on head lice
 Self-care information on head lice 2 What are head lice? Head lice are tiny grey/brown insects. They are the size of a pinhead when hatched and about the size of a sesame seed (the seeds on burger buns)
Self-care information on head lice 2 What are head lice? Head lice are tiny grey/brown insects. They are the size of a pinhead when hatched and about the size of a sesame seed (the seeds on burger buns)
Arthropods. Arachnida
 Arthropods Insecta Arachnida Crustacea Diptera Siphonaptera Hemiptera Anoplura Medical importance Vector Cause disease Mechanical Biological Dermatitis Mechanical Biological Direct Propagative Indirect
Arthropods Insecta Arachnida Crustacea Diptera Siphonaptera Hemiptera Anoplura Medical importance Vector Cause disease Mechanical Biological Dermatitis Mechanical Biological Direct Propagative Indirect
AN EASY-TO-USE GUIDE FOR PARENTS TO FIGHT BACK AGAINST HEAD LICE
 AN EASY-TO-USE GUIDE FOR PARENTS TO FIGHT BACK AGAINST HEAD LICE Developed in partnership with: Head Lice Together We Can Fight Them! Head lice are a normal part of childhood - surveys among primary school
AN EASY-TO-USE GUIDE FOR PARENTS TO FIGHT BACK AGAINST HEAD LICE Developed in partnership with: Head Lice Together We Can Fight Them! Head lice are a normal part of childhood - surveys among primary school
3/27/2017. Head Lice. Learning Objectives. Disclosures
 Head Lice Andi L. Shane, MD, MPH, MSc Associate Professor and Interim Division Director, Division of Pediatric Infectious Disease Marcus Professor of Hospital Epidemiology and Infection Control Learning
Head Lice Andi L. Shane, MD, MPH, MSc Associate Professor and Interim Division Director, Division of Pediatric Infectious Disease Marcus Professor of Hospital Epidemiology and Infection Control Learning
ALL THERE IS TO KNOW ABOUT HEAD LICE
 ALL THERE IS TO KNOW ABOUT HEAD LICE Lice have been around for a long time and they are not about to disappear any time soon. They are not dangerous, although they can be annoying. Did You Know Head lice
ALL THERE IS TO KNOW ABOUT HEAD LICE Lice have been around for a long time and they are not about to disappear any time soon. They are not dangerous, although they can be annoying. Did You Know Head lice
BENZYL BENZOATE (benz-el benz-o-ate) Common brands include: Ascabiol, Benzemul. CROTAMITON (crow-ta-mi-ton) Common brands include: Eurax
 DERMATOLOGICAL Scabicides and pedicuicides Active ingredients (generic names) BENZYL BENZOATE (benz-el benz-o-ate) Common brands include: Ascabiol, Benzemul CROTAMITON (crow-ta-mi-ton) Common brands include:
DERMATOLOGICAL Scabicides and pedicuicides Active ingredients (generic names) BENZYL BENZOATE (benz-el benz-o-ate) Common brands include: Ascabiol, Benzemul CROTAMITON (crow-ta-mi-ton) Common brands include:
Does lotrimin work for scabies
 P ford residence southampton, ny Does lotrimin work for scabies Aug 14, 2017. Ringworm can develop on the scalp and skin. On the. Scabies can appear anywhere on the body, but the mite tends to burrow into
P ford residence southampton, ny Does lotrimin work for scabies Aug 14, 2017. Ringworm can develop on the scalp and skin. On the. Scabies can appear anywhere on the body, but the mite tends to burrow into
Managing Head Lice at Home
 Managing Head Lice at Home Please keep this book for Future Reference Contents Introduction Page 3 The Facts about Head Lice Page 4 Preventing the Spread of Head Lice Page 5 How to Find Head Lice Page
Managing Head Lice at Home Please keep this book for Future Reference Contents Introduction Page 3 The Facts about Head Lice Page 4 Preventing the Spread of Head Lice Page 5 How to Find Head Lice Page
Standard Operating Procedure for Administering creams and ointments in care homes within NHS Sutton CCG
 Standard Operating Procedure for Administering creams and ointments in care homes within NHS Sutton CCG Introduction All health and social care organisations are accountable for ensuring the safe management
Standard Operating Procedure for Administering creams and ointments in care homes within NHS Sutton CCG Introduction All health and social care organisations are accountable for ensuring the safe management
Albany Hills State School
 Albany Hills State School Parent Information Keong Road ALBANY CREEK QLD 4035 PO Box 378 ALBANY CREEK QLD 4035 Ph: 07 3264 0777 Fax: 07 3264 0700. Email: Website: admin@albahillss.eq.edu.au www.albahillss.eq.edu.au
Albany Hills State School Parent Information Keong Road ALBANY CREEK QLD 4035 PO Box 378 ALBANY CREEK QLD 4035 Ph: 07 3264 0777 Fax: 07 3264 0700. Email: Website: admin@albahillss.eq.edu.au www.albahillss.eq.edu.au
Parents Guide Patienten-Ratgeber Englisch
 Headlice Kopfläuse Parents Guide Patienten-Ratgeber Englisch 2 The family business InfectoPharm and Pädia are among the leading manufacturers of medicines and health products for children in particular.
Headlice Kopfläuse Parents Guide Patienten-Ratgeber Englisch 2 The family business InfectoPharm and Pädia are among the leading manufacturers of medicines and health products for children in particular.
Head Lice PTA Presentation. RISD Health Services
 Head Lice PTA Presentation RISD Health Services PEDICULOSIS Pediculosis is an infestation of head lice. Has been spreading from one person to another for at least as long as recorded history. Commonly
Head Lice PTA Presentation RISD Health Services PEDICULOSIS Pediculosis is an infestation of head lice. Has been spreading from one person to another for at least as long as recorded history. Commonly
Approval Signature: Date of Approval: October 29, 2015 Review Date: October 29, 2018
 Long Term Care Infection Prevention and Control Program Operational Guideline Scabies in Long Term Care Facilities (LTCF), Management of Approval Signature: Date of Approval: October 29, 2015 Review Date:
Long Term Care Infection Prevention and Control Program Operational Guideline Scabies in Long Term Care Facilities (LTCF), Management of Approval Signature: Date of Approval: October 29, 2015 Review Date:
SCABIES PREVENTION AND CONTROL GUIDELINES ACUTE AND LONG-TERM CARE FACILITIES
 Acute Communicable Disease Control Program SCABIES PREVENTION AND CONTROL GUIDELINES ACUTE AND LONG-TERM CARE FACILITIES August 2015 www.lacounty.gov/acd/disease/scabies.htm TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction...
Acute Communicable Disease Control Program SCABIES PREVENTION AND CONTROL GUIDELINES ACUTE AND LONG-TERM CARE FACILITIES August 2015 www.lacounty.gov/acd/disease/scabies.htm TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction...
Head Lice Fact Sheet
 APPENDIX A Head Lice Fact Sheet What are head lice? Head lice are tiny insects that live on the human scalp. These insects lay eggs called nits, which stick to the hair close to the scalp. Head lice do
APPENDIX A Head Lice Fact Sheet What are head lice? Head lice are tiny insects that live on the human scalp. These insects lay eggs called nits, which stick to the hair close to the scalp. Head lice do
Why should you self-care? How can my local pharmacist help? How your pharmacist can help
 Be self-care aware Many common illnesses or symptoms are best treated at home with rest or with advice from a community pharmacist with no need to see a doctor or nurse. This leaflet contains advice and
Be self-care aware Many common illnesses or symptoms are best treated at home with rest or with advice from a community pharmacist with no need to see a doctor or nurse. This leaflet contains advice and
LICE: BIOLOGY AND PUBLIC HEALTH RISK
 E-245-W Public Health Department of Entomology HUMAN LICE: BIOLOGY AND PUBLIC HEALTH RISK Catherine A. Hill and John F. MacDonald, Department of Entomology Lice are parasitic insects that must live, feed,
E-245-W Public Health Department of Entomology HUMAN LICE: BIOLOGY AND PUBLIC HEALTH RISK Catherine A. Hill and John F. MacDonald, Department of Entomology Lice are parasitic insects that must live, feed,
INFORMATION ABOUT YOUR TREATMENT
 INFORMATION ABOUT YOUR TREATMENT Indication OXISTAT Lotion is indicated for the topical treatment of the following dermal infections: tinea pedis, tinea cruris, and tinea corporis due to Trichophyton rubrum,
INFORMATION ABOUT YOUR TREATMENT Indication OXISTAT Lotion is indicated for the topical treatment of the following dermal infections: tinea pedis, tinea cruris, and tinea corporis due to Trichophyton rubrum,
Chapter 19. Grooming Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 19 Grooming Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 18.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Explain why grooming is important. Explain how to
Chapter 19 Grooming Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 18.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Explain why grooming is important. Explain how to
