INTREM-GUIDELINE FOR MULTI-SECTORIAL SCABIES OUTBREAK EMERGENCY RESPONSE ETHIOPIA
|
|
|
- Terence Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTREM-GUIDELINE FOR MULTI-SECTORIAL SCABIES OUTBREAK EMERGENCY RESPONSE ETHIOPIA December 2015
2 TABLE OF CONTENTS SUMMARY INTRODUCTION TO SCABIES PUBLIC HEALTH RESPONSE HEALTH WASH COMMUNICATION NON FOOD ITEMS (NFI) COORDINATION...14 ANNEX 1: Behavioral objectives, messages and approaches by segmented audiences..15 2
3 SUMMARY Country: Ethiopia Title: Guideline to control and prevent scabies outbreak in Ethiopia 2015 Rationale: The impact of the severe drought in Ethiopia attributed to El Niño weather conditions ensuing high levels of malnutrition that increased the potential for diseases outbreak. Currently Ethiopia is experiencing scabies outbreak in drought affected areas where there is shortage of safe water for drinking and personal hygiene as a result of direct impact of the drought. In this regard, the Federal Ministry of Health (FMOH) in collaboration with partners is planning to respond that aims to rapidly stop community level transmission of scabies outbreak using multi-sectoral intervention approach in affected and high risk woredas selected based on nutrition and scabies outbreak risk criteria. Planned interventions include Health, WASH and Communication for development. Goal: To reduce morbidity and contained scabies outbreak. Objectives: To provide multispectral response to the outbreak. Dates: December 2015 Implementer: Federal Ministry of Health, Ethiopia Partners: WHO, UNICEF, NFI cluster and other partners 3
4 1. INTRODUCTION TO SCABIES Epidemiology Scabies is a contagious ectoparasite of the skin caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis. Approximately 130 million cases of scabies occur worldwide each year. The incidence of scabies can increase during natural and manmade disasters. Life cycle scabies mites Infestation begins when one or several pregnant female mites are transferred from the skin of an infested person to the skin of an un-infested person. After transfer from the skin of an infested person, or, rarely, from fomites, to the skin of an un-infested person, the adult female mite travels on the skin surface seeking a burrow site. At a suitable location, the pregnant female mite burrows into superficial layers of the skin, forming a slightly elevated narrow tunnel where it deposits eggs. The eggs progress through larval and nymphal stages to form adults in 10 to 17 days. The adults migrate to the skin surface and mate. The males die quickly and the females penetrate the skin and repeat the cycle. The mite requires human skin to complete its life cycle and is unable to survive off the host at room temperature for more than 2 to 3 days. The severity of scabies infestation is directly related to the number of mites residing on the skin and the length of time between initial infestation and subsequent diagnosis and treatment. If diagnosis and treatment are delayed, the number of live mites multiplies resulting in heavier or atypical infestations. Mode of Transmission Scabies usually is spread by direct, prolonged, skin-to-skin contact with a person who has scabies. Contact generally must be prolonged; a quick handshake or hug usually will not spread scabies. Scabies is spread easily to sexual partners and household members. Scabies sometimes is spread indirectly by sharing articles such as clothing, towels, or bedding used by an infested person. An infested person can spread scabies even if he or she has no symptoms. Humans are the source of infestation and animals do not spread human scabies. On a person, scabies mites can live for as long as 1-2 months. Off a person, scabies mites usually do not survive more than hours. Scabies mites will die if exposed to a temperature of 50 C (122 F) for 10 minutes. Risk factors Scabies affects people of all races and social classes. Scabies can spread easily under crowded conditions where close body and skin contact is common. Institutions such as schools, refugee camps, sanitarium and prisons are often sites of scabies outbreaks. Some immunocompromised, elderly, neurological disabled, or debilitated persons are at risk for a severe form of scabies called crusted,, scabies. Persons with crusted scabies have thick crusts of skin that contain large numbers of scabies mites and eggs. The mites in crusted scabies are much more numerous (up to 2 million per patient). 4
5 Because they are infested with such large numbers of mites and therefore persons with crusted scabies are very contagious to other persons. The mite can survive for much longer than the conventional 2 to 3 days inn the thick skin shade. So in addition to spreading scabies through brief direct skin-to-skin contact, persons with crusted scabies have also a high probability to transmit scabies indirectly by shedding mites that contaminate items such as their clothing, bedding, and furniture. Persons with crusted scabies should receive quick and aggressive medical treatment for their infestation to prevent outbreaks of scabies. Case Definitions and Outbreak Definition Suspected case: A person with signs and symptoms consistent with scabies. Confirmed case: A person who has a skin scraping in which mites, mite eggs or mite feces have been identified by a trained health care professional. Contact: A person without signs and symptoms consistent with scabies who has had direct contact (particularly prolonged, direct, skin-to-skin contact) with a suspected or confirmed case in the two months preceding the onset of scabies signs and symptoms in the case. Clinical Features Incubation Period and Period of Infectivity Symptoms of scabies typically begin three to six weeks after primary infestation. However, in patients who have previously been infested with scabies, symptoms usually begin within one to three days after re-infestation, presumably because of prior sensitization of the patient's immune system. Infested persons can transmit scabies, even if they do not have symptoms, until they are successfully treated and the mites and eggs are destroyed Signs and Symptoms The characteristic symptoms of a scabies infection include superficial burrows, intense pruritus (itching) especially at night, a generalized rash and secondary infection. Acropustulosis, or blisters and pustules on the palms and soles of the feet, are characteristic symptoms of scabies in infants. Itching and rash may affect much of the body or be limited to common sites. Scabies can develop anywhere on the skin. The distribution of scabies usually involves the sides and webs of the fingers, the flexor aspects of the wrists, the extensor aspects of the elbows, anterior and posterior axillary folds, the skin immediately adjacent to the nipples (especially in women), the periumbilical areas, waist, male genitalia (scrotum, penile shaft, and glans), the extensor surface of the knees, the lower half of the buttocks and adjacent thighs, and the lateral and posterior aspects of the feet. The back is relatively free of involvement, and the head is spared except in very young children. Mites also like to burrow in skin covered by a bracelet, watchband, or ring. 5
6 Scabies in children Some children develop widespread scabies lesion. The scabies rash can cover most of the body. Even a child s palms, soles, and scalp can have skin manifestation. In infants, the rash often appears on the palms and soles. Infants who have scabies are very irritable and often do not want to eat or sleep. Children, too, are often very irritable. The itch can keep them awake at night. Crusted scabies Crusted scabies is a severe form of scabies. People Crusted scabies develops in people who have a weak immune system due to a medical condition, neurologic problem and the elderly. Crusted scabies develops when the person s body cannot develop any resistance to the mites. Without resistance, the mites quickly multiply. A common sign of crusted scabies is widespread crusts on the skin. These crusts tend to be thick, crumble easily when touched, and look grayish in color. Sometimes the crusts appear on 1 or a few areas of the body such as the scalp, back, or feet. Possible Complications The direct effect of scabies is debilitating itching, leading to scratching, which is in turn followed by complications due to bacterial infection of the skin, ranging from impetigo, abscesses and cellulitis, through to septicaemia, renal failure and possibly rheumatic heart disease Diagnosis of scabies Diagnosis of a scabies infestation usually is clinical, made based upon presence of the typical rash and symptoms of unrelenting and worsening itch, particularly at night. The definitive diagnosis is made when evidence of mites is found from a skin scraping test. By scraping the skin (covered with a drop of mineral oil) sideways with a scalpel blade over an area of a burrow and examining the scrapings microscopically, it is possible to identify mites, eggs, or pellets. 2. PUBLIC HEALTH RESPONSE 2.1. HEALTH Case management: The following assumptions should be used for case management Prevalence Treatment strategies In villages or kebeles or Treat all the people in the village/kebele/woreda (mass woreda with prevalence > treatment contacts and other community members except 15% children<2 yrs, Pregnant women and lactating mothers). In villages or kebelesor Treat cases individual cases and contact (family member) and woreda with prevalence < contacts. 15% NB: Average number of contacts for each case is assumed to be 5 people, i.e. household members. All persons should be treated at the same time to prevent infestation and contained the outbreak. A family member with who doesn t have itching doesn t mean he did not have scabies. Treatment campaign should be organized at the sub village (Gote) level closer to the household. Communities are mobilized using community mobilizers to come to the site for treatment. During the treatment campaign, community need to be aware and practice the prevention methods, 6
7 including hygiene practice during and after treatment such as cleaning clothes, sleeping materials and houses, etc. Individuals affected by the disease has to be advised the cut (clip) their nail. Water availability for personal hygiene is crucial for effective control of the outbreak. Drugs used for management of scabies There are two routs of anti-scabies drugs application to treat scabies 1. Systemic or oral scabicide in the form of tablets: Ivermectin 2. Application of a topical scabicide in the form of ointments, lotions, or cream. 5% Permethrin, 12.5 to 25% Benzyl Benzoate Lotion and Sulfur (5%-10%) ointment There is increasing interest in the use of oral ivermectin. Evidence from the country are showing best results are obtained by treating the whole household at the same time. Scabicide drugs used for topical application should be applied to all areas of the body from the neck down to the feet and toes. In addition, when treating infants and young children, also should be applied to their entire head and neck because scabies can affect their face, scalp, and neck, as well as the rest of their body. The scabicide should be applied to a clean body and left on for the recommended time before washing it off. Clean clothing should be worn after treatment. As the symptoms of scabies are due to a hypersensitivity reaction (allergy) to mites and their feces (scybala), itching may continue for two to four weeks after treatment even if all the mites and eggs are killed and anti-histamines can be used as described below. If itching still is present more than 4 weeks after treatment, re-treatment is required. Secondary Skin infection including impetigo or bullous should be treated with an appropriate oral antibiotics as described below. First-line treatment to contain the scabies outbreak. 1. Ivermectine For > 2 years of age or 15 kg, adults except pregnant women and lactating mothers: Dosage 200 micrograms/kg once orally for all except children less than2 years old or 15 kg body weight, pregnant mothers and breast feeding women. Repeat the treatment after 2 weeks. Weight Age 3 mg tablet 12.5 to 25 2 to to 35 7 to to to 18 3 Above 50 Above 18 4 NB: Ivermectine tablets and Benzyl Benzoate Lotion (BBL) are contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women and children under 2 years of age or <15kg Ivermectine is very safe and effective anti-parasitic agent. Two rounds of MDA within roughly a two week period have the highest cure rate than other regimens. Below is the list with the most 7
8 common side effect of Ivermectin. Participants must be asked if they have any of this before the first and second dose. If there are no side effects, just write NO in the MDA form. 1. Headache 2. Dizziness 3. Itch 4. Tummy pain 5. Nausea 6. Vomiting 7. Diarrhea 8. Fever 9. Other 2. Permethrin 5% lotion/cream /ointment For all except for infant less than 2 months of age. Dosage: Full tube of 30 ml for all adults. Half tube for children. Second dose will be applied after one week. How to apply: Thin film of cream is applied on the whole body once and repeat after one week. All the skin below the neck should be treated, including the genital, inter-gluteal space, palm and soles and under the nails. Treat the head and neck regions in infants (up 2 month to the age of 2 years). Wash after 8-14 hours and repeated after one week. Side effect of Permethrin; Allergic contact dermatitis and rarely irritation NB: If Permethrin is not available, use sulfur ointment. Benzyl Benzoate Lotion (BBL) Second-line treatment to contain the scabies outbreak. 1. Benzyl Benzoate Lotion (BBL): Dosage: One bottle of 100 ml BBL will be enough for 3 days whole body application for adult and leave on for 24 hour before washing off. For adult :- 25% Benzyl Benzoate Lotion (BBL)once per day for 3 days or (not recommended for pregnant women and lactating mothers) For children above 2 years of age up to % Benzyl Benzoate Lotion (BBL) once per day for three days. How to apply: All the skin below the neck should be treated, including the genital, buttock, palm and soles and under the nails. After application, the patient s hands can be washed before eating food (not just after application). In case if the mother breast feed her child she may be forced to wash her hands, provided that she has to be re-apply the treatment again accordingly. Side effect of Benzyl Benzoate Lotion (BBL); Irritation, allergic contact dermatitis and rarely neurotoxicity 2. Sulfur (5%-10%) ointment For all specially for children under 2 years, pregnant mothers and breast feeding women 8
9 Dosage: - For children under 10 year: 1 tube (50gm) of 5% sulfur apply once per day for three days, leave on for 1 day before washing off. For children above 10 years old and adult: 2 tubes of 10% sulfur will be needed for three days whole body applications. Leave on for 1 day before washing off How to apply: All the skin below the neck should be treated, including the genital, buttock, palm and soles and under the nails. Treat the head and neck regions in infants (up to the age of 2 years). Side effect of Sulfur; messy, malodorous, irritation and allergic contact dermatitis. 3. Permethrin 5% cream or lotion: Dosage: For children under 2 years 1 tube (30 ml) of 5% permethrin need to apply the whole body once.all the skin below the neck should be treated, including the genital, inter-gluteal space, palm and soles and under the nails. Apply on the head and neck regions and Wash after 8 hours. Repeated after one week. After application, lactating mother has to wash her hands before breast feeding the child. She has to re-apply the treatment on her hands after feeding. For children above 10 years old and adult: 2 tubes of 5% permethrin of 30 ml will be needed.apply once the whole body,leave on for 1 day before washing off. After application, hands can be washed, if there is a need to eat before 8 hours but has to be re-applied after eating. Repeat after one week. Treatment of crusted scabies: Both oral and topical agents should be used together. Ivermectin should be administered together with a topical agent. Dosage: Oral ivermectin (200µg/kg/dose) should be taken with food. Depending on infection severity, ivermectin should be taken in three doses (day 1, 2, and 8) NB: Use of insecticide sprays and fumigants is not recommended. Treatment of secondary infections Secondary management involves prompt treatment of the complications of scabies, such as impetigo using appropriate antibiotics or antiseptics. Recommended antibiotics First line antibiotic Cephalexin Dosage For children25-50 mg/kg/day orally in 3-4 divided doses for 7days, For adults 500mg orally every 6 hourly for 7 days If Cephalexin is not available use Amoxicillin For children25-50 mg/kg/day orally in 3-4 divided doses for 7days, For adults 500mg orally every 6 hourly for 7 days 2nd line antibiotic Cloxaciline mg/kg/day for 7days (Preferred drug for bullous form of skin lesions) Treatment of Hypersensitivity reaction First line 9
10 Phenergan po 25 mg once per day (for adult) Diphenhydramine 2 50 mg cap PO Every 6 hourly Alternative Chlorpheniramine, 4 6 my PO every 6 hourly Reasons for failure of control measures 1. The following from the body during the treatment period, failure to follow to scabicide directions and failure to apply treatment to the entire body. 2. Continued exposure to infested persons due to failure to identify cases. 3. Continued exposure to infested materials such as bedding, clothing,, and furniture Failure to identify reasons may attribute to the failure of control measures. 4. Inadequate treatment application which includes failure to reapply medication after it has been removed 5. and report symptomatic patients 6. Failure to properly identify and monitor close contacts of cases 7. Suppressed immune response to scabcide due to immunocompromised status Any identified control measures that have not been followed should be corrected immediately. If any of the above reasons for control measure failure is identified, re-administration of scabicide may be necessary. Coordination of Mass Drug Administration (MDA) and Monitoring The MDA will be done using the guideline of Zithromax campaign for the coordination. Post treatment Surveillance of the effectiveness of the campaign in 6 weeks time after the first does is mandatory. 2.2 WASH Considering scabies as a water washed disease, the key intervention is the provision of access to sufficient safe water for personal hygiene: Washing of clothing Washing of body using soaps especially the affected areas Appropriate hand washing at critical times Clothing or bedding that were used by an infested individual during and before effective treatment should be dried for 3 days in the sun to allow time for mites and eggs to die. All patients and their contacts coming to mass treatment center or health facility will be provide with body and laundry soap irrespective of water availability at household levels. In addition to this, Patients will be also advised to buy and use soap for personal hygiene a. Body Soap: 1/per person /month b. laundry soap : 1/per person /month c. Appropriate messages on personal hygiene practices d. Sun drying of clothing and beddings for at least 3 days 2.3. COMMUNICATION The C4D strategy emphasizes the need for multi-sectoral coordination and response to contain the spread of the epidemics. The Communication strategy for scabies prevention needs an 10
11 integrated and multi-level intervention comprising advocacy, social mobilization, social and behavioral change communication at different levels and capacities. The C4D strategy proposes a mix of multi-level social and behavior change communication approaches targeting various groups as briefly described below: The immediate response focus on a mix of social mobilization and BCC campaign as briefly outlined below: Social Mobilization: undertake sensitization meetings at Regional and Woreda level, convening key actors (including schools, CBOs, and religious institutions) that can mobilize their respective groups in promoting prevention education and communicating on mass treatment days. BCC campaign: focus on 3 elements; - Use Audio Vans to disseminate information on treatment days and key prevention messages. - Disseminate key messages through regional/community media (See attached 2 radio spot messages in 3 languages, and select your preferred language). - Disseminate the available Job aids for HEWs, illustrative foldable posters to HDA/WDA/DAs to support interpersonal communication (see attached job aid messages). Follow-up response by main strategies: 1. Advocacy - Sensitization of key actors/advocacy: In this strategy, aim at ensuring government leadership in coordination and monitoring of prevention intervention by engaging respective sectors and organizations. Hence: Organize a sensitization workshops/meetings at different levels, together with the other emergency response taskforce and technical working groups. Engage sectors, including health, water, education and DPPA in the advocacy workshops In the workshops focus on enhancing understanding of current prevalence, multidimensional impact of the outbreak. Following the sensitization sessions and discussions, allow the respective actors to prepare and produce an integrated cross-sectoral prevention and response intervention operational plan, specified by responsible actors, and agree on the implementation, and agree on the implementation modality. Potential Advocacy Participants Decision makers in the government, Command Post, non-government, FBOs and CSOs at different levels and capacities. Interventions: Sensitization meetings/workshops at regional level Woreda and Kebele to enhance coordination and management of sensitization meetings at regional level Use the following required resources for Advocacy: Fact Sheet on current scabies situation, prevention and control aspects Advocacy material for government/non-government officials, religious and other related community influential leaders. 2. Social Mobilization 11
12 The General aim is at enlisting the participation of key institutions like community networks/cbos and religious groups to use their membership and other resources to strengthen participation in prevention activities at the community level. Use the Women Development Army and/or the Health Development Army structures that are instrumental to engage large number of populations through ongoing dialogue. Use religious institutions and influential Community Based Organizations, in order to critically concrete the effort towards behavior change communication and action. Conduct sensitization meetings, engaging all the concerned, such as: GOs,/NGOs, CSOs, RBOs and share them key messages and draw joint commitment of actions, aligned with the advocacy actions, and more. Immediate Potential Participants for Social Mobilization: School Community (PTA, Clubs, Mini-Media) Religious institution Health/Women Development Armies Interventions: Orient Health Extension Workers on Case management and prevention. Moreover, introduce specific sessions to be included on social/community mobilization, awareness raising and behavioral change communication for scabies prevention. (Note: the orientation will not require an exclusive budgeting from C4D as it s part of the case management) Use the attached ready job aid to help health extension workers understand the major curative and preventive steps and actions. This tool serves you a dual purpose, one for HEWs to take appropriate actions to contain the epidemic and two, to mentor and coach the HDA/WDAs under their supervision Disseminate Scabies prevention material that help HDAs/WDAs and religious leaders to conduct effective community mobilization on scabies prevention through community gathering, community conversation, religious sermons and house to house visits Disseminate Scabies prevention brochures to school community (PTAs, school clubs and mini-medias) for wider information sharing and to create multiplying effects in their respective families and their neighbors. The following are the required resources for use and reference: Job Aid for Health Extension Workers High pictorial A3 size foldable material Brochure (with illustration and detail text) A3 and foldable Short Audio Messages for school mini-media 3. Social and Behavior change Communication (SBCC) The main purposes of the behavioral change communication is; To bring about improved knowledge and awareness on scabies epidemics, prevention and treatment mechanisms, To increase the level of acceptance on the nature of the disease and To motivate the community to dialogue and come up with informed practice appropriate prevention and curative actions. Focus on influencing knowledge and attitude, adoption of appropriate hygiene and care practices and tackling of misconceptions at individual and family levels. 12
13 In this strategy, don t stick to one channel and media in order to attain the SBCC purposes, deploy a mix of SBCC approaches, including interpersonal communication/dialogue, mini-media, such as school mini-media, mobile vans and loudspeakers, mass media campaigns to reach children in schools, families and the concerned communities at large, based on the agreed and prepared required resources, listed below, and attached. Immediate potential participants are (where by you expand as need to include others): The community at large in scabies affected Kebeles and neighboring Kebeles Scabies affected individuals and families Interventions: Create awareness using mobile audio-visual vans, using same prepared audio messages, deploy the vans during mass treatment days/community gatherings to complement message retention and encourage action Disseminate Scabies prevention audience high pictorial materials. Hand the materials to the community during community conversations and other community mobilization interventions. Disseminate the prepared poster to amplify scabies prevention core messages and post in the public gathering areas like market places, football fields, schools, health post, churches, mosques and other public service sites Disseminate audio messages through community and local radio stations (see the attached radio messages) SBCC required references/resource: High pictorial A3 size foldable material Poster Audio Message Capacity building- Focus on enhancing the skills of key actors (like HEWs, HAD/WDA) 2.4. NON FOOD ITEMS (NFI) The objective of NFI response is to improve access to hygiene and sanitation kits, water collection and storage materials, changing cloths to address specific needs of women, men, boys, girls, elderly and disabled which are the most vulnerable community members to cope from and better prevent scabies transmission. The flowing are 1. Provision of personal hygiene and sanitation options a. Provide dignity kit to woman and girls in reproductive age group (15-49 years of age) (sanitary pad and underwear) Sanitary Pad-3packs and 3pcs underwear /person/month b. Provide Sanitary towel, diaper, sanitizer and wiper to pregnant, lactating, skin sores( patients with secondary infection) 5 Sanitary towel, 5 diaper packs, 2 liquid sanitizer bottle and 5 wiper/person/month 2. Provision of clothing and night wears a. Clothing for children, elder, woman b. Bed sheets and blankets for vulnerable households c. Shoes and sandals d. Safe disposal of infected clothing and beddings 13
14 Partners working on scabies response should access Health, WASH, C4D and NFI supplies from RHBs or ZHOs or woreda health offices and provide reports to respective offices where they received the supplies. 3. COORDINATION Multi-sector coordination is critical to ensure scabies treatments are effective rather than considerable efforts of sectors individually. As multi sector coordination is the responsibility of Regional zonal woreda health and sector office at all levels; tremendous efforts needed at the regional level with support from NGOs to strengthen the coordination at woreda level through the existing structure to avert the spread of scabies. In addition, it is important to have coordination meetings to share information, who does what, where and when specific to scabies response so that the gaps can be addressed timely based on the identified gaps. International NGOs are encouraged to partner with local NGO s and or authorities and strengthen their capacities. Support system strengthening should be provided to government facilities as well as NGO supported facilities in scabies affected regions, zones, woredas and health facilities. All partners are expected to attend relevant cluster meetings to ensure a coordinated response. 14
15 ANNEX 1: BEHAVIORAL OBJECTIVES, MESSAGES AND APPROACHES BY SEGMENTED AUDIENCES Audience segmentation Families and communities affected by scabies Behavior Change Objectives/Desired Behaviors -Increase knowledge and skills on appropriate and preventive and treatment actions -Tackle misconceptions related to scabies Action Oriented Key Messages Primary participant group Cause Scabies is not a curse, it is a disease caused by a microscopic scabies mite that burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. Symptoms The most common symptoms of scabies are intense itching and a pimple-like skin rash. If not treated, it causes massive infection and other internal complications. Risk factors Direct skin-to-skin contact with an affected person, poor hygiene and overcrowded conditions and poor nutrition Transmission Scabies is spread by direct, prolonged, skinto-skin contact with a person who has scabies. Scabies is spread easily to sexual partners and household members. Scabies sometimes is spread indirectly by sharing articles such as clothing, towels, or bedding used by an infested person. Treatment -Always follow carefully the instructions provided by the health worker and complete medication as ordered The day you start treatment, wash your clothes, bedding, towels, and washcloths. Take a bath or shower before you apply the medicine. -When treating adults and older children, apply the medication cream or lotion to all areas of the body, from the neck down to the feet and toes; -When treating infants and young children, apply the cream or lotion to the head and neck. -Leave the medication on the body for the recommended time before it is washed off. -Wear clean after treatment. - Leave used clothes out in the sun for at least 4 days before using again Prevention/Control the spread Personal hygiene - Wash hands with soap before and after contact with infected body -Improve personal hygiene Treatment is recommended for household members and sexual contacts, in addition to the infected person particularly those who Approaches/Strat egies Inter personal communication and counseling Mass media Print media Channels IPC through HDAs Local media during mass treatment days/audio vans Posters/brochures for general public and illustrative materials for HDAs 15
16 Key influential networks, CBOs, religious networks HEWs//HDAs Regional and Woreda sector bureaus (health, education, water, DPP) Ensure the participation of key institutions like community networks/cbos and religious groups to use their membership and other resources to strengthen participation in prevention activities at the community level Equipped with necessary knowledge and skills to undertake interpersonal communication and to train HDAs Support coordinated prevention interventions have had prolonged skin-to-skin contact with the infested person. - All persons should be treated at the same time in order to prevent re-infestation. - Retreatment may be necessary if itching continues more than 2-4 weeks after treatment or if new burrows or rash continue to appear. - Never use a medications intended for veterinary or agricultural use to treat humans - Houses need to be cleaned - carpets and similar items) should be put on the sun on the day you start treatment. - All clothes including bed sheets and blankets that are in contact with scabies infected individuals should be washed in boiling water and detergent and put in the sun for four days - Where water is scarce; Leave all clothes including bed sheets and blankets that are in contact with scabies infected individuals out in the sun for at least 4 days Secondary participant groups - Current status, - Risk factors, - Prevention and control mechanisms - What the key community level networks can do to stop the outbreak - Risk factors - Prevention and control mechanisms - Prevention and control mechanisms - facilitation tips Tertiary participant groups Social mobilization through sensitization meetings, orientation, dissemination of BCC materials Capacity building Sensitization meetings Fact sheets, Brochures Job aids for HEWs Illustrative materials for use by DAs/HDAs/ WDAs) 16
Frequently asked questions about. Scabies. From the Branch-Hillsdale-St. Joseph Community Health Agency
 Frequently asked questions about Scabies From the Branch-Hillsdale-St. Joseph Community Health Agency What is scabies? Scabies is an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var.
Frequently asked questions about Scabies From the Branch-Hillsdale-St. Joseph Community Health Agency What is scabies? Scabies is an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var.
SCABIES. Signs and symptoms
 SCABIES Scabies is caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which burrows into the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Scabies is a contagious skin infection that spreads rapidly in crowded conditions
SCABIES Scabies is caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which burrows into the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Scabies is a contagious skin infection that spreads rapidly in crowded conditions
Scabies Identification, Treatment and Environmental Cleaning
 Scabies Identification, Treatment and Environmental Cleaning Level III Purpose The purpose of this procedure is to treat residents infected with and sensitized to Sarcoptes scabiei and to prevent the spread
Scabies Identification, Treatment and Environmental Cleaning Level III Purpose The purpose of this procedure is to treat residents infected with and sensitized to Sarcoptes scabiei and to prevent the spread
Severe itching (pruritus), especially at night; a pimple-like (papular) itchy (pruritic) is also common
 Typical Scabies vs Crusted Scabies Human scabies is caused by an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis). The adult female scabies mites burrow into the upper layer
Typical Scabies vs Crusted Scabies Human scabies is caused by an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis). The adult female scabies mites burrow into the upper layer
What Is Scabies? Learning how to manage the spread of the human itch mite Sarcoptes scabiei
 What Is Scabies? Learning how to manage the spread of the human itch mite Sarcoptes scabiei IMPORTANT Scabies is a human itch mite infection that causes a rash and itching. It can vary in how long it lasts
What Is Scabies? Learning how to manage the spread of the human itch mite Sarcoptes scabiei IMPORTANT Scabies is a human itch mite infection that causes a rash and itching. It can vary in how long it lasts
IPC-PGN-13.5 Part of NTW(C)23 Infection, Prevention and Control Policy
 Infection Prevention and Control Practice Guidance Note Scabies V03 Date issued Issue 1 Apr 15 Planned review April 2018 IPC-PGN-13.5 Part of NTW(C)23 Infection, Prevention and Control Policy Author/Designation
Infection Prevention and Control Practice Guidance Note Scabies V03 Date issued Issue 1 Apr 15 Planned review April 2018 IPC-PGN-13.5 Part of NTW(C)23 Infection, Prevention and Control Policy Author/Designation
There are three types of lice: Body lice (Pediculus humanus corporis) Larger in size than head or pubic lice Live in seams of clothing
 Lice (head, body, pubic) and Scabies What are they? Lice are small parasites that live entirely on humans. Pediculosis is the term for an infestation of lice. The female lice hold on to skin or hairs and
Lice (head, body, pubic) and Scabies What are they? Lice are small parasites that live entirely on humans. Pediculosis is the term for an infestation of lice. The female lice hold on to skin or hairs and
Scabies is a very common skin condition caused by an infestation of mites.
 Scabies is a very common skin condition caused by an infestation of mites. The most common symptom is a very itchy rash, which may increase in severity if left untreated. Prescription topical creams and
Scabies is a very common skin condition caused by an infestation of mites. The most common symptom is a very itchy rash, which may increase in severity if left untreated. Prescription topical creams and
Scabies. Dr. Ghassan Salah
 Scabies Dr. Ghassan Salah Scabies Scabies is a skin infestation caused by a mite Causes: The female scabies mite (Sarcoptes scabei ) burrows through the stratum corneum of the skin and lays its eggs just
Scabies Dr. Ghassan Salah Scabies Scabies is a skin infestation caused by a mite Causes: The female scabies mite (Sarcoptes scabei ) burrows through the stratum corneum of the skin and lays its eggs just
Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care
 Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Scabies Version 1.01 May 2015 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Scabies May 2015 Version 1.01 Page 1 of 10 Please
Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Scabies Version 1.01 May 2015 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Scabies May 2015 Version 1.01 Page 1 of 10 Please
ECTOPARASITIC INFESTATIONS / INFECTIONS: FLEAS, LICE AND MITES (SCABIES) PROCEDURE
 Reference Number: UHB 275 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: 23 rd June 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: 141 ECTOPARASITIC INFESTATIONS / INFECTIONS: FLEAS, LICE AND MITES (SCABIES) PROCEDURE
Reference Number: UHB 275 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: 23 rd June 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: 141 ECTOPARASITIC INFESTATIONS / INFECTIONS: FLEAS, LICE AND MITES (SCABIES) PROCEDURE
NITS AND ITCHY BITS. (Table 1)
 NITS AND ITCHY BITS Head Lice(Pediculosis Cipitis): Children are often brought to the surgery complaining of itchy scalps. Parents will usually have already thought of Head Lice and applied a number of
NITS AND ITCHY BITS Head Lice(Pediculosis Cipitis): Children are often brought to the surgery complaining of itchy scalps. Parents will usually have already thought of Head Lice and applied a number of
SCABIES Medical Author: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD Medical Editor: William C. Shiel Jr., MD, FACP, FACR
 SCABIES Medical Author: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD Medical Editor: William C. Shiel Jr., MD, FACP, FACR 1) Scabies Facts Scabies is an itchy, highly contagious skin condition caused by an infestation
SCABIES Medical Author: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD Medical Editor: William C. Shiel Jr., MD, FACP, FACR 1) Scabies Facts Scabies is an itchy, highly contagious skin condition caused by an infestation
BEDBUGS, SCABIES AND HEAD LICE OH MY! Dermatologists address the growing incidence of parasitic infestations linked to skin and hair problems
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE BEDBUGS, SCABIES AND HEAD LICE OH MY! Dermatologists address the growing incidence of parasitic infestations linked to skin and hair problems MIAMI (March 4, 2010) If simply the thought
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE BEDBUGS, SCABIES AND HEAD LICE OH MY! Dermatologists address the growing incidence of parasitic infestations linked to skin and hair problems MIAMI (March 4, 2010) If simply the thought
SCABIES PREVENTION AND CONTROL GUIDELINES ACUTE AND LONG-TERM CARE FACILITIES
 Acute Communicable Disease Control Program SCABIES PREVENTION AND CONTROL GUIDELINES ACUTE AND LONG-TERM CARE FACILITIES August 2015 www.lacounty.gov/acd/disease/scabies.htm TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction...
Acute Communicable Disease Control Program SCABIES PREVENTION AND CONTROL GUIDELINES ACUTE AND LONG-TERM CARE FACILITIES August 2015 www.lacounty.gov/acd/disease/scabies.htm TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction...
SECTION 10.3 SCABIES
 SECTION 10.3 SCABIES Scabies: General Information Scabies: How is it Treated? Scabies: Diagnosis and Treatment for Health Professionals Scabies: Management of Scabies in Health and Social Care Settings
SECTION 10.3 SCABIES Scabies: General Information Scabies: How is it Treated? Scabies: Diagnosis and Treatment for Health Professionals Scabies: Management of Scabies in Health and Social Care Settings
Policy Document Control Page
 Policy Document Control Page Title Title: Management of Scabies Policy Version: 6 Reference Number: CL80 Supersedes Supersedes: Version 5 Alterations Specific treatment/medications removed Updated references
Policy Document Control Page Title Title: Management of Scabies Policy Version: 6 Reference Number: CL80 Supersedes Supersedes: Version 5 Alterations Specific treatment/medications removed Updated references
Guideline for Managing Scabies in Aged Residential Care Facilitator: Julie Daltrey NZRN Clinical Nurse Specialist Gerontology
 Document JD01 for Managing Scabies in Aged Residential Facilitator: Julie Daltrey NZRN145770 Clinical Nurse Specialist Gerontology Clinical reviewer: Associate Professor Amanda M M Oakley MBChB FRACP DipHealInf
Document JD01 for Managing Scabies in Aged Residential Facilitator: Julie Daltrey NZRN145770 Clinical Nurse Specialist Gerontology Clinical reviewer: Associate Professor Amanda M M Oakley MBChB FRACP DipHealInf
Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: TREATMENT OF PEDICULOSIS (LICE) AND SCABIES
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 412 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: TREATMENT OF PEDICULOSIS (LICE) AND SCABIES 1. PURPOSE: This
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 412 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: TREATMENT OF PEDICULOSIS (LICE) AND SCABIES 1. PURPOSE: This
Does lotrimin work for scabies
 P ford residence southampton, ny Does lotrimin work for scabies Aug 14, 2017. Ringworm can develop on the scalp and skin. On the. Scabies can appear anywhere on the body, but the mite tends to burrow into
P ford residence southampton, ny Does lotrimin work for scabies Aug 14, 2017. Ringworm can develop on the scalp and skin. On the. Scabies can appear anywhere on the body, but the mite tends to burrow into
HOW TO MANAGE TREATMENT. Lydia Snell Paediatric Liaison Nurse March 15 th 2018 HEALTHY SKIN WORKSHOP
 HOW TO MANAGE TREATMENT Lydia Snell Paediatric Liaison Nurse March 15 th 2018 HEALTHY SKIN WORKSHOP The beauty of skin! It is all one organ Protects what is inside is a barrier Holds us all in We don t
HOW TO MANAGE TREATMENT Lydia Snell Paediatric Liaison Nurse March 15 th 2018 HEALTHY SKIN WORKSHOP The beauty of skin! It is all one organ Protects what is inside is a barrier Holds us all in We don t
OAK HILL ACADEMY Policy on Lice
 1 OAK HILL ACADEMY Policy on Lice If a child is suspected to have nits or lice during the school day, the child will be checked by the nurse. If it is determined that the child has nits or lice, they will
1 OAK HILL ACADEMY Policy on Lice If a child is suspected to have nits or lice during the school day, the child will be checked by the nurse. If it is determined that the child has nits or lice, they will
Treat the infested person(s): Requires using an Over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription medication.
 Pursuant to Texas Education Code, Section 38.031, this notice regarding head lice is being provided to parents. CDC Head Lice Treatment General Guidelines Treatment for head lice is recommended for persons
Pursuant to Texas Education Code, Section 38.031, this notice regarding head lice is being provided to parents. CDC Head Lice Treatment General Guidelines Treatment for head lice is recommended for persons
HEAD LICE. What are head lice? Who is at risk for getting head lice?
 HEAD LICE What are head lice? The head louse, or Pediculus humanus capitis, is a parasitic insect that can be found on the head, eyebrows, and eyelashes of people. Head lice feed on human blood several
HEAD LICE What are head lice? The head louse, or Pediculus humanus capitis, is a parasitic insect that can be found on the head, eyebrows, and eyelashes of people. Head lice feed on human blood several
Looking after. and treating skin infections. A guide for parents and families
 Looking after and treating skin infections A guide for parents and families Healthy Skin These things help keep your child s skin healthy: Eating healthy food like meat, fruit and vegetables. Drinking
Looking after and treating skin infections A guide for parents and families Healthy Skin These things help keep your child s skin healthy: Eating healthy food like meat, fruit and vegetables. Drinking
Balhousie School Presentation
 Balhousie School Presentation Presented by: Paula Muir Subject leader Hairdressing www.perth.uhi.ac.uk Perth College is a registered Scottish charity, number SC021209. Head Lice Aims Our aim today is to
Balhousie School Presentation Presented by: Paula Muir Subject leader Hairdressing www.perth.uhi.ac.uk Perth College is a registered Scottish charity, number SC021209. Head Lice Aims Our aim today is to
FACTS & MYTHS ABOUT HEAD LICE
 FACTS & MYTHS ABOUT HEAD LICE Head lice are generally misunderstood. Below are facts and myths about lice. FACTS Head lice do not fly (they have no wings), jump or hop About half of all infested individuals
FACTS & MYTHS ABOUT HEAD LICE Head lice are generally misunderstood. Below are facts and myths about lice. FACTS Head lice do not fly (they have no wings), jump or hop About half of all infested individuals
Head Lice Information
 Head Lice Information The adult head louse is 2 to 3 mm long (the size of a sesame seed), has 6 legs, and is usually tan to grayish-white in color. The female lives up to 3 to 4 weeks and, once mature,
Head Lice Information The adult head louse is 2 to 3 mm long (the size of a sesame seed), has 6 legs, and is usually tan to grayish-white in color. The female lives up to 3 to 4 weeks and, once mature,
Procedure/ Care Plan for Domiciliary Care Workers/ Support Workers - Application of Prescribed Creams/ Ointments/ Lotions (Adult)
 Application of Prescribed Creams/ Ointments/ Lotions (Adult) CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Medicines Management Specific Title: Procedure: Application of prescribed Creams/ Ointments/ Lotions (Adult) Author:
Application of Prescribed Creams/ Ointments/ Lotions (Adult) CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Medicines Management Specific Title: Procedure: Application of prescribed Creams/ Ointments/ Lotions (Adult) Author:
Fleas, Lice and Scabies - Management of Patients. Ref IPC v1.1. Status: Approved Document type: Approved document
 Fleas, Lice and Scabies - Management of Patients Ref IPC-0001-012 v1.1 Status: Approved Document type: Approved document Contents 1. Purpose... 4 2. Related documents... 4 3. Fleas... 5 3.1. What do fleas
Fleas, Lice and Scabies - Management of Patients Ref IPC-0001-012 v1.1 Status: Approved Document type: Approved document Contents 1. Purpose... 4 2. Related documents... 4 3. Fleas... 5 3.1. What do fleas
Replacement. Status: Replacing: Policy for the Management of Parasitic Infestations Version: V 1.0 Date: August 2015
 Clinical Parasitic Infestations, SOP Document Control Summary Replacement. Status: Replacing: Policy for the Management of Parasitic Infestations Version: V 1.0 Date: August 2015 Author/Owner: Judy Carr
Clinical Parasitic Infestations, SOP Document Control Summary Replacement. Status: Replacing: Policy for the Management of Parasitic Infestations Version: V 1.0 Date: August 2015 Author/Owner: Judy Carr
Policy Document Control Page. Designation: Infection Prevention & Control Specialist
 Policy Document Control Page Title Title: Management of Head, Body and Pubic Lice Policy Version: 6 Reference Number: CL74 Supersedes Supersedes: V5 Amendments: Specific treatment medications removed Originator
Policy Document Control Page Title Title: Management of Head, Body and Pubic Lice Policy Version: 6 Reference Number: CL74 Supersedes Supersedes: V5 Amendments: Specific treatment medications removed Originator
Panic Pests - Head Lice. Shujuan (Lucy) Li University of Arizona
 Panic Pests - Head Lice Shujuan (Lucy) Li University of Arizona Head Lice Blood feeding ectoparasites associated with the scalp. More commonly found in school age students (3-11 years old) and girls. Transfer
Panic Pests - Head Lice Shujuan (Lucy) Li University of Arizona Head Lice Blood feeding ectoparasites associated with the scalp. More commonly found in school age students (3-11 years old) and girls. Transfer
Head Lice Information for Parents from CDC
 Head Lice Information for Parents from CDC You should examine your child's head, especially behind the ears and at the nape of the neck, for crawling lice and nits if your child exhibits symptoms of a
Head Lice Information for Parents from CDC You should examine your child's head, especially behind the ears and at the nape of the neck, for crawling lice and nits if your child exhibits symptoms of a
(NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122)
 (NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122) Y ou must prevent skin disease if you can. But, if you fail to prevent it, then you must aim to limit the damage. In tropical areas, this means
(NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122) Y ou must prevent skin disease if you can. But, if you fail to prevent it, then you must aim to limit the damage. In tropical areas, this means
Main Title. Head Lice 101 Description. An Overview for Parents, Teachers and Communities
 Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers and Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers and Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
Approval Signature: Date of Approval: October 29, 2015 Review Date: October 29, 2018
 Long Term Care Infection Prevention and Control Program Operational Guideline Scabies in Long Term Care Facilities (LTCF), Management of Approval Signature: Date of Approval: October 29, 2015 Review Date:
Long Term Care Infection Prevention and Control Program Operational Guideline Scabies in Long Term Care Facilities (LTCF), Management of Approval Signature: Date of Approval: October 29, 2015 Review Date:
By treatments.net
 Natural Scabies Treatments FFiinndd R Reelliieeff tthhee N Naattuurraall W Waayy By www.scabies- treatments.net Introduction If you have downloaded this report, you have no doubt been suffering with scabies
Natural Scabies Treatments FFiinndd R Reelliieeff tthhee N Naattuurraall W Waayy By www.scabies- treatments.net Introduction If you have downloaded this report, you have no doubt been suffering with scabies
What does permethrin do to scabies
 What does permethrin do to scabies The Borg System is 100 % What does permethrin do to scabies If You Checked 3 or more Symptoms, It Is 97% Likely That You Or Your Loved One Has Scabies. If You Or A Loved
What does permethrin do to scabies The Borg System is 100 % What does permethrin do to scabies If You Checked 3 or more Symptoms, It Is 97% Likely That You Or Your Loved One Has Scabies. If You Or A Loved
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory NEDAX -5 LOTION. Permethrin Lotion 5% w/w
 For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory NEDAX -5 LOTION Permethrin Lotion 5% w/w QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Permethrin 5% w/w in a aqueous base
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory NEDAX -5 LOTION Permethrin Lotion 5% w/w QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Permethrin 5% w/w in a aqueous base
Nits (Eggs) Smaller than lice but easier to detect. Each nit is attached firmly to a single hair strand with a gluelike
 HEAD LICE (PEDICULOSIS)........ KEEP ON TRACK Head lice are tiny insects that are about one to two mm (one-eighth of an in.) long. They have special mouth parts for piercing the human scalp. The scalp
HEAD LICE (PEDICULOSIS)........ KEEP ON TRACK Head lice are tiny insects that are about one to two mm (one-eighth of an in.) long. They have special mouth parts for piercing the human scalp. The scalp
Managing Head Lice in the School Setting AN OUNCE OF PREVENTION IS WORTH A POUND OF CURE
 Managing Head Lice in the School Setting AN OUNCE OF PREVENTION IS WORTH A POUND OF CURE What is Head Lice A small parasitic insect that lives on the scalp and neck hairs of a human host Originated and
Managing Head Lice in the School Setting AN OUNCE OF PREVENTION IS WORTH A POUND OF CURE What is Head Lice A small parasitic insect that lives on the scalp and neck hairs of a human host Originated and
What Are Lice, Scabies, and Bed Bugs?
 A collaborative effort of Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC and The Pennsylvania Child Welfare Resource Center What Are Lice, Scabies, and Bed Bugs? Lice, scabies, and bed bugs affect people all
A collaborative effort of Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC and The Pennsylvania Child Welfare Resource Center What Are Lice, Scabies, and Bed Bugs? Lice, scabies, and bed bugs affect people all
Main Title. Head Lice 101. Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities
 Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
HEAD LICE. The most up-to-date version of this policy can be viewed at the following website:
 Page Page 1 of 9 Policy Objective To ensure that patients with head lice are cared for appropriately and actions are taken to minimise the risk of cross-infection. This policy applies to all staff employed
Page Page 1 of 9 Policy Objective To ensure that patients with head lice are cared for appropriately and actions are taken to minimise the risk of cross-infection. This policy applies to all staff employed
Standard Operating Procedure for Administering creams and ointments in care homes within NHS Sutton CCG
 Standard Operating Procedure for Administering creams and ointments in care homes within NHS Sutton CCG Introduction All health and social care organisations are accountable for ensuring the safe management
Standard Operating Procedure for Administering creams and ointments in care homes within NHS Sutton CCG Introduction All health and social care organisations are accountable for ensuring the safe management
A GUIDE TO HEAD LICE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
 A GUIDE TO HEAD LICE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT May 2018 What are Head Lice? Head lice are very small, tan-colored insects about the size of a sesame seed which live only on human heads. They live and lay
A GUIDE TO HEAD LICE PREVENTION AND TREATMENT May 2018 What are Head Lice? Head lice are very small, tan-colored insects about the size of a sesame seed which live only on human heads. They live and lay
Clinical Policy: Lindane Shampoo Reference Number: CP.PMN.09 Effective Date: Last Review Date: Line of Business: Oregon Health Plan
 Clinical Policy: Lindane Shampoo Reference Number: CP.PMN.09 Effective Date: 10.01.18 Last Review Date: 07.13.18 Line of Business: Oregon Health Plan Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this
Clinical Policy: Lindane Shampoo Reference Number: CP.PMN.09 Effective Date: 10.01.18 Last Review Date: 07.13.18 Line of Business: Oregon Health Plan Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this
Occupational Health and Safety Unit. Preventing, treating and controlling head lice in the community
 Originator : OHSU/cmm Date: January 2010 Occupational Health and Safety Unit Working with you for a safer, healthier future Preventing, treating and controlling head lice in the community Contents Page
Originator : OHSU/cmm Date: January 2010 Occupational Health and Safety Unit Working with you for a safer, healthier future Preventing, treating and controlling head lice in the community Contents Page
NORTH STAR NURSERY AND HOLIDAY CLUB SUN PROTECTION POLICY
 NORTH STAR NURSERY AND HOLIDAY CLUB SUN PROTECTION POLICY North Star Nursery has consulted Cancer Research UK`s Sun Protection Policy Guidelines for Nurseries and Pre-Schools and Early Years publications
NORTH STAR NURSERY AND HOLIDAY CLUB SUN PROTECTION POLICY North Star Nursery has consulted Cancer Research UK`s Sun Protection Policy Guidelines for Nurseries and Pre-Schools and Early Years publications
Main Title. Head Lice 101. An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities. Description
 Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
Main Title Head Lice 101 Description An Overview for Parents, Teachers, & Communities Head Lice Fast Facts Head lice are a common community issue In the United States, an estimated 6 to 12 million lice
Rheumon Gel 1 g of gel contains 50 mg of etofenamate. For use in adults.
 New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information Rheumon Gel 1 g of gel contains 50 mg of etofenamate. For use in adults. Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine. This medicine
New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information Rheumon Gel 1 g of gel contains 50 mg of etofenamate. For use in adults. Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine. This medicine
Public Schools Branch
 Public Schools Branch Pediculosis (Head Lice) Management Protocol General Information Head lice are tiny insects that live only on the scalp of human beings and are the size of a pinhead. They do not have
Public Schools Branch Pediculosis (Head Lice) Management Protocol General Information Head lice are tiny insects that live only on the scalp of human beings and are the size of a pinhead. They do not have
CLEANING, SANITIZING, AND DISINFECTING
 CLEANING, SANITIZING, AND DISINFECTING This section provides general information about cleaning, sanitizing, and disinfecting; guidelines for specific items commonly used in childcare and school settings;
CLEANING, SANITIZING, AND DISINFECTING This section provides general information about cleaning, sanitizing, and disinfecting; guidelines for specific items commonly used in childcare and school settings;
ARE YOU? PsA TREAT YOUR SYMPTOMS WITH FOUR DOSES A YEAR. RECOGNIZE THE FOUR SIGNS OF PsA.
 PsA STELARA is a prescription medicine approved to treat adults 18 years and older with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), either alone or with methotrexate. WHICH YOU ARE YOU? RECOGNIZE THE FOUR SIGNS
PsA STELARA is a prescription medicine approved to treat adults 18 years and older with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), either alone or with methotrexate. WHICH YOU ARE YOU? RECOGNIZE THE FOUR SIGNS
Permethrin cream for athletes foot
 P ford residence southampton, ny Permethrin cream for athletes foot For Customer Service Please Call 602-324-5500 or 800-317- 7202. Dr. Scabies Homeopathic Treatment Cream-Scabies, Parasites, Athlete's
P ford residence southampton, ny Permethrin cream for athletes foot For Customer Service Please Call 602-324-5500 or 800-317- 7202. Dr. Scabies Homeopathic Treatment Cream-Scabies, Parasites, Athlete's
Chapter 18. Grooming. All items and derived items 2015, 2011 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 18 Grooming Grooming Hair care, shaving, and nail and foot care: Prevent infection and promote comfort Affect love, belonging, and self-esteem needs 2 Hair Care You assist with hair care whenever
Chapter 18 Grooming Grooming Hair care, shaving, and nail and foot care: Prevent infection and promote comfort Affect love, belonging, and self-esteem needs 2 Hair Care You assist with hair care whenever
ACETOCAUSTIN 0,5 ml, Cutaneous solution
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ACETOCAUSTIN 0,5 ml, Cutaneous solution MONOCHLOROACETIC ACID This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER ACETOCAUSTIN 0,5 ml, Cutaneous solution MONOCHLOROACETIC ACID This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet
Handbook regarding Lice Management
 Handbook regarding Lice Management 2009-2010 School Year Information provided by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention http://www.cdc.gov/ 1 P a g e This Package Contains the Following: Fact Sheet
Handbook regarding Lice Management 2009-2010 School Year Information provided by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention http://www.cdc.gov/ 1 P a g e This Package Contains the Following: Fact Sheet
Can I remove the hair from my nipples? Absolutely, the flash represents no risk. Caution is advised on dark nipples.
 F r e q u e n t l y A s k e d Q u e s t i o n s Clinical topics I want to remove all hair from the bikini zone, are there any risks? E>One is safe to use on every part of the body, without exception. Therefore,
F r e q u e n t l y A s k e d Q u e s t i o n s Clinical topics I want to remove all hair from the bikini zone, are there any risks? E>One is safe to use on every part of the body, without exception. Therefore,
MOIRA HOUSE GIRLS SCHOOL HEAD LICE
 Head Lice Introduction The aim of this Policy is to ensure a consistent, coordinated and cooperative approach to managing head lice in the school community. Roles and Responsibilities The Parents responsibilities
Head Lice Introduction The aim of this Policy is to ensure a consistent, coordinated and cooperative approach to managing head lice in the school community. Roles and Responsibilities The Parents responsibilities
SCOTT COUNTY AREA SCHOOLS & COMMUNITY HEAD LICE MANAGEMENT PLAN
 SCOTT COUNTY AREA SCHOOLS & COMMUNITY HEAD LICE MANAGEMENT PLAN DEVELOPED BY SCOTT COUNTY KIDS HEALTH COMMITTEE With representatives from Bettendorf Community School District Davenport Community School
SCOTT COUNTY AREA SCHOOLS & COMMUNITY HEAD LICE MANAGEMENT PLAN DEVELOPED BY SCOTT COUNTY KIDS HEALTH COMMITTEE With representatives from Bettendorf Community School District Davenport Community School
Infection Prevention and Joint Replacement
 Infection Prevention and Joint Replacement Background Infection after joint replacement surgery can be devastating and require further surgery and prolonged treatment with antibiotics Our skin and our
Infection Prevention and Joint Replacement Background Infection after joint replacement surgery can be devastating and require further surgery and prolonged treatment with antibiotics Our skin and our
The most up-to-date version of this policy can be viewed at the following website:
 Page 1 of 9 Review SOP Objective To ensure that patients with head lice are cared for appropriately and actions are taken to minimise the risk of cross-infection. This SOP applies to all staff employed
Page 1 of 9 Review SOP Objective To ensure that patients with head lice are cared for appropriately and actions are taken to minimise the risk of cross-infection. This SOP applies to all staff employed
W - WHO IS THE PATIENT H HOW LONG HAS THIS BEEN OCCURRING. Self Care
 HEAD LICE Possible head lice infestation Head lice are acquired from other infected people, mainly by direct head-to-head contact. Empty egg sacs are white and shiny and may be found further along the
HEAD LICE Possible head lice infestation Head lice are acquired from other infected people, mainly by direct head-to-head contact. Empty egg sacs are white and shiny and may be found further along the
Literature Scan: Topical Antiparasitics
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Skin Reactions from Radiation Treatments
 Skin Reactions from Radiation Treatments Skin reactions are a common side effect of radiation treatments. They are caused when repeated doses of radiation pass through the skin. Skin reactions occur within
Skin Reactions from Radiation Treatments Skin reactions are a common side effect of radiation treatments. They are caused when repeated doses of radiation pass through the skin. Skin reactions occur within
HEAD LICE (Pediculus Humanus Capitis)
 What are head lice and some facts? HEAD LICE (Pediculus Humanus Capitis) Head lice are annoying parasitic insects that live in the hair and on the scalp of humans. They are about the size of a sesame seed
What are head lice and some facts? HEAD LICE (Pediculus Humanus Capitis) Head lice are annoying parasitic insects that live in the hair and on the scalp of humans. They are about the size of a sesame seed
HEAD LICE INFORMATION
 HEAD LICE INFORMATION HOW DO I KNOW IF MY CHILD HAS HEAD LICE? Many head lice infections cause no symptoms, and probably less than half cause itch. So you have to LOOK to find out if your child has head
HEAD LICE INFORMATION HOW DO I KNOW IF MY CHILD HAS HEAD LICE? Many head lice infections cause no symptoms, and probably less than half cause itch. So you have to LOOK to find out if your child has head
Head Lice 101 What You Should Know About Head Lice
 Head Lice 101 What You Should Know About Head Lice Overview Head lice are a common community problem. An estimated 6 to 12 million infestations occur each year in the United States, most commonly among
Head Lice 101 What You Should Know About Head Lice Overview Head lice are a common community problem. An estimated 6 to 12 million infestations occur each year in the United States, most commonly among
- F - PEDICULOSIS (HEAD LICE)
 - F - PEDICULOSIS (HEAD LICE) What are they? Head lice are tiny gray insects (about 1/16 long) that live in human hair and feed on human blood. Head lice do not spread any disease. The head louse crawls
- F - PEDICULOSIS (HEAD LICE) What are they? Head lice are tiny gray insects (about 1/16 long) that live in human hair and feed on human blood. Head lice do not spread any disease. The head louse crawls
BINDIS TOOLKIT. In This Issue. Steps for Bindi development. Measures of Success. Annex: Sustainable models for bindis. 3.
 BINDIS TOOLKIT 3.0 June 2014 How to identify and develop Bindis, community Concierge and Caretakers, to share knowledge, empower women within and across communities. In This Issue Steps for Bindi development
BINDIS TOOLKIT 3.0 June 2014 How to identify and develop Bindis, community Concierge and Caretakers, to share knowledge, empower women within and across communities. In This Issue Steps for Bindi development
Head Lice. KidsHealth.org. Signs of Head Lice. The most-visited site devoted to children's health and development
 KidsHealth.org The most-visited site devoted to children's health and development Head Lice The head louse is a tiny, wingless parasitic insect that lives among human hairs and feeds on tiny amounts of
KidsHealth.org The most-visited site devoted to children's health and development Head Lice The head louse is a tiny, wingless parasitic insect that lives among human hairs and feeds on tiny amounts of
POLYTAR Plus Liquid PRODUCT INFORMATION. Polytar Plus Liquid medicated scalp cleanser, contains coal tar solution.
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE POLYTAR Plus Liquid PRODUCT INFORMATION Polytar Plus Liquid medicated scalp cleanser, contains coal tar solution. DESCRIPTION Polytar Plus Liquid contains coal tar solution 4% w/w.
NAME OF THE MEDICINE POLYTAR Plus Liquid PRODUCT INFORMATION Polytar Plus Liquid medicated scalp cleanser, contains coal tar solution. DESCRIPTION Polytar Plus Liquid contains coal tar solution 4% w/w.
Total Skin Electron Beam Therapy (TSEBT)
 Total Skin Electron Beam Therapy (TSEBT) Radiotherapy A guide for patients and carers Contents When is total body electron radiotherapy used?... 1 Planning your treatment... 1 Treatment... 1 Radioactivity...
Total Skin Electron Beam Therapy (TSEBT) Radiotherapy A guide for patients and carers Contents When is total body electron radiotherapy used?... 1 Planning your treatment... 1 Treatment... 1 Radioactivity...
Estill County 76 Golden Court Irvine, KY (606) Fax: (606)
 Estill County 76 Golden Court Irvine, KY 40336-6917 (606) 723-4557 Fax: (606) 723-5912 http://extension.ca.uky.edu When & Where: Friday, June 15 Monday, June 18 at J.M. Feltner 4-H Camp in London, KY.
Estill County 76 Golden Court Irvine, KY 40336-6917 (606) 723-4557 Fax: (606) 723-5912 http://extension.ca.uky.edu When & Where: Friday, June 15 Monday, June 18 at J.M. Feltner 4-H Camp in London, KY.
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH KWELLADA-P LOTION. Permethrin Lotion 5% w/w. Topical Scabicide
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH KWELLADA-P LOTION Permethrin Lotion 5% w/w Topical Scabicide Medtech Products Inc. 90 N. Broadway Tarrytown, NY 10591,USA Date of Preparation: 20 June 2012 --------------------------------
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH KWELLADA-P LOTION Permethrin Lotion 5% w/w Topical Scabicide Medtech Products Inc. 90 N. Broadway Tarrytown, NY 10591,USA Date of Preparation: 20 June 2012 --------------------------------
Psoralen Tablets (Methoxypsoralen)
 Psoralen Tablets (Methoxypsoralen) Psoralen (Methoxypsoralen) Tablets This information is intended to provide you with information about your treatment and should be read thoroughly so that you are aware
Psoralen Tablets (Methoxypsoralen) Psoralen (Methoxypsoralen) Tablets This information is intended to provide you with information about your treatment and should be read thoroughly so that you are aware
THE DIAGNOSIS SCABIES AND PUBIC LICE AND TREATMENT OF. Scabies PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. of the body and usually presents. of nits
 INFECTIOUS DISEASES UPDATE THE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF SCABIES AND PUBIC LICE Barbara M. Faber MD ELSEVIER Scabies and pediculosis pubis (infestation with pubic lice) are examples of infections caused
INFECTIOUS DISEASES UPDATE THE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF SCABIES AND PUBIC LICE Barbara M. Faber MD ELSEVIER Scabies and pediculosis pubis (infestation with pubic lice) are examples of infections caused
ADMINISTRATIVE PROCEDURE
 ADMINISTRATIVE PROCEDURE B1:4 School Operations Safety and Security Pediculosis in Schools Page 1 of 9 1. Purpose: To ensure that issues and procedures related to pediculosis (head lice) are dealt with
ADMINISTRATIVE PROCEDURE B1:4 School Operations Safety and Security Pediculosis in Schools Page 1 of 9 1. Purpose: To ensure that issues and procedures related to pediculosis (head lice) are dealt with
University of Wisconsin-Madison Hazard Communication Standard Policy Dept. of Environment, Health & Safety Office of Chemical Safety
 University of Wisconsin-Madison Hazard Communication Standard Policy Dept. of Environment, Health & Safety Office of Chemical Safety 1.0 Introduction... 1 1.1 Purpose... 1 1.2 Regulatory Background...
University of Wisconsin-Madison Hazard Communication Standard Policy Dept. of Environment, Health & Safety Office of Chemical Safety 1.0 Introduction... 1 1.1 Purpose... 1 1.2 Regulatory Background...
Dealing With Head Lice
 Dealing With Head Lice Step 1: Don t panic! It can be upsetting to find out that your child has head lice. However, before you freak out, here are some facts you should know about head lice. Head lice
Dealing With Head Lice Step 1: Don t panic! It can be upsetting to find out that your child has head lice. However, before you freak out, here are some facts you should know about head lice. Head lice
Basic section perm winding
 Basic section perm winding Learning outcomes Maintain effective and safe methods of working when perming and neutralising hair. Prepare for perming and neutralising. Perm and neutralise hair. Introduction
Basic section perm winding Learning outcomes Maintain effective and safe methods of working when perming and neutralising hair. Prepare for perming and neutralising. Perm and neutralise hair. Introduction
Burns. Chapter contents. A) Description of burns. B) Cause of burns. C) Treatment. D) Indications for professional burn care
 Burns Nearly everyone has had a burn at one time or another. We all know how painful a burn can be. Fortunately, most burns are minor and heal without serious scars or deformity but not all. Burns can
Burns Nearly everyone has had a burn at one time or another. We all know how painful a burn can be. Fortunately, most burns are minor and heal without serious scars or deformity but not all. Burns can
To provide a policy that documents John Street s approach to identification, exclusion, and treatment of head lice.
 1 3.12 Head Lice Purpose To provide a policy that documents John Street s approach to identification, exclusion, and treatment of head lice. Objective For educators and families at John Street to be guided
1 3.12 Head Lice Purpose To provide a policy that documents John Street s approach to identification, exclusion, and treatment of head lice. Objective For educators and families at John Street to be guided
Pharmacy Coverage Guidelines are subject to change as new information becomes available.
 TOPICAL CLINDAMYCIN PRODUCTS: ACANYA (clindamycin phosphate-benzoyl peroxide) gel BENZACLIN (clindamycin phosphate-benzoyl peroxide) gel CLEOCIN-T (clindamycin phosphate) gel, lotion, solution, swab CLINDAGEL
TOPICAL CLINDAMYCIN PRODUCTS: ACANYA (clindamycin phosphate-benzoyl peroxide) gel BENZACLIN (clindamycin phosphate-benzoyl peroxide) gel CLEOCIN-T (clindamycin phosphate) gel, lotion, solution, swab CLINDAGEL
Managing Head Lice at Home
 Managing Head Lice at Home Please keep this book for Future Reference Contents Introduction Page 3 The Facts about Head Lice Page 4 Preventing the Spread of Head Lice Page 5 How to Find Head Lice Page
Managing Head Lice at Home Please keep this book for Future Reference Contents Introduction Page 3 The Facts about Head Lice Page 4 Preventing the Spread of Head Lice Page 5 How to Find Head Lice Page
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Drapolene Cream 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Drapolene contains: Benzalkonium chloride solution 0.02% w/w Equivalent to
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Drapolene Cream 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Drapolene contains: Benzalkonium chloride solution 0.02% w/w Equivalent to
Creepy Crawlies and Kids
 Focus on CME at The University of Western Ontario Creepy Crawlies and Kids Michael J. Rieder, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FAAP, FRCP (Glasgow) Presented at Drug Therapy Update Day, London, Ontario, September 19, 2003
Focus on CME at The University of Western Ontario Creepy Crawlies and Kids Michael J. Rieder, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FAAP, FRCP (Glasgow) Presented at Drug Therapy Update Day, London, Ontario, September 19, 2003
CARE OF THE SKIN: GUIDELINES FOR ENSURING SKIN INTEGRITY LESSON PLAN
 CARE OF THE SKIN: GUIDELINES FOR ENSURING SKIN INTEGRITY LESSON PLAN Lesson overview Time: One Hour This lesson discusses the structure, functions, aging processes, and care of the skin. Learners will
CARE OF THE SKIN: GUIDELINES FOR ENSURING SKIN INTEGRITY LESSON PLAN Lesson overview Time: One Hour This lesson discusses the structure, functions, aging processes, and care of the skin. Learners will
FACT SHEET: ISOTRETINOIN INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
 FACT SHEET: ISOTRETINOIN INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS You have been prescribed isotretinoin (=Roaccutane, Oratane) for your acne. It is used for acne which does not respond to other treatments, scarring and
FACT SHEET: ISOTRETINOIN INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS You have been prescribed isotretinoin (=Roaccutane, Oratane) for your acne. It is used for acne which does not respond to other treatments, scarring and
Parents Guide Patienten-Ratgeber Englisch
 Headlice Kopfläuse Parents Guide Patienten-Ratgeber Englisch 2 The family business InfectoPharm and Pädia are among the leading manufacturers of medicines and health products for children in particular.
Headlice Kopfläuse Parents Guide Patienten-Ratgeber Englisch 2 The family business InfectoPharm and Pädia are among the leading manufacturers of medicines and health products for children in particular.
Managing Head Lice at Home
 Managing Head Lice at Home Please keep this booklet for Future Reference Contents Introduction 3 Head Lice Life Cycle 4 The Facts about Head Lice 5 Preventing the Spread of Head Lice 5 How to Find Head
Managing Head Lice at Home Please keep this booklet for Future Reference Contents Introduction 3 Head Lice Life Cycle 4 The Facts about Head Lice 5 Preventing the Spread of Head Lice 5 How to Find Head
PUVA (Psoralen + ultra violet light - wavelength A)
 PUVA (Psoralen + ultra violet light - wavelength A) What is PUVA? Ultra violet light occurs naturally in the sun s rays and is divided into three types - A, B and C - according to its wavelength. Psoralens
PUVA (Psoralen + ultra violet light - wavelength A) What is PUVA? Ultra violet light occurs naturally in the sun s rays and is divided into three types - A, B and C - according to its wavelength. Psoralens
Brick winding technique
 Brick winding technique Learning outcomes Maintain effective and safe methods of working when perming and neutralising hair. Prepare for perming and neutralising. Perm and neutralise hair. Introduction
Brick winding technique Learning outcomes Maintain effective and safe methods of working when perming and neutralising hair. Prepare for perming and neutralising. Perm and neutralise hair. Introduction
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Clindamycin 300 mg Capsules Clindamycin (as hydrochloride)
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Clindamycin 300 mg Capsules Clindamycin (as hydrochloride) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Clindamycin 300 mg Capsules Clindamycin (as hydrochloride) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important
GRAND FORKS PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT HEAD LICE POLICY AND PROCEDURE
 GRAND FORKS PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT HEAD LICE POLICY AND PROCEDURE MEDICAL IMPACT OF HEAD LICE Pediculosis is an infestation of head lice, not an infection. It does not pose a significant health hazard
GRAND FORKS PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT HEAD LICE POLICY AND PROCEDURE MEDICAL IMPACT OF HEAD LICE Pediculosis is an infestation of head lice, not an infection. It does not pose a significant health hazard
LICE: BIOLOGY AND PUBLIC HEALTH RISK
 E-245-W Public Health Department of Entomology HUMAN LICE: BIOLOGY AND PUBLIC HEALTH RISK Catherine A. Hill and John F. MacDonald, Department of Entomology Lice are parasitic insects that must live, feed,
E-245-W Public Health Department of Entomology HUMAN LICE: BIOLOGY AND PUBLIC HEALTH RISK Catherine A. Hill and John F. MacDonald, Department of Entomology Lice are parasitic insects that must live, feed,
INFORMATION ABOUT YOUR TREATMENT
 INFORMATION ABOUT YOUR TREATMENT Indication OXISTAT Lotion is indicated for the topical treatment of the following dermal infections: tinea pedis, tinea cruris, and tinea corporis due to Trichophyton rubrum,
INFORMATION ABOUT YOUR TREATMENT Indication OXISTAT Lotion is indicated for the topical treatment of the following dermal infections: tinea pedis, tinea cruris, and tinea corporis due to Trichophyton rubrum,
The Ultimate PRPer: PRP with PRP
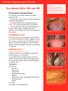 PRP Profile Philip Richard Popham: PRP on PRP 1 The Ultimate PRPer: PRP with PRP Pre-Emergent & Emergent Phases It is a year ago this month that I started on my medical treatment for PRP. The following
PRP Profile Philip Richard Popham: PRP on PRP 1 The Ultimate PRPer: PRP with PRP Pre-Emergent & Emergent Phases It is a year ago this month that I started on my medical treatment for PRP. The following
