ARCH202 History of Architecture Spring
|
|
|
- Evan Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Nizwa College of Engineering & Architecture Dept. of Architecture & Interior Design ARCH202 History of Architecture Spring Dr. Janon Kadhim Associate Professor of Architecture
2 ARCH 202 History of Architecture Lecture #2 Mesopotamian ARCHITECTURE Dr. Janon A. W. Kadhim Associate Professor of Architecture University of Nizwa Spring
3 Mesopotamia: The Cradle of civilization On the land of Mesopotamia we can trace the growth and development of human existence and civilization from the earliest times in a continuous sequence. The caves in Northern Mesopotamia contain remains of the ancient Cavemen. The first Agrarian settlements in the world formed in the north of Mesopotamia some of which go back to BC. Dr. Janon Kadhim 3
4 The fertile Crescent Arab Gulf Mesopotamia, the land between the rivers, is situated in the region called the fertile crescent Dr. Janon Kadhim 4
5 Mesopotamia: Attributes of the Natural Environment Mesopotamia is part of what is known as the Fertile Crescent ; It contains some of the most fertile and rich land in the world; Diverse topography and climate: which provided a variety of building materials, and led to the creation of a variety of art forms and architectural types; Mesopotamia does not have any natural means of fortification other than the mountains that create the North and North-Eastern boundaries of the region. This has created a continuous problem for Mesopotamia over history causing it to be invaded many times over history by surrounding entities. Dr. Janon Kadhim 5
6 Other Natural attributes: Characterized by the two large rivers, The Tigris and the Euphrates, and their many tributaries; The rivers are known for their annual floods. The flood waters carry particles of clay and minerals which they carry from the mountainous region they go through as they flow from their main origins downwards; The flood over-flows create plains called the Sedimentary Plains that were created over thousands of years by the residue that covers the land during the floods; The major part of southern Mesopotamia is created of Sedimentary Plains. At one time the waters of the Arabian Gulf reached all the way up to the south of present - day Baghdad. Dr. Janon Kadhim 6
7 Mesopotamia: The land between the Two Rivers Rivers Dijla Tigris and Furat Euphrates and their many branches, main life stream; irrigating the whole land A land of diverse topography, climate, and natural resources Dr. Janon Kadhim 7
8 Local building materials and other natural resources Mud and mud brick: the main building material in Mesopotamia; It is the natural material available in the land; It was also considered to be a sacred material, sent to the people by the Gods. Various types of bricks were used: Sun-burned brick; Kiln fried brick; Glazed and colored Glazed brick (used in decoration) Dr. Janon Kadhim 8
9 Other Building materials Natural Stone was used in northern Mesopotamia, but only as a façade material over a base of mud or mud brick; Stone also used to build bridges and cross-overs, and for sculptures and carved Murals; Lime Mortar to bond the brick; Tar, as a natural sealant and bonding material; Stucco wash for façade treatments, and also Stucco panels for Fresco art work; Various minerals are available and widely used especially in artwork, tools, and decoration, like Copper, Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Iron. Dr. Janon Kadhim 9
10 Climatic Factors in Mesopotamia The climate has highly impacted Mesopotamian architecture. Mainly it is hot and dry with cold, short winters with little rain; The prevailing winds are the north-western which are pleasant winds, while the summer brings the south-eastern winds that are hot and cause severe dust storms. This is an important factor considered in buildings; Most of the cities are built on the river banks with the buildings in the direction of the prevailing winds; Some very important historic cities were abandoned when the course of the river changed and the city became far from the river banks, as the ancient city of Ur ; Dr. Janon Kadhim 10
11 Climatic Factors in Mesopotamia To overcome the harsh climate, buildings were inwardlooking, depending on their inner courtyard to provide light and ventilation for the building. The openings take prevailing winds into account; The courtyard also became the main social area in houses and buildings; The facades are mostly window-less or with very few and small openings to protect from the heat & dust, Buildings are usually built adjacent to each other with narrow alley-ways for walkways and roads to prevent exposure to the harsh weather as well as for privacy and defense purposes. Dr. Janon Kadhim 11
12 Cultural Attributes of Mesopotamia Architecture reflects the Spirit of its Age, meaning it is affected by the general cultural environment of the people who create it; The Mesopotamian people were highly influenced by their religious and spiritual beliefs; These beliefs influenced their understanding and outlook to life and to the world around them and was reflected in their art and architecture, as well as in their poetry, literature, and even music. Dr. Janon Kadhim 12
13 Cultural Attributes of Mesopotamia The Mesopotamians believed in many Gods and their temples were dedicated to these Gods; The Sumerians had a special theory of creation. They believed Man was created from Mud or clay which was the gift from the Gods. Therefore, they believed Mud was a sacred material and ensured to build all structures from Mud or mud brick, even in areas where there was Stone, as Northern Mesopotamia. Dr. Janon Kadhim 13
14 Cultural Attributes of Mesopotamia They believed Man was created to serve the Gods, therefore they dedicated their temples to them; They were very superstitious, they believed a person could be cursed if his name was known, therefore they used fake names ; They believed Man s strength is in his head, the place of his mind, therefore in sculptures the proportion of the head was lager than reality; They believed the eyes were the mirror of the spirit therefore, in sculptures the eyes were very large or were inlaid with precious stones. Dr. Janon Kadhim 14
15 Cultural Attributes of Mesopotamia They did not believe in the Divine King, or that the King was the God, as the Egyptians did, but rather the king was to serve the God; They did not believe in life after death, as the Egyptians did, therefore they concentrated on secular (worldly) matters. They built temples for the Gods, and built elaborate palaces and others to celebrate everyday life. They also used perishable materials in building; They did not have funerary architecture (burials, tombs, etc.) since they feared death; The only example is the Royal Burial in UR (the 1st dynasty of UR), which contains the remains of three of the Sumerian kings. Dr. Janon Kadhim 15
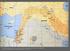
16 A map showing some of the most famous sites of the Mesopotamian Civilization Dr. Janon Kadhim 16
17 Mesopotamian Era C B.C. 539 B.C. Dr. Janon Kadhim 17
18 Early shelters and settlements The Paleolithic Age in Mesopotamia: Remains of the Cave Man were found in three caves in the mountains of northern Mesopotamia. Human remains in addition to small stone tools and gadgets were found in these caves. Early Settlements of Mesopotamia: The earliest dated back to 10,000 B.C They were founded in northern Mesopotamia; The first huts were circular, built of mud on a foundation of large rocks. Dr. Janon Kadhim 18
19 The Settlement of Jermo (around 6750 B.C.) Located in northern Mesopotamia; The first agrarian settlement (village) in the world; They planted barely and wheat; The settlement remained inhabited for over 400 yrs; The remains of more than houses were found in the settlement; The houses were of rectangular floor plans; Built of Mud on foundations of natural rock; Other settlements followed. The later ones had fortifying walls to protect them. Dr. Janon Kadhim 19
20 The ancient Mesopotamians were the first to discover means of growing wheat and barley. (The Agrarian Revolution) They invented weaving, pottery and other art forms as early as BC. Most of all they invented the Wheel. Some of the ancient Mesopotamian agrarian settlements were highly developed. Dr. Janon Kadhim 20
21 Ancient Mesopotamian Era Pre Dynastic Era ( c B.C B.C. ) Late Ubaid Jamdet Nasir Warka Ubaid Eridu Early Dynastic Era ( c2900 B.C B.C. ) Kish II Dynasty (Kingdom of Misilim) UR I Dynasty Sumerian dynasty Akkadian Empire ( c2371 B.C B.C. ) UR III Dynasty Neo Sumerians ( c2110 B.C B.C. ) Assyrians ( B.C.) Babylonians ( B.C.) In the North in the south Dr. Janon Kadhim 21
22 Pre Dynastic Era 5300 B.C B.C. Also known as the Pre-Sumerian and Sumerian Era; Very important era since many great developments happened at this time, especially the invention of writing, and the wheel; Many of the typical art forms of Mesopotamia originated in this era; Great architectural achievements: the prototypes of most Mesopotamian architectural types originated in this era including the first cities.
23 Cuneiform Script Cuneiform script is one of the earliest known forms of written expression. It emerged in Sumer around the 30th century BC, with predecessors reaching into the late 4th millennium (the Uruk IV period), cuneiform writing began as a system of pictographs. In the course of the 3rd millennium BC the pictorial representations became simplified and more abstract. The number of characters in use also grew gradually smaller, from about 1,000 unique characters in the Early Bronze Age to about 400 unique characters in Late Bronze Age (Hittite cuneiform). Cuneiform writing was gradually replaced by alphabetic writing in the Iron Age Neo-Assyrian Empire and was practically extinct by the beginning of the Common Era. It was deciphered from scratch in 19th century scholarship. Dr. Janon Kadhim 23
24 Cuneiform documents were written on clay tablets, by means of a blunt reed for a stylus. The impressions left by the stylus were wedge shaped, thus giving rise to the name cuneiform "wedge shaped," from the Latin cuneus, meaning "wedge". Dr. Janon Kadhim 24
25 Dr. Janon Kadhim 25
26 Art forms typical to Mesopotamia A. Cylindrical seals: An art form typical of Mesopotamia exclusively. A small clay cylinder with bas-relief carving on it. When rolled on a wet clay sled the cylinder leaves an decorative imprint. Cylindrical Seal with imprint Dr. Janon Kadhim 26
27 First artifacts are traced back to the predynastic era and continuing in Mesopotamian Art through the following eras. Cylinders made of clay, lime or gypsum stone or shell. Dr. Janon Kadhim 27
28 Cylinders rolled on a surface of wet clay. Imprint is made on wet surface that is then left to dry. Dr. Janon Kadhim 28
29 Other main art forms: B. Pottery: made of clay, main building and art material in Mesopotamia. Colored and painted pottery becoming typical as early as the 4 th millennium B.C. * Key work Sacred cup, Warka, 3 rd mill. B.C., Pre-dynastic era, Mesopotamia Bas-relief on lime stone Dr. Janon Kadhim 29
30 C. Small sculptures. 1. Bas-Relief sculpture: usually using clay as a main material. 2. Sculptures in-the-round, made mostly of limestone 3. Inlaid bas-relief sculptures: most typical inlays in shell, stones or colored stone. One of the earliest works of sculpture, Head statue of the Sumerian woman, Warka, 2800 B.C., Pre-Dynastic Era D. Jewelry: mostly made of gold, silver, bronze and inlaid with precious and semi precious stones. Some designs are very elaborate and fashionable Dr. Janon Kadhim 30
31 E. The art of colored cones (Mosaic like): Cone shaped objects made of clay and colored in vibrant colors are nailed into the wet mud wall. It creates a beautiful decoration in addition to embracing and strengthening the wall. This art form is typical of the pre-dynastic era and disappeared afterwards Cone mosaics, Warka, Temple of Inanna, hall of the pillars, Pre-dynastic era * Key work Dr. Janon Kadhim 31
32 Cone mosaics, Warka, Temple of Inanna, hall of the pillars, Pre-dynastic era Dr. Janon Kadhim 32
33 1. Temples: Pre-Dynastic Architecture The first Mesopotamian temples were built in this era forming the basic prototype. No Palaces in this era; They believed the temple was the God s home on earth; They believed the Gods chose certain places to reside in, that s why certain sites were sacred and temples were always built on these sites and old temples continuously renovated; They also had the tradition of building new temples on top of the old. This eventually led to the high temple; Sites like Uruk, Warka, and UR were considered sacred; Dr. Janon Kadhim 33
34 Mesopotamian Temples First temples had simple rectangular plans; They contained the basic spaces: Entrance Courtyard; Antecella: the space that leads to the Cella; The Cella or Sanctuary: place of worship, contained an offering table, and a nitch; Fortification: in some of the temples Dr. Janon Kadhim 34
35 Types of Mesopotamian Temples Low Temples: The first type of temples were of this type. They are built directly on the ground; High Temples: 1. Mastaba type: the first type of high temples developed naturally due to building new temples on top of the old leading over time to a raised ground level; 2. The Ziggurat: the first one built was in the Neo- Sumerian era, Ur Dynasty III, in 2100 B.C. (will explain later) Dr. Janon Kadhim 35
36 Building materials used in Temples Temples were built of sun-baked Mud brick, on foundation of large rocks; Recessed Paneling is used on the outer facades to strengthen the wall. Also creating a beautiful shade and shadow effect on the window-less elevation; The exterior facades were coated with a layer of slurry mud or plaster to protect them; Some decorative means were used on the temple walls like a frieze (strip) decorated with inlays of colored stone or shells; The art of cone mosaics was used in some examples. Dr. Janon Kadhim 36
37 The White Temple, Uruk, c B.C., Pre-Dynastic (high temple) Called the White temple because the exterior walls were coated with a layer of Plaster to protect them *Key Work Very simple floor plan, typical of Mesopotamian Temples Dr. Janon Kadhim 37
38 Pre-Dynastic Cities The Sumerian city of Warka, in southern Mesopotamia was the first planned city in history; Built c B.C.; It contains the 3 typical elements of the Mesopotamian city: The city walls: the walls of Warka were fortified with towers; The urban center (or Core): which contained the main temple, also the white temple; The residential district: Organic in planning, with adjacent courtyard houses and narrow alley ways. Dr. Janon Kadhim 38
39 Warka, 3000 B.C., Southern Mesopotamia, The first planned city in history, Warka is a sacred site therefore it contains many famous Mesopotamian temples Warka * Key work Dr. Janon Kadhim 39
40 Early Dynastic era 2500 B.C B.C. City States: Many cities formed in this era in the southern part of the region on the river banks. Some of these cities become self governing states called city stats ruled by families or dynasties. Most famous are Warka, Ur, Kish, Lagash. Famous dynasties of the era: UR Dynasty I B.C., (Sumerian dynasty) Dynasty of Kish II, (Tribes from Arab Peninsula), their king Misilim started the palace as a new building typeseparating the (religious) power from the secular power of the king. Dr. Janon Kadhim 40
41 Early Dynastic Era Also known as the Sumerian era. Famous Sumerian city state of UR and the royal dynasty of Ur I Sumerian woman with gold jewelry, Early Dynastic era, UR Dynasty I 2600 B.C. * Key work Dr. Janon Kadhim 41
42 The Dynasty of UR I was famous for its Gold Jewelry works with some outstanding designs; Many of these objects were found in the Royal Burial in UR, 2600 B.C., the only example of burial architecture in Mesopotamia Dr. Janon Kadhim 42
43 They were also famous for tools, weapons and musical instruments that were made of Bronze, gold and other precious materials, using inlays of shells and precious and semi-precious stones Sumerian Golden Harp Early dynastic, UR Dynasty I 2600 B.C. Dr. Janon Kadhim 43
44 Early Dynastic Era Standard of UR, Wall Mural UR Dynasty I, 2600 B.C. Bas-Relief filed with shell on Bitumen backing Dr. Janon Kadhim 44
45 Early Dynastic Architecture Temples: Followed the same style of those of the predynastic era, but became larger and a little more elaborate or complicated; Some Temples were surrounded by a fortifying wall, like the mustaba temple in Khafaja; Cities: New cities were built following the main concepts and elements developed in the previous era. Famous cities: Ur and Kish; The Palace: New building type created by Misilim the ruler of Kish; He built the first Palace Misilim Palace, Kish, 2600 B.C. Dr. Janon Kadhim 45
46 The Temple in Khafaji, c B.C., Early- Dynastic era, Mastaba type temple. Enclosed in an oval shape enclosure Dr. Janon Kadhim 46
47 The Akkadian Empire B.C. The Stele, a new art form invented by the Akkadians which later also became typical of Mesopotamian art The Stele of King Naram-Sin Akkadian Empire B.C. * Key work Dr. Janon Kadhim 47
48 King Sargon of Akkad, founder of Akkadian Empire, B.C. Head Sculpture in bronze Dr. Janon Kadhim 48
49 The Neo- Sumerians UR Dynasty III B.C. Created by king Ur-Nammu the ruler of the third dynasty of UR; He defeated the Akkadian Empire and reunited all of Mesopotamia under his leadership; Great developments especially in the arts and architecture happened in this era; Dr. Janon Kadhim 49
50 The Ziggurat An outstanding development by the Dynasty of Ur III; The ziggurat is a high temple; It is called the God s heavenly home. So it is built on a very high platform to ensure that is closer to the sky; The first ziggurat is the great ziggurat of Ur- Nammu in Ur, 2100 B.C. Dr. Janon Kadhim 50
51 Neo-Sumerian Era ; Ur, B.C. Ziggurat of UR-NAMMU, UR Neo-Sumerians, UR dynasty III 2100 B.C. / main feature of the neo-sumerians * Key work Dr. Janon Kadhim 51
52 Ziggurat of UR-NAMMU, UR Neo-Sumerians, UR dynasty III 2100 B.C. A reconstruction drawing of the ziggurat Aerial view of the ruins of Ur and the reconstruction of the ziggurat base Dr. Janon Kadhim 52
53 The City of Ur in the Neo-Sumerian era (Ur Dynasty III) With a contemporary day Arial view Dr. Janon Kadhim 53
54 The Citadel of ancient Ur, 2100 B.C., Ur Dynasty III Contains the main elements of the urban core which are the main temples, the Ziggurat and the palace. All contained within the fortified walls forming the citadel Dr. Janon Kadhim 54
55 The residential district, City of Ur, 2100 B.C. Adjacent courtyard houses with narrow, twisty alleys and road Dr. Janon Kadhim 55
56 Other typical Mesopotamian art forms continued to flourish and develop in the era, as the cylindrical seals, pottery, and Stella. Stele of Ur-Nammu, Ur, Neo Sumerian, Ur Dynasty III, 2100 B.C. * Key work Dr. Janon Kadhim 56
57 Key works 1) Sacred cup, Warka, 3 rd mill. B.C., Pre-dynastic era, Mesopotamia, Basrelief on lime stone 2) Cone mosaics, Temple of Inanna, hall of the pillars, Warka, Pre-dynastic era 3) The White Temple, Uruk, c B.C., Pre-Dynastic (high temple) 4) City of Warka, 3000 B.C., Southern Mesopotamia, 5) Sumerian woman with gold jewelry, Early Dynastic era, Ur Dynasty I, 2600 B.C. 6) Ziggurat of UR-NAMMU, Ur, Neo-Sumerians, Ur dynasty III, 2100 B.C. (High Temple) 7) Stele of Ur-Nammu, Ur, Neo Sumerian, Ur Dynasty III, 2100 B.C. 8) The Stele of King Naram-Sin, Akkadian Empire, Akad, B.C. Dr. Janon Kadhim 57
Art of the Ancient Near East Day 1. Chapter 2
 Art of the Ancient Near East Day 1 Chapter 2 Getting Started When we start a chapter you need Your image cards on your desk as well as 2-4 extra index cards These cards should be have images and titles,
Art of the Ancient Near East Day 1 Chapter 2 Getting Started When we start a chapter you need Your image cards on your desk as well as 2-4 extra index cards These cards should be have images and titles,
Arsitektur & Seni SEJARAH ARSITEKTUR. Marble (granite) figure
 Marble (granite) figure More than 4,000 years ago the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers began to teem with life--first the Sumerian, then the Babylonian, Assyrian, Chaldean, and Persian empires.
Marble (granite) figure More than 4,000 years ago the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers began to teem with life--first the Sumerian, then the Babylonian, Assyrian, Chaldean, and Persian empires.
Gardner s Art Through the Ages, 13e. Chapter 2 The Ancient Near East
 Gardner s Art Through the Ages, 13e Chapter 2 The Ancient Near East 1 The Ancient Near East 2 Goals Understand the cultural changes in the Neolithic Revolution as they relate to the art and architecture.
Gardner s Art Through the Ages, 13e Chapter 2 The Ancient Near East 1 The Ancient Near East 2 Goals Understand the cultural changes in the Neolithic Revolution as they relate to the art and architecture.
Chapter 2 The First River-Valley Civilizations, B.C.E.
 Chapter 2 The First River-Valley Civilizations, 3500 1500 B.C.E. Gilgamesh Strangling a Lion This eighth-century B.C.E. sculpture of a king, possibly Gilgamesh, from the palace of the Assyrian king Sargon
Chapter 2 The First River-Valley Civilizations, 3500 1500 B.C.E. Gilgamesh Strangling a Lion This eighth-century B.C.E. sculpture of a king, possibly Gilgamesh, from the palace of the Assyrian king Sargon
Ancient Mesopotamia and the Sumerians (Room 56)
 Ancient Mesopotamia and the Sumerians (Room 56) The Sumerians are thought to have formed the first human civilization in world history. They lived in southern Mesopotamia, between the Tigris and Euphrates
Ancient Mesopotamia and the Sumerians (Room 56) The Sumerians are thought to have formed the first human civilization in world history. They lived in southern Mesopotamia, between the Tigris and Euphrates
Foods of Mesopotamia/Sumer: YOUR TURN! Draw a picture in each box. barley onions apples (for bread/beer) sheep cucumbers figs
 Civilization of Sumer FOOD SUPPLY: The people of Sumer created the first civilization, advancing their way of life over time. The first step towards creating a civilization was when the Sumerians established
Civilization of Sumer FOOD SUPPLY: The people of Sumer created the first civilization, advancing their way of life over time. The first step towards creating a civilization was when the Sumerians established
Euphrates. Version 1.0
 Mesopotamia: the Tigris and Euphrates from Baghdad to the Arabian Gulf Version 1.0 These programmes on The World of Ancient Art for students and the public. have been designed They use material on the
Mesopotamia: the Tigris and Euphrates from Baghdad to the Arabian Gulf Version 1.0 These programmes on The World of Ancient Art for students and the public. have been designed They use material on the
Table of Contents. How to Use This Product Introduction to Primary Sources Activities Using Primary Sources... 15
 Table of Contents How to Use This Product........... 3 Introduction to Primary Sources..... 5 Activities Using Primary Sources... 15 Photographs Dagger and Sheath................15 16 Take a Stab.......................15
Table of Contents How to Use This Product........... 3 Introduction to Primary Sources..... 5 Activities Using Primary Sources... 15 Photographs Dagger and Sheath................15 16 Take a Stab.......................15
Marshall High School Mr. Cline Western Civilization I: Ancient Foundations Unit Two BA
 Marshall High School Mr. Cline Western Civilization I: Ancient Foundations Unit Two BA Have you ever happened across a dollar on the sidewalk? What about a gold ring or an expensive watch? Perhaps you
Marshall High School Mr. Cline Western Civilization I: Ancient Foundations Unit Two BA Have you ever happened across a dollar on the sidewalk? What about a gold ring or an expensive watch? Perhaps you
Sumerian Achievements
 Sumerian Achievements The Invention of Writing The Sumerians made one of the greatest cultural advances in history. They developed cuneiform (kyoo-neeuh-fohrm writing. But Sumerians did not have pencils,
Sumerian Achievements The Invention of Writing The Sumerians made one of the greatest cultural advances in history. They developed cuneiform (kyoo-neeuh-fohrm writing. But Sumerians did not have pencils,
006 Hª MAN english_maquetación 1 21/02/14 12:09 Página 105 Ancient Near East
 Ancient Near East Ancient Near East The history of the Ancient Near East, documented in various sources, unfolded in different geographic locations scattered across nearly 9 million square kilometres,
Ancient Near East Ancient Near East The history of the Ancient Near East, documented in various sources, unfolded in different geographic locations scattered across nearly 9 million square kilometres,
The origin of man is believed to have started some 3 million years ago in southern Africa.
 The origin of man is believed to have started some 3 million years ago in southern Africa. Thousands of years ago Human migratory patterns can be traced back almost 200,000 years by using bones, tools
The origin of man is believed to have started some 3 million years ago in southern Africa. Thousands of years ago Human migratory patterns can be traced back almost 200,000 years by using bones, tools
BASRAH MUSEUM SPACE PLAN
 BASRAH MUSEUM SPACE PLAN The Lakeside Palace on the outskirts of Basrah will make an ideal museum. It is in surprisingly good condition and requires only a modest amount of refurbishment and renovation.
BASRAH MUSEUM SPACE PLAN The Lakeside Palace on the outskirts of Basrah will make an ideal museum. It is in surprisingly good condition and requires only a modest amount of refurbishment and renovation.
Ancient Mediterranean
 Ancient Mediterranean 3500 BCE 300 CE Unit 2 Chapter 2 Mesopotamia and Persia Mesopotamia is the Greek name for the land between the rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in this case Often called the
Ancient Mediterranean 3500 BCE 300 CE Unit 2 Chapter 2 Mesopotamia and Persia Mesopotamia is the Greek name for the land between the rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in this case Often called the
Kendra Magill ANCIENT NEAR EAST. Mesopotamia
 Kendra Magill ANCIENT NEAR EAST Mesopotamia ICONOGRAPHY = SYMBOLS OF A CULTURE People honor and protect their own symbols but often destroy the symbols of adversaries as a token of dominance, or they adapt
Kendra Magill ANCIENT NEAR EAST Mesopotamia ICONOGRAPHY = SYMBOLS OF A CULTURE People honor and protect their own symbols but often destroy the symbols of adversaries as a token of dominance, or they adapt
Ubaid Society Evidence for Economic & Social Differentiation
 Ubaid Society Evidence for Economic & Social Differentiation Distinctions between houses and temples Tell Abada Major differences in artefacts between houses Susa (Late Ubaid, 10 ha) 10 m tall platform
Ubaid Society Evidence for Economic & Social Differentiation Distinctions between houses and temples Tell Abada Major differences in artefacts between houses Susa (Late Ubaid, 10 ha) 10 m tall platform
Assyrian Reliefs Bowdoin College Museum of Art
 Assyrian Reliefs Bowdoin College Museum of Art Middle School Resource Created by Blanche Froelich 19 Student Education Assistant What is a relief? All words appearing in a bold color are defined in the
Assyrian Reliefs Bowdoin College Museum of Art Middle School Resource Created by Blanche Froelich 19 Student Education Assistant What is a relief? All words appearing in a bold color are defined in the
7 URUK CIVILIZATION 1080L
 7 URUK CIVILIZATION 1080L URUK THE WORLD S FIRST BIG CITY By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Nestled between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the world s first major city sprang up in a fertile
7 URUK CIVILIZATION 1080L URUK THE WORLD S FIRST BIG CITY By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Nestled between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the world s first major city sprang up in a fertile
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Class 9 The emergence of civilization in Mesopotamia: Ubaid and Uruk Copyright Bruce Owen 2007
 Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Class 9 The emergence of civilization in Mesopotamia: Ubaid and Uruk Copyright Bruce Owen 2007 Ubaid period (I, II, III, IV; about 5600-3900 BC) Ubaid style pottery
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Class 9 The emergence of civilization in Mesopotamia: Ubaid and Uruk Copyright Bruce Owen 2007 Ubaid period (I, II, III, IV; about 5600-3900 BC) Ubaid style pottery
Difference between Architecture and Sculpture. Architecture refers to the design and construction of buildings
 Art and Culture 1.1 Introduction Difference between Architecture and Sculpture Classification of Indian Architecture Indus Valley Civilization and their archaeological findings BY CIVIL JOINT The Word
Art and Culture 1.1 Introduction Difference between Architecture and Sculpture Classification of Indian Architecture Indus Valley Civilization and their archaeological findings BY CIVIL JOINT The Word
Art of the Ancient Near East
 Art of the Ancient Near East Ancient Near East Time Period 3500 bce 641 ce Regions Sumerian Art c. 3500-2340 bce Iraq Babylonian Art 1792-1750 bce Iraq Assyrian Art 883-612 bce Iraq Persian Art c. 559-331
Art of the Ancient Near East Ancient Near East Time Period 3500 bce 641 ce Regions Sumerian Art c. 3500-2340 bce Iraq Babylonian Art 1792-1750 bce Iraq Assyrian Art 883-612 bce Iraq Persian Art c. 559-331
200 mm annual rainfall line and the distribution of barley and wheat in the Near East, with some Epipalaeolithic and Proto-Neolithic settlements.
 200 mm annual rainfall line and the distribution of barley and wheat in the Near East, with some Epipalaeolithic and Proto-Neolithic settlements. Neolithic in the Near East: early sites of socialization
200 mm annual rainfall line and the distribution of barley and wheat in the Near East, with some Epipalaeolithic and Proto-Neolithic settlements. Neolithic in the Near East: early sites of socialization
History Ch-4 (W.B Answer Key) Pakistan 2. The bricks were laid in an interlocking pattern and that made the walls strong.
 History Ch-4 (W.B Answer Key) W.B (pp-42, 43) 1. The site of Harappa is in the present day Pakistan. 2. How were the bricks of ancient settlement used? The bricks were laid in an interlocking pattern and
History Ch-4 (W.B Answer Key) W.B (pp-42, 43) 1. The site of Harappa is in the present day Pakistan. 2. How were the bricks of ancient settlement used? The bricks were laid in an interlocking pattern and
IMAGES OF POWER: ANCIENT NEAR EAST: FOCUS (Sumerian Art and Architecture)
 IMAGES OF POWER: ANCIENT NEAR EAST: FOCUS (Sumerian Art and Architecture) TITLE or DESIGNATION: White Temple and its Ziggurat CULTURE or ART HISTORICAL PERIOD: Ancient Sumerian DATE: c. 3500-3000 B.C.E.
IMAGES OF POWER: ANCIENT NEAR EAST: FOCUS (Sumerian Art and Architecture) TITLE or DESIGNATION: White Temple and its Ziggurat CULTURE or ART HISTORICAL PERIOD: Ancient Sumerian DATE: c. 3500-3000 B.C.E.
ANP363. EXAM 2 Monday, April 1, 2013
 ANP363 EXAM 2 Monday, April 1, 2013 NAME: PID: Be absolutely sure to put your name and PID on the exam sheet Write your answers in the space provided - If you need extra space, use the back of the sheet
ANP363 EXAM 2 Monday, April 1, 2013 NAME: PID: Be absolutely sure to put your name and PID on the exam sheet Write your answers in the space provided - If you need extra space, use the back of the sheet
The Chalcolithic in the Near East: Mesopotamia and the Levant
 The Chalcolithic in the Near East: Mesopotamia and the Levant Prof. Susan Pollock Institut für Vorderasiatische Archäologie, Freie Universität Berlin Department of Anthropology, Binghamton University Chronological
The Chalcolithic in the Near East: Mesopotamia and the Levant Prof. Susan Pollock Institut für Vorderasiatische Archäologie, Freie Universität Berlin Department of Anthropology, Binghamton University Chronological
Sunday, February 12, 17. The Shang Dynasty
 The Shang Dynasty The Shang Dynasty The Shang Dynasty is one of the earliest dynasties in China This dynasty was centered in the Huang He (Yellow River) Valley and ruled from 1700-1122 B.C. For many years,
The Shang Dynasty The Shang Dynasty The Shang Dynasty is one of the earliest dynasties in China This dynasty was centered in the Huang He (Yellow River) Valley and ruled from 1700-1122 B.C. For many years,
Tell Shiyukh Tahtani (North Syria)
 Tell Shiyukh Tahtani (North Syria) Report of the 2010 excavation season conducted by the University of Palermo Euphrates Expedition by Gioacchino Falsone and Paola Sconzo In the summer 2010 the University
Tell Shiyukh Tahtani (North Syria) Report of the 2010 excavation season conducted by the University of Palermo Euphrates Expedition by Gioacchino Falsone and Paola Sconzo In the summer 2010 the University
Mesopotamian Art and Architecture I INTRODUCTION
 Mesopotamian Art and Architecture I INTRODUCTION Mesopotamian Art and Architecture, the arts and buildings of the ancient Middle Eastern civilizations that developed in the area (now Iraq) between the
Mesopotamian Art and Architecture I INTRODUCTION Mesopotamian Art and Architecture, the arts and buildings of the ancient Middle Eastern civilizations that developed in the area (now Iraq) between the
IN THE EARLIEST CITIES
 CHAPTER 4 IN THE EARLIEST CITIES Saving an old building Jaspal and Harpreet were playing cricket in the lane outside their home when they noticed the people who were admiring the dilapidated old building
CHAPTER 4 IN THE EARLIEST CITIES Saving an old building Jaspal and Harpreet were playing cricket in the lane outside their home when they noticed the people who were admiring the dilapidated old building
THE ANCIENT CITY OF UR
 Expository Text THE ANCIENT CITY OF UR BY MARIA GILL PAIRED READ The Game STRATEGIES & SKILLS Comprehension Strategy: Summarize Skill: Sequence Vocabulary Strategy Greek Roots Vocabulary bedrock, embarked,
Expository Text THE ANCIENT CITY OF UR BY MARIA GILL PAIRED READ The Game STRATEGIES & SKILLS Comprehension Strategy: Summarize Skill: Sequence Vocabulary Strategy Greek Roots Vocabulary bedrock, embarked,
Chapter 14. Unlocking the Secrets of Mohenjodaro
 Chapter 14 Unlocking the Secrets of Mohenjodaro Chapter 14 Unlocking the Secrets of Mohenjodaro What can artifacts tell us about daily life in Mohenjodaro? 14.1 Introduction The geography of the Indian
Chapter 14 Unlocking the Secrets of Mohenjodaro Chapter 14 Unlocking the Secrets of Mohenjodaro What can artifacts tell us about daily life in Mohenjodaro? 14.1 Introduction The geography of the Indian
XXXXXXX XXXXXXX Final Paper
 XXXXXXX XXXXXXX Final Paper ----- Art 101.01: History of Western Art I: Prehistoric to the 14th Century Valerie Lalli April 30, 2018 Artist: Unknown Title: Statuette of a female Period: Iran, Ancient Near
XXXXXXX XXXXXXX Final Paper ----- Art 101.01: History of Western Art I: Prehistoric to the 14th Century Valerie Lalli April 30, 2018 Artist: Unknown Title: Statuette of a female Period: Iran, Ancient Near
Nippur under Assyrian Domination: 15th Season of Excavation,
 Nippur under Assyrian Domination: 15th Season of Excavation, 1981-82. McGuire Gibson Nippur, during the seventh century B.C., was controlled by the Assyrians, but was essentially Babylonian in its artifacts
Nippur under Assyrian Domination: 15th Season of Excavation, 1981-82. McGuire Gibson Nippur, during the seventh century B.C., was controlled by the Assyrians, but was essentially Babylonian in its artifacts
Cuneiform Objects at the Museum of Peoples and Cultures
 Studia Antiqua Volume 13 Number 2 Article 3 December 2014 Cuneiform Objects at the Museum of Peoples and Cultures Bethany Jensen Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/studiaantiqua
Studia Antiqua Volume 13 Number 2 Article 3 December 2014 Cuneiform Objects at the Museum of Peoples and Cultures Bethany Jensen Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/studiaantiqua
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 16 Egypt through Naqada II Copyright Bruce Owen 2009
 Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 16 Egypt through Naqada II Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Egypt: The setting The Nile Flows NORTH, into the Mediterranean Sea (up on the map) so the UPPER Nile
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 16 Egypt through Naqada II Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Egypt: The setting The Nile Flows NORTH, into the Mediterranean Sea (up on the map) so the UPPER Nile
DIYALA OBJECTS PROJECT
 ARCHAEOLOGY McGuire Gibson During the 1930s, the Oriental Institute carried out an ambitious program of excavation in the Diyala Region, an area to the north and east of Baghdad. The project yielded an
ARCHAEOLOGY McGuire Gibson During the 1930s, the Oriental Institute carried out an ambitious program of excavation in the Diyala Region, an area to the north and east of Baghdad. The project yielded an
The Euphrates Valley Expedition
 The Euphrates Valley Expedition HANS G. GUTERBOCK, Director MAURITS VAN LOON, Field Director For the third consecutive year we have spent almost three months digging at Korucutepe, the site assigned to
The Euphrates Valley Expedition HANS G. GUTERBOCK, Director MAURITS VAN LOON, Field Director For the third consecutive year we have spent almost three months digging at Korucutepe, the site assigned to
HISTORY. Subject : History (For under graduate student) Lecture No. & Title : Lecture 4 Religious Beliefs, Practices & Script
 HISTORY Subject : History (For under graduate student) Paper No. : Paper-I History of India Unit, Topic & Title : Unit- 4 Topic- 2 Indus Civilization Lecture No. & Title : Lecture 4 Religious Beliefs,
HISTORY Subject : History (For under graduate student) Paper No. : Paper-I History of India Unit, Topic & Title : Unit- 4 Topic- 2 Indus Civilization Lecture No. & Title : Lecture 4 Religious Beliefs,
Global Prehistory. 30, BCE The Origins of Images
 Global Prehistory 30,000-500 BCE The Origins of Images Key Points for Global Prehistory Periods and definitions Prehistory (or the prehistoric period) refers to the time before written records, however,
Global Prehistory 30,000-500 BCE The Origins of Images Key Points for Global Prehistory Periods and definitions Prehistory (or the prehistoric period) refers to the time before written records, however,
An early pot made by the Adena Culture (800 B.C. - A.D. 100)
 Archaeologists identify the time period of man living in North America from about 1000 B.C. until about 700 A.D. as the Woodland Period. It is during this time that a new culture appeared and made important
Archaeologists identify the time period of man living in North America from about 1000 B.C. until about 700 A.D. as the Woodland Period. It is during this time that a new culture appeared and made important
BULLETIN OF THE MUSEUM OF FINE ARTS VOLUME XXXVII BOSTON, JUNE, 1939 NUMBER 221. Harvard University-Museum of Fine Arts Egyptian Expedition
 BULLETIN OF THE MUSEUM OF FINE ARTS VOLUME XXXVII BOSTON, JUNE, 1939 NUMBER 221 Prince Ankh-haf Harvard University-Museum of Fine Arts Egyptian Expedition PUBLISHED BIMONTHLY SUBSCRIPTION ONE DOLLAR XXXVII,
BULLETIN OF THE MUSEUM OF FINE ARTS VOLUME XXXVII BOSTON, JUNE, 1939 NUMBER 221 Prince Ankh-haf Harvard University-Museum of Fine Arts Egyptian Expedition PUBLISHED BIMONTHLY SUBSCRIPTION ONE DOLLAR XXXVII,
Pre-visit Guide for Teachers. Art of the. Ancient. Use this guide to prepare for your self-guided visit to the Metropolitan Museum with your students.
 E d u c a t i o n Pre-visit Guide for Teachers Art of the Ancient Near EasT Use this guide to prepare for your self-guided visit to the Metropolitan Museum with your students. The Metropolitan Museum of
E d u c a t i o n Pre-visit Guide for Teachers Art of the Ancient Near EasT Use this guide to prepare for your self-guided visit to the Metropolitan Museum with your students. The Metropolitan Museum of
Art History: Introduction 10 Form 5 Function 5 Decoration 5 Method 5
 Art History: Introduction 10 Form 5 Function 5 Decoration 5 Method 5 Pre-Christian Ireland Intro to stone age art in Ireland Stone Age The first human settlers came to Ireland around 7000BC during the
Art History: Introduction 10 Form 5 Function 5 Decoration 5 Method 5 Pre-Christian Ireland Intro to stone age art in Ireland Stone Age The first human settlers came to Ireland around 7000BC during the
The Shang Dynasty CHAPTER Introduction. 4 A chariot buried in a Shang ruler's tomb was to serve the king in the afterlife.
 4 A chariot buried in a Shang ruler's tomb was to serve the king in the afterlife. CHAPTER I The Shang Dynasty 20.1 Introduction In Chapter 19, you explored five geographic regions of China. You learned
4 A chariot buried in a Shang ruler's tomb was to serve the king in the afterlife. CHAPTER I The Shang Dynasty 20.1 Introduction In Chapter 19, you explored five geographic regions of China. You learned
The Vikings Begin. This October, step into the magical, mystical world of the early Vikings. By Dr. Marika Hedin
 This October, step into the magical, mystical world of the early Vikings The Vikings Begin By Dr. Marika Hedin Director of Gustavianum, Uppsala University Museum This richly adorned helmet from the 7th
This October, step into the magical, mystical world of the early Vikings The Vikings Begin By Dr. Marika Hedin Director of Gustavianum, Uppsala University Museum This richly adorned helmet from the 7th
Everyday Life In Ancient Mesopotamia By Jean Bottéro READ ONLINE
 Everyday Life In Ancient Mesopotamia By Jean Bottéro READ ONLINE Everyday Life in Ancient Mesopotamia, based on articles originally published in L'Histoire by Jean Bottéro, André Finet, Bertrand Lafont,
Everyday Life In Ancient Mesopotamia By Jean Bottéro READ ONLINE Everyday Life in Ancient Mesopotamia, based on articles originally published in L'Histoire by Jean Bottéro, André Finet, Bertrand Lafont,
AP Art History Presentation. By: Emmarie Moran
 AP Art History Presentation By: Emmarie Moran Required Works: Chavin de Huantar Plan Lanzon Stela Relief Sculpture Nose Ornament Yaxchilan Structure 40 Lintel 25 Structure 33 Mesa Verde Cliff Dwellings
AP Art History Presentation By: Emmarie Moran Required Works: Chavin de Huantar Plan Lanzon Stela Relief Sculpture Nose Ornament Yaxchilan Structure 40 Lintel 25 Structure 33 Mesa Verde Cliff Dwellings
FONDAZIONE SAN DOMENICO
 FONDAZIONE SAN DOMENICO FONDAZIONE SAN DOMENICO History & Mission Fondazione San Domenico was established in 2001 by its founder, Marisa Lisi Melpignano, entrepreneur and tourist agent, owner of Masseria
FONDAZIONE SAN DOMENICO FONDAZIONE SAN DOMENICO History & Mission Fondazione San Domenico was established in 2001 by its founder, Marisa Lisi Melpignano, entrepreneur and tourist agent, owner of Masseria
1. Introduction. 2. A Shang Capital City
 1. Introduction In ancient times, most of China s early farmers settled on the North China Plain, near the Huang He (Yellow River). In this chapter, you will explore one of China s earliest dynasties,
1. Introduction In ancient times, most of China s early farmers settled on the North China Plain, near the Huang He (Yellow River). In this chapter, you will explore one of China s earliest dynasties,
Elam & Susa BC
 Elam & Susa 2000 1000 BC Another beautiful and large ancient city was Susa (Shush) in southern Iran. Much is known about the people who lived in this area 4000 years ago. They were called Elamites, and
Elam & Susa 2000 1000 BC Another beautiful and large ancient city was Susa (Shush) in southern Iran. Much is known about the people who lived in this area 4000 years ago. They were called Elamites, and
Downloaded from
 Key concepts in nutshells Period:- I. Early Harappan culture - Before 2600 BCE II. Mature Harappan culture-2600bce to 1900 BCE III. Later Harappan culture-after 1900 BCE - 1500 AD Extent of Harappan civilization:-
Key concepts in nutshells Period:- I. Early Harappan culture - Before 2600 BCE II. Mature Harappan culture-2600bce to 1900 BCE III. Later Harappan culture-after 1900 BCE - 1500 AD Extent of Harappan civilization:-
Chalcatzingo, Morelos, Mexico
 Chalcatzingo, Morelos, Mexico From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Photos: Josef Otto Chalcatzingo is a Mesoamerican archaeological site in the Valley of Morelos dating from the Formative Period of Mesoamerican
Chalcatzingo, Morelos, Mexico From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Photos: Josef Otto Chalcatzingo is a Mesoamerican archaeological site in the Valley of Morelos dating from the Formative Period of Mesoamerican
UNCOVERING THE PAST CHAPTER 1
 Uncovering the past 00 Page 1 Monday, August 5, 2002 8:10 AM CHAPTER 1 UNCOVERING THE PAST When archaeologists uncover evidence of the past, they are finding objects that were made to last, or everyday
Uncovering the past 00 Page 1 Monday, August 5, 2002 8:10 AM CHAPTER 1 UNCOVERING THE PAST When archaeologists uncover evidence of the past, they are finding objects that were made to last, or everyday
Where is Egypt? Egypt is in the North of Africa. It is in the middle of the Sahara Desert where nothing can grow but sand. ..but Egypt has the Nile
 Egypt Where is Egypt? Egypt is in the North of Africa It is in the middle of the Sahara Desert where nothing can grow but sand..but Egypt has the Nile http://www.snaithprimary.eril.net/eggeo.htm The Egyptians
Egypt Where is Egypt? Egypt is in the North of Africa It is in the middle of the Sahara Desert where nothing can grow but sand..but Egypt has the Nile http://www.snaithprimary.eril.net/eggeo.htm The Egyptians
School and Teacher Programs Teacher Professional Development Workshop Mesopotamia to the Mediterranean December 12, 2012
 School and Teacher Programs 2013 2014 Teacher Professional Development Workshop Mesopotamia to the Mediterranean December 12, 2012 Mesopotamia to the Mediterranean I. Timeline of the Ancient World A. c.
School and Teacher Programs 2013 2014 Teacher Professional Development Workshop Mesopotamia to the Mediterranean December 12, 2012 Mesopotamia to the Mediterranean I. Timeline of the Ancient World A. c.
NEWS RELEASE Pam Kosty, Public Relations Director
 NEWS RELEASE Pam Kosty, Public Relations Director 215.898.4045 pkosty@upenn.edu EXPLORE AN ONGOING HUMAN STORY PENN MUSEUM S NEW MIDDLE EAST GALLERIES OPEN APRIL 21, 2018 New exhibition is first in a planned
NEWS RELEASE Pam Kosty, Public Relations Director 215.898.4045 pkosty@upenn.edu EXPLORE AN ONGOING HUMAN STORY PENN MUSEUM S NEW MIDDLE EAST GALLERIES OPEN APRIL 21, 2018 New exhibition is first in a planned
Linguistics 051 Proto-Indo-European Language and Society. Early Bronze Age Developments
 Linguistics 051 Proto-Indo-European Language and Society Rolf Noyer Early Bronze Age Developments What happened in the Pontic-Caspian region after the Suvorovo- Danilovka Incursion into the Balkans and
Linguistics 051 Proto-Indo-European Language and Society Rolf Noyer Early Bronze Age Developments What happened in the Pontic-Caspian region after the Suvorovo- Danilovka Incursion into the Balkans and
A Sense of Place Tor Enclosures
 A Sense of Place Tor Enclosures Tor enclosures were built around six thousand years ago (4000 BC) in the early part of the Neolithic period. They are large enclosures defined by stony banks sited on hilltops
A Sense of Place Tor Enclosures Tor enclosures were built around six thousand years ago (4000 BC) in the early part of the Neolithic period. They are large enclosures defined by stony banks sited on hilltops
Dilmun. Unknown Culture. Is Dilmun the praised Paradise? by Thomas Kummert
 Dilmun Unknown Culture Is Dilmun the praised Paradise? by Thomas Kummert www.ancient-cultures.info www.paleolithic-neolithic.com The Dilmun Culture is an interesting part of our history. The more you start
Dilmun Unknown Culture Is Dilmun the praised Paradise? by Thomas Kummert www.ancient-cultures.info www.paleolithic-neolithic.com The Dilmun Culture is an interesting part of our history. The more you start
Check for updates on the web now!
 Click anywhere in the slide to view the next item on the slide or to advance to the next slide. Use the buttons below to navigate to another page, close the presentation or to open the help page. Slide
Click anywhere in the slide to view the next item on the slide or to advance to the next slide. Use the buttons below to navigate to another page, close the presentation or to open the help page. Slide
Each object here must have served a purpose. Archaeologists must do their best to explain what that purpose was.
 Archaeologists have to use many different forms of reasoning to decipher the what and how about artifacts they discover. I mean seriously, what in the world are these things? Each object here must have
Archaeologists have to use many different forms of reasoning to decipher the what and how about artifacts they discover. I mean seriously, what in the world are these things? Each object here must have
Xian Tombs of the Qin Dynasty
 Xian Tombs of the Qin Dynasty By History.com, adapted by Newsela staff In 221 B.C., Qin Shi Huang became emperor of China, and started the Qin Dynasty. At this time, the area had just emerged from over
Xian Tombs of the Qin Dynasty By History.com, adapted by Newsela staff In 221 B.C., Qin Shi Huang became emperor of China, and started the Qin Dynasty. At this time, the area had just emerged from over
Check for updates on the web now!
 Click anywhere in the slide to view the next item on the slide or to advance to the next slide. Use the buttons below to navigate to another page, close the presentation or to open the help page. Slide
Click anywhere in the slide to view the next item on the slide or to advance to the next slide. Use the buttons below to navigate to another page, close the presentation or to open the help page. Slide
Chapter 2-Art of Ancient Near East
 Jan 14, 17-Art of the Ancient Near East & Ancient Egypt: Reading Notes Chapter 2-Art of Ancient Near East Stele of Naram-Sin (found at present day Iran) ruled 2254-2218 BCE tab Stele: upright stone -Mesopotamia
Jan 14, 17-Art of the Ancient Near East & Ancient Egypt: Reading Notes Chapter 2-Art of Ancient Near East Stele of Naram-Sin (found at present day Iran) ruled 2254-2218 BCE tab Stele: upright stone -Mesopotamia
Ancient Mediterranean 3500 B.C.E.-300 C.E.
 Ancient Mediterranean 3500 B.C.E.-300 C.E. Art in this place and time focuses on funerary and palatial complexes, is influenced heavily by religion/mythology, provides us narratives, and displays of authority
Ancient Mediterranean 3500 B.C.E.-300 C.E. Art in this place and time focuses on funerary and palatial complexes, is influenced heavily by religion/mythology, provides us narratives, and displays of authority
What Scientists Just Found Deep In The Ocean Is Seriously Unbelievable.
 What Scientists Just Found Deep In The Ocean Is Seriously Unbelievable. Off the coast of Egypt divers have discovered something that was thought to be lost a long time ago. It was said that the ancient
What Scientists Just Found Deep In The Ocean Is Seriously Unbelievable. Off the coast of Egypt divers have discovered something that was thought to be lost a long time ago. It was said that the ancient
INDUS VALLEY CIVILISATION
 INDUS VALLEY CIVILISATION 2500-1500 DISCOVERY 1826 a British army deserter, James Lewis, noticed the presence of mounded ruins at a small town in Punjab called Harappa. Alexander Cunningham, who headed
INDUS VALLEY CIVILISATION 2500-1500 DISCOVERY 1826 a British army deserter, James Lewis, noticed the presence of mounded ruins at a small town in Punjab called Harappa. Alexander Cunningham, who headed
Evolution of the Celts Unetice Predecessors of Celts BCE Cultural Characteristics:
 Evolution of the Celts Unetice Predecessors of Celts 2500-2000 BCE Associated with the diffusion of Proto-Germanic and Proto-Celto-Italic speakers. Emergence of chiefdoms. Long-distance trade in bronze,
Evolution of the Celts Unetice Predecessors of Celts 2500-2000 BCE Associated with the diffusion of Proto-Germanic and Proto-Celto-Italic speakers. Emergence of chiefdoms. Long-distance trade in bronze,
Indus-Saraswati Valley Civilization Arts and Culture
 Indus-Saraswati Valley Civilization Arts and Culture Srabonti Bandyopadhyay 1 Discoveries Creativity and the arts subsumed everyday life Technologically advanced techniques used No direct evidence but
Indus-Saraswati Valley Civilization Arts and Culture Srabonti Bandyopadhyay 1 Discoveries Creativity and the arts subsumed everyday life Technologically advanced techniques used No direct evidence but
IRAQI CULTURAL OBJECTS AT RISK
 2015, ICOM, all rights reserved. - Graphic design: TAM TAM TEAM. Cover: Alabaster votive statue, Ashur, 2400 BC, H 46 cm. RED LIST OF IRAQI CULTURAL OBJECTS AT RISK 2015 Update RED LIST OF IRAQI CULTURAL
2015, ICOM, all rights reserved. - Graphic design: TAM TAM TEAM. Cover: Alabaster votive statue, Ashur, 2400 BC, H 46 cm. RED LIST OF IRAQI CULTURAL OBJECTS AT RISK 2015 Update RED LIST OF IRAQI CULTURAL
Timescale: Jemdat Nasr: 3,000 to 2,900. ED I Period- 2,900 to 2,500 JN ED I- 2,900/2,500 Temples:
 Timescale: a) Archtecture: b) Pottery: c) Misc. Finds: Jemdat Nasr: 3,000 to 2,900 JN - 3000-2900 Palaces: JN: Palace? a01 Bevel-rim bowls-b01 conical cupsb01 Polycrome pottery- b01 four-lugged jars- b01
Timescale: a) Archtecture: b) Pottery: c) Misc. Finds: Jemdat Nasr: 3,000 to 2,900 JN - 3000-2900 Palaces: JN: Palace? a01 Bevel-rim bowls-b01 conical cupsb01 Polycrome pottery- b01 four-lugged jars- b01
The early Kushite kings adopted all Egyptian customs and beliefs. kings were buried on beds placed on stone platforms within their pyramids.
 the kushite period 747 BC 350 AD Funeral practice After the time of Egyptian new kingdom there was a political and artistic decline and Egypt entered one of the obscure periods of its history, the weakening
the kushite period 747 BC 350 AD Funeral practice After the time of Egyptian new kingdom there was a political and artistic decline and Egypt entered one of the obscure periods of its history, the weakening
BALNUARAN. of C LAVA. a prehistoric cemetery. A Visitors Guide to
 A Visitors Guide to BALNUARAN of C LAVA a prehistoric cemetery Milton of Clava Chapel (?) Cairn River Nairn Balnuaran of Clava is the site of an exceptionally wellpreserved group of prehistoric burial
A Visitors Guide to BALNUARAN of C LAVA a prehistoric cemetery Milton of Clava Chapel (?) Cairn River Nairn Balnuaran of Clava is the site of an exceptionally wellpreserved group of prehistoric burial
The History of Jewelry-making: Throughout the Timeline
 Art-1040-fall 2011 Jewelry Culture and Creation James Lund The History of Jewelry-making: Throughout the Timeline The art of jewelry making dates back to ancient man. Many techniques and materials such
Art-1040-fall 2011 Jewelry Culture and Creation James Lund The History of Jewelry-making: Throughout the Timeline The art of jewelry making dates back to ancient man. Many techniques and materials such
Ancient Chinese Chariots
 Reading Practice Ancient Chinese Chariots A The Shang Dynasty or Yin Dynasty, according to traditional historiography, ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium. Archaeological work at
Reading Practice Ancient Chinese Chariots A The Shang Dynasty or Yin Dynasty, according to traditional historiography, ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium. Archaeological work at
Excavations at Shikarpur, Gujarat
 Excavations at Shikarpur, Gujarat 2008-2009 The Department of Archaeology and Ancient History, the M. S. University of Baroda continued excavations at Shikarpur in the second field season in 2008-09. In
Excavations at Shikarpur, Gujarat 2008-2009 The Department of Archaeology and Ancient History, the M. S. University of Baroda continued excavations at Shikarpur in the second field season in 2008-09. In
Nubia. Sphinx of Taharqo Kawa, Sudan 680 BC. Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2
 Sphinx of Taharqo Kawa, Sudan 680 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities During your visit Gallery
Sphinx of Taharqo Kawa, Sudan 680 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities During your visit Gallery
INLAID AND ENGRAVED VASES OF 6500 YEARS AGO.
 INLAID AND ENGRAVED VASES OF 6500 YEARS AGO. BY EDGAR JAMES BANKS. Field Director of the recent Expedition of the University of Chicago to Babylonia. IT was 4500 3'ears B. C. or nearly 6500 years ago,
INLAID AND ENGRAVED VASES OF 6500 YEARS AGO. BY EDGAR JAMES BANKS. Field Director of the recent Expedition of the University of Chicago to Babylonia. IT was 4500 3'ears B. C. or nearly 6500 years ago,
Which of above statement is/ are true about the Indus Valley Civilization? a. I Only b. II Only c. I, II and III d. III Only. Answer: c.
 Ancient History Quiz for IAS Preparation - Indus Valley Civilisation III The NCERT Books are still high in demand for IAS Preparation because it has extensive coverage of the topics given in the UPSC IAS
Ancient History Quiz for IAS Preparation - Indus Valley Civilisation III The NCERT Books are still high in demand for IAS Preparation because it has extensive coverage of the topics given in the UPSC IAS
oi.uchicago.edu HAMOUKAR McGuire Gibson
 Research Molded vessels from Hadir Qinnasrin, Syria modern town. This will result in a distributional map that may lead toward the most likely locations for future excavations. As in the 2000 season, archaeology
Research Molded vessels from Hadir Qinnasrin, Syria modern town. This will result in a distributional map that may lead toward the most likely locations for future excavations. As in the 2000 season, archaeology
Weetwood Moor. What are cup & ring marks?
 Weetwood Moor On this small stretch of moorland you can find some of the most recognisable ancient cup and ring marked stones in the UK. There are three interesting spots we d like to share with you. What
Weetwood Moor On this small stretch of moorland you can find some of the most recognisable ancient cup and ring marked stones in the UK. There are three interesting spots we d like to share with you. What
Palette of King Narmer
 Palette of King Narmer Palette of King Narmer, from Hierakonpolis, Egypt, Predynastic, c. 3000-2920 B.C.E., slate, 2' 1" high (Egyptian Museum, Cairo) Vitally important, but difficult to interpret Some
Palette of King Narmer Palette of King Narmer, from Hierakonpolis, Egypt, Predynastic, c. 3000-2920 B.C.E., slate, 2' 1" high (Egyptian Museum, Cairo) Vitally important, but difficult to interpret Some
History Around 800 BC, Etruscans settle in Etruria, north of the Palatine. Historians believe first that they came from Lydia in Asia Minor.
 Founding of Rome In 1200 BC, after the fall of Troy, the gods ordered Aeneas to lead his people to the promised land. Aeneas's group joined forces with Latins in Italy. Groups with iron weapons invaded
Founding of Rome In 1200 BC, after the fall of Troy, the gods ordered Aeneas to lead his people to the promised land. Aeneas's group joined forces with Latins in Italy. Groups with iron weapons invaded
Human with Feline Head from Hohlenstein-Stadel, Germany. ca. 30,000-28,000 B.C.E. mammoth ivory 11 5/8 in. high
 Prehistoric Art Paleolithic Old Stone Age = Paleolithic period (Greek paleo = old and lithos = stone) Works from this period vary greatly Focus on animal representation with some human representation Human
Prehistoric Art Paleolithic Old Stone Age = Paleolithic period (Greek paleo = old and lithos = stone) Works from this period vary greatly Focus on animal representation with some human representation Human
SCOTLAND. Belfast IRISH SEA. Dublin THE REPUBLIC OF IRELAND ENGLAND ENGLISH CHANNEL. Before and After
 ALL ABOUT BRITAIN This book tells the story of the people who have lived in the British Isles, and is packed with fascinating facts and f un tales. The British Isles is a group of islands that consists
ALL ABOUT BRITAIN This book tells the story of the people who have lived in the British Isles, and is packed with fascinating facts and f un tales. The British Isles is a group of islands that consists
STONES OF STENNESS HISTORIC ENVIRONMENT SCOTLAND STATEMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE
 Property in Care (PIC) ID: PIC321 Designations: Scheduled Monument (SM90285); Taken into State care: 1906 (Guardianship) Last reviewed: 2003 HISTORIC ENVIRONMENT SCOTLAND STATEMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE STONES
Property in Care (PIC) ID: PIC321 Designations: Scheduled Monument (SM90285); Taken into State care: 1906 (Guardianship) Last reviewed: 2003 HISTORIC ENVIRONMENT SCOTLAND STATEMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE STONES
THE LOOTING OF THE BAGHDAD MUSEUM
 d THE LOOTING OF THE BAGHDAD MUSEUM Susan E. Wood By now, everyone who has been following the news knows the basic story. On April 9, Baghdad fell to American-led coalition forces. Over the following two
d THE LOOTING OF THE BAGHDAD MUSEUM Susan E. Wood By now, everyone who has been following the news knows the basic story. On April 9, Baghdad fell to American-led coalition forces. Over the following two
BLACK HISTORY MONTH - Week 1 #BlackHistoryMatters
 BLACK HISTORY MONTH - Week 1 #BlackHistoryMatters classroomconnection.ca WEEK 1: AFRICAN CIVILIZATIONS Africa is the cradle of humankind and Nubia, an early African society, is the oldest civilization
BLACK HISTORY MONTH - Week 1 #BlackHistoryMatters classroomconnection.ca WEEK 1: AFRICAN CIVILIZATIONS Africa is the cradle of humankind and Nubia, an early African society, is the oldest civilization
7. Prehistoric features and an early medieval enclosure at Coonagh West, Co. Limerick Kate Taylor
 7. Prehistoric features and an early medieval enclosure at Coonagh West, Co. Limerick Kate Taylor Illus. 1 Location of the site in Coonagh West, Co. Limerick (based on the Ordnance Survey Ireland map)
7. Prehistoric features and an early medieval enclosure at Coonagh West, Co. Limerick Kate Taylor Illus. 1 Location of the site in Coonagh West, Co. Limerick (based on the Ordnance Survey Ireland map)
SARMIZEGETUSA ULPIA TRAIANA CAPITAL OF THE DACIAN PROVINCES
 SARMIZEGETUSA ULPIA TRAIANA CAPITAL OF THE DACIAN PROVINCES ROMAM IMPERIAL URBAN EXCAVATION TRANSYLVANIA, ROMANIA July 5 August 8, 2015 aria sacra extra muros FOR MORE INFORMATION: www.archaeotek-archaeology.org
SARMIZEGETUSA ULPIA TRAIANA CAPITAL OF THE DACIAN PROVINCES ROMAM IMPERIAL URBAN EXCAVATION TRANSYLVANIA, ROMANIA July 5 August 8, 2015 aria sacra extra muros FOR MORE INFORMATION: www.archaeotek-archaeology.org
Prebles' Artforms An Introduction to the Visual Arts
 Prebles' Artforms An Introduction to the Visual Arts ELEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 15 From the Earliest Art to the Bronze Age Learning Objectives 1. Trace the origins of early art in the Paleolithic and Neolithic
Prebles' Artforms An Introduction to the Visual Arts ELEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 15 From the Earliest Art to the Bronze Age Learning Objectives 1. Trace the origins of early art in the Paleolithic and Neolithic
Cambridge Archaeology Field Group. Fieldwalking on the Childerley Estate, Cambridgeshire. Autumn 2014 to Spring Third interim report
 Cambridge Archaeology Field Group Fieldwalking on the Childerley Estate, Cambridgeshire Autumn 2014 to Spring 2015 Third interim report Summary Field walking on the Childerley estate of Martin Jenkins
Cambridge Archaeology Field Group Fieldwalking on the Childerley Estate, Cambridgeshire Autumn 2014 to Spring 2015 Third interim report Summary Field walking on the Childerley estate of Martin Jenkins
1. Presumed Location of French Soundings Looking NW from the banks of the river.
 SG02? SGS SG01? SG4 1. Presumed Location of French Soundings Looking NW from the banks of the river. The presumed location of SG02 corresponds to a hump known locally as the Sheikh's tomb. Note also (1)
SG02? SGS SG01? SG4 1. Presumed Location of French Soundings Looking NW from the banks of the river. The presumed location of SG02 corresponds to a hump known locally as the Sheikh's tomb. Note also (1)
HISTORY OF THE YORUBA PEOPLE. The Yoruba people, of which there is at the present time more than 25 million, occupies the
 HISTORY OF THE YORUBA PEOPLE The Yoruba people, of which there is at the present time more than 25 million, occupies the western South corner of Nigeria, by all the edge of Dahomey and it extends until
HISTORY OF THE YORUBA PEOPLE The Yoruba people, of which there is at the present time more than 25 million, occupies the western South corner of Nigeria, by all the edge of Dahomey and it extends until
The Jawan Chamber Tomb Adapted from a report by F.S. Vidal, Dammam, December 1953
 Figure 1 - The Jawan tomb as photographed from helicopter by Sgt. W. Seto, USAF, in May 1952 The Jawan Chamber Tomb Adapted from a report by F.S. Vidal, Dammam, December 1953 I. Description of work and
Figure 1 - The Jawan tomb as photographed from helicopter by Sgt. W. Seto, USAF, in May 1952 The Jawan Chamber Tomb Adapted from a report by F.S. Vidal, Dammam, December 1953 I. Description of work and
Scotland possesses a remarkable
 CARVED STONES The Picts carved unique symbols that were not just decorative but conveyed a message, although the meaning is now lost to us. Crown copyright: Historic Scotland houses, in both cases dating
CARVED STONES The Picts carved unique symbols that were not just decorative but conveyed a message, although the meaning is now lost to us. Crown copyright: Historic Scotland houses, in both cases dating
INGRAM GALLERY FEBRUARY 23 MAY 28, 2018
 Cover: Statue head of Augustus (Rome, Italy), ca. 30 BCE. Marble, 14 3/4 x 8 1/4 x 8 5/8 in. The British Museum, 1888,1210.1. The Trustees of the British Museum INGRAM GALLERY FEBRUARY 23 MAY 28, 2018
Cover: Statue head of Augustus (Rome, Italy), ca. 30 BCE. Marble, 14 3/4 x 8 1/4 x 8 5/8 in. The British Museum, 1888,1210.1. The Trustees of the British Museum INGRAM GALLERY FEBRUARY 23 MAY 28, 2018
Cetamura Results
 Cetamura 2000 2006 Results A major project during the years 2000-2006 was the excavation to bedrock of two large and deep units located on an escarpment between Zone I and Zone II (fig. 1 and fig. 2);
Cetamura 2000 2006 Results A major project during the years 2000-2006 was the excavation to bedrock of two large and deep units located on an escarpment between Zone I and Zone II (fig. 1 and fig. 2);
Experiential Activity: Ancient Artifacts
 Experiential Activity: Ancient Artifacts Dig Site: Ancient Mesopotamia Artifact 1--Mesopotamia ARTIFACT 1 (Mesopotamia)--Details (close ups) from artifact: Artifact 2--Mesopotamia Artifact 3--Mesopotamia
Experiential Activity: Ancient Artifacts Dig Site: Ancient Mesopotamia Artifact 1--Mesopotamia ARTIFACT 1 (Mesopotamia)--Details (close ups) from artifact: Artifact 2--Mesopotamia Artifact 3--Mesopotamia
