IN THE EARLIEST CITIES
|
|
|
- Edmund Holland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 4 IN THE EARLIEST CITIES Saving an old building Jaspal and Harpreet were playing cricket in the lane outside their home when they noticed the people who were admiring the dilapidated old building that the children called the haunted house. Look at the architecture! said one of the men. Have you seen the fine wood carving? asked one of the women. We must write to the Minister so that she makes arrangements to repair and preserve this beautiful house. Why, they wondered, would anybody be interested in the old, run down house? 32 The story of Harappa Very often, old buildings have a story to tell. Nearly a hundred and fifty years ago, when railway lines were being laid down for the first time in the Punjab, engineers stumbled upon the site of Harappa in present-day Pakistan. To them, it seemed like a mound that was a rich source of ready made, high quality bricks. So they carried off thousands of bricks from the walls of the old buildings of the city to build railway lines. Many buildings were completely destroyed. Then, about eighty years ago, archaeologists found the site, and realised that this was one of the oldest cities in the subcontinent. As this was the first city to be discovered, all other sites from where similar buildings (and other things) were found were described as Harappan. These cities developed about 4700 years ago. Very often, old buildings are pulled down to make way for new construction. Do you think it is important to preserve old buildings?
2 What was special about these cities? Many of these cities were divided into two or more parts. Usually, the part to the west was smaller but higher. Archaeologists describe this as the citadel. Generally, the part to the east was larger but lower. This is called the lower town. Very often walls of baked brick were built around each part. The bricks were so well made that they have lasted for thousands of years. The bricks were laid in an interlocking pattern and that made the walls strong. In some cities, special buildings were constructed on the citadel. For example, in Mohenjodaro, a very special tank, which archaeologists call the Great Bath, was built in this area. This was lined with bricks, coated with plaster, and made water-tight with a layer of natural tar. There were steps leading down to it from two sides, while there were rooms on all sides. Water was probably brought in from a well, and drained out after use. Perhaps important people took a dip in this tank on special occasions. Other cities, such as Kalibangan and Lothal had fire altars, where sacrifices may have been performed. And some cities like Mohenjodaro, Harappa, and Lothal had elaborate store houses. MAP : 3 The Earliest Cities in the Subcontinent These cities were found in the Punjab and Sind in Pakistan, and in Gujarat, Rajasthan, Haryana and the Punjab in India. Archaeologists have found a set of unique objects in almost all these cities: red pottery painted with designs in black, stone weights, seals, special beads, copper tools, and long stone blades. 33
3 The Great Bath How bricks were arranged to build walls in Harappan cities 34 Houses, drains and streets Generally, houses were either one or two storeys high, with rooms built around a courtyard. Most houses had a separate bathing area, and some had wells to supply water. Many of these cities had covered drains. Notice how carefully these were laid out, in straight lines. Although you cannot see it, each drain had a gentle slope so that water could flow through it. Very often, drains in houses were connected to those on the streets and smaller drains led into bigger ones. As the drains were covered, inspection holes were provided at intervals to clean them. All three houses, drains and streets were probably planned and built at the same time. List at least two differences between the houses described here and those that you studied about in Chapter 3.
4 Life in the city A Harappan city was a very busy place. There were people who planned the construction of special buildings in the city. These were probably the rulers. It is likely that the rulers sent people to distant lands to get metal, precious stones, and other things that they wanted. They may have kept the most valuable objects, such as ornaments of gold and silver, or beautiful beads, for themselves. And there were scribes, people who knew how to write, who helped prepare the seals, and perhaps wrote on other materials that have not survived. Besides, there were men and women, crafts persons, making all kinds of things either in their own homes, or in special workshops. People were travelling to distant lands or returning with raw materials and, perhaps, stories. Many terracotta toys have been found and a long time ago children must have played with these. Make a list of the people who lived in the city. Were any of these people listed as living in villages such as Mehrgarh? Top : A street in Mohenjodaro with a drain. Above : A well. Far Left : A Harappan seal. The signs on the top of the seal are part of a script. This is the earliest form of writing known in the subcontinent. Scholars have tried to read these signs but we still do not know exactly what they mean. Left : Terracotta toys. 35 IN THE EARLIEST CITIES
5 Top : Stone weights. Notice how carefully and precisely these weights are shaped. These were made of chert, a kind of stone. These were probably used to weigh precious stones or metals. Right : Beads. Many of these were made out of carnelian, a beautiful red stone. The stone was cut, shaped, polished and finally a hole was bored through the centre so that a string could be passed through it. Far right : Stone blades. Bottom Right : Embroidered cloth. A stone statue of an important man found from Mohenjodaro shows him wearing an embroidered garment. 36 New crafts in the city Let us look at some of the objects that were made and found in Harappan cities. Most of the things that have been found by archaeologists are made of stone, shell and metal, including copper, bronze, gold and silver. Copper and bronze were used to make tools, weapons, ornaments and vessels. Gold and silver were used to make ornaments and vessels. Perhaps the most striking finds are those of beads, weights, and blades. The Harappans also made seals out of stone. These are generally rectangular (See illustration on page 35) and usually have an animal carved on them. The Harappans also made pots with beautiful black designs, such as the one shown on page 6. Was metal used in the villages you learnt about in Chapter 3? Was stone used to make weights? Cotton was probably grown at Mehrgarh from about 7000 years ago. Actual pieces of cloth were found attached to the lid of a silver vase and some copper objects at Mohenjodaro. Archaeologists have also found spindle whorls,
6 Faience Unlike stone or shell, that are found naturally, faience is a material that is artificially produced. A gum was used to shape sand or powdered quartz into an object. The objects were then glazed, resulting in a shiny, glassy surface. The colours of the glaze were usually blue or sea green. Faience was used to make beads, bangles, earrings, and tiny vessels. made of terracotta and faience. These were used to spin thread. Many of the things that were produced were probably the work of specialists. A specialist is a person who is trained to do only one kind of work, for example, cutting stone, or polishing beads, or carving seals. Look at the illustration (page 36) and see how well the face is carved and how carefully the beard is shown. This must have been the work of an expert crafts person. Not everybody could have been a specialist. We do not know whether only men were specialists or only women were specialists. Perhaps some women and men may have been specialists. In search of raw materials Raw materials are substances that are either found naturally (such as wood, or ores of metals) or produced by farmers or herders. These are then processed to produce finished goods. For example, cotton, produced by farmers, is a raw material that may be processed to make cloth. While some of the raw materials that the Harappans used were available locally, many items such as copper, tin, gold, silver and precious stones had to be brought from distant places. The Harappans probably got copper from present-day Rajasthan, and even from Oman in 37 IN THE EARLIEST CITIES
7 West Asia. Tin, which was mixed with copper to produce bronze, may have been brought from present-day Afghanistan and Iran. Gold could have come all the way from present-day Karnataka, and precious stones from present-day Gujarat, Iran and Afghanistan. How were goods carried from one place to another? Look at the illustrations. One shows a toy and the other is a seal. Can you suggest what the modes of transport used by the Harappans were? Did you come across illustrations of wheeled vehicles in earlier lessons? A toy plough. Today, in many farming communities, only men use the plough. We do not know whether the Harappans followed such customs or not. 38 Food for people in the cities While many people lived in the cities, others living in the countryside grew crops and reared animals. These farmers and herders supplied food to crafts persons, scribes and rulers in the cities. We know from remains of plants that the Harappans grew wheat, barley, pulses, peas, rice, sesame, linseed and mustard. A new tool, the plough, was used to dig the earth for turning the soil and planting seeds. While real ploughs, which were probably made of wood, have not survived, toy models have been found. As this region does not receive heavy rainfall, some form of irrigation may have been used. This means that water was stored and supplied to the fields when the plants were growing. The Harappans reared cattle, sheep, goat and buffalo. Water and pastures were available around settlements. However, in the dry summer months large herds of animals were probably taken to greater distances in search of grass and water. They also collected fruits like
8 ber, caught fish and hunted wild animals like the antelope. A closer look Harappan towns in Gujarat The city of Dholavira was located on Khadir Beyt in the Rann of Kutch, where there was fresh water and fertile soil. Unlike some of the other Harappan cities, which were divided into two parts, Dholavira was divided into three parts, and each part was surrounded with massive stone walls, with entrances through gateways. There was also a large open area in the settlement, where public ceremonies could be held. Other finds include large letters of the Harappan script that were carved out of white stone and perhaps inlaid in wood. This is a unique find as generally Harappan writing has been found on small objects such as seals. The city of Lothal stood beside a tributary of the Sabarmati, in Gujarat, close to the Gulf of Khambat. It was situated near areas where raw materials such as semi-precious stones were easily available. This was an important centre for making objects out of stone, shell and metal. There was also a store house in the city. Many seals and sealings (the impression of seals on clay) were found in this storehouse. A dockyard at Lothal. This huge tank may have been a dockyard, where boats and ships came in from the sea and through the river channel. Goods were probably loaded and unloaded here. 39
9 A building that was found here was probably a workshop for making beads: pieces of stone, half made beads, tools for bead making, and finished beads have all been found here. Seals and sealings Seals may have been used to stamp bags or packets containing goods that were sent from one place to another. After a bag was closed or tied, a layer of wet clay was applied on the knot, and the seal was pressed on it. The impression of the seal is known as a sealing. If the sealing was intact, one could be sure that the goods had arrived safely. Seals are used even today. Find out what they are used for. The mystery of the end KEYWORDS city citadel ruler scribe crafts person metal seal specialist raw material plough irrigation 40 Around 3900 years ago we find the beginning of a major change. People stopped living in many of the cities. Writing, seals and weights were no longer used. Raw materials brought from long distances became rare. In Mohenjodaro, we find that garbage piled up on the streets, the drainage system broke down, and new, less impressive houses were built, even over the streets. Why did all this happen? We are not sure. Some scholars suggest that the rivers dried up. Others suggest that there was deforestation. This could have happened because fuel was required for baking bricks, and for smelting copper ores. Besides, grazing by large herds of cattle, sheep and goat may have destroyed the green cover. In some areas there were floods. But none of these reasons can explain the end of all the cities. Flooding, or a river drying up would have had an effect in only some areas.
10 It appears as if the rulers lost control. In any case, the effects of the change are quite clear. Sites in Sind and west Punjab (present-day Pakistan) were abandoned, while many people moved into newer, smaller settlements to the east and the south. New cities emerged about 1400 years later. You will read about them in Chapters 6 and 9. Elsewhere Find Egypt in your atlas. Most of Egypt is a dry desert, except for the lands along the river Nile. Around 5000 years ago, kings ruled over Egypt. These kings sent armies to distant lands to get gold, silver, ivory, timber, and precious stones. They also built huge tombs, known as pyramids. When they died, the bodies of kings were preserved and buried in these pyramids. These carefully preserved bodies are known as mummies. A large number of objects were also buried with them. These included food and drink, clothes, ornaments, utensils, musical instruments, weapons and animals. Sometimes even serving men and women were buried with the rulers. These are amongst the most elaborate burials known in world history. Do you think kings would have needed these things after death? Imagine You are travelling with your parents, about 4000 years ago, from Lothal to Mohenjodaro. Describe how you would travel, what your parents might carry with them, and what you would see in Mohenjodaro. 41 IN THE EARLIEST CITIES
11 SOME IMPORTANT DATES Cotton cultivation at Mehrgarh (about 7000 years ago) Beginning of cities (about 4700 years ago) Beginning of the end of these cities (about 3900 years ago) The emergence of other cities (about 2500 years ago) Let s recall 1. How do archaeologists know that cloth was used in the Harappan civilisation? 2. Match the columns Copper Gold Tin Precious stones Gujarat Afghanistan Rajasthan Karnataka 3. Why were metals, writing, the wheel, and the plough important for the Harappans? Let s discuss 4. Make a list of all the terracotta toys shown in the lesson. Which do you think children would have enjoyed playing with the most? 5. Make a list of what the Harappans ate, and put a tick mark against the things you eat today. 6. Do you think that the life of farmers and herders who supplied food to the Harappan cities was different from that of the farmers and herders you read about in Chapter 3? Give reasons for your answer. Let s do 7. Describe three important buildings in your city or village. Are they located in a special part of the settlement (e.g. the centre)? What are the activities that take place in these buildings? Are there any old buildings in your locality? Find out how old they are and who looks after them.
History Ch-4 (W.B Answer Key) Pakistan 2. The bricks were laid in an interlocking pattern and that made the walls strong.
 History Ch-4 (W.B Answer Key) W.B (pp-42, 43) 1. The site of Harappa is in the present day Pakistan. 2. How were the bricks of ancient settlement used? The bricks were laid in an interlocking pattern and
History Ch-4 (W.B Answer Key) W.B (pp-42, 43) 1. The site of Harappa is in the present day Pakistan. 2. How were the bricks of ancient settlement used? The bricks were laid in an interlocking pattern and
Which of above statement is/ are true about the Indus Valley Civilization? a. I Only b. II Only c. I, II and III d. III Only. Answer: c.
 Ancient History Quiz for IAS Preparation - Indus Valley Civilisation III The NCERT Books are still high in demand for IAS Preparation because it has extensive coverage of the topics given in the UPSC IAS
Ancient History Quiz for IAS Preparation - Indus Valley Civilisation III The NCERT Books are still high in demand for IAS Preparation because it has extensive coverage of the topics given in the UPSC IAS
INDUS VALLEY CIVILISATION
 INDUS VALLEY CIVILISATION 2500-1500 DISCOVERY 1826 a British army deserter, James Lewis, noticed the presence of mounded ruins at a small town in Punjab called Harappa. Alexander Cunningham, who headed
INDUS VALLEY CIVILISATION 2500-1500 DISCOVERY 1826 a British army deserter, James Lewis, noticed the presence of mounded ruins at a small town in Punjab called Harappa. Alexander Cunningham, who headed
Chapter 14. Unlocking the Secrets of Mohenjodaro
 Chapter 14 Unlocking the Secrets of Mohenjodaro Chapter 14 Unlocking the Secrets of Mohenjodaro What can artifacts tell us about daily life in Mohenjodaro? 14.1 Introduction The geography of the Indian
Chapter 14 Unlocking the Secrets of Mohenjodaro Chapter 14 Unlocking the Secrets of Mohenjodaro What can artifacts tell us about daily life in Mohenjodaro? 14.1 Introduction The geography of the Indian
Where is Egypt? Egypt is in the North of Africa. It is in the middle of the Sahara Desert where nothing can grow but sand. ..but Egypt has the Nile
 Egypt Where is Egypt? Egypt is in the North of Africa It is in the middle of the Sahara Desert where nothing can grow but sand..but Egypt has the Nile http://www.snaithprimary.eril.net/eggeo.htm The Egyptians
Egypt Where is Egypt? Egypt is in the North of Africa It is in the middle of the Sahara Desert where nothing can grow but sand..but Egypt has the Nile http://www.snaithprimary.eril.net/eggeo.htm The Egyptians
Indus Valley Civilization
 Indus Valley Civilization What is Civilisation and Culture The Word Civilisation has been derived from Latin Word Civilis, which means citizens. Civilisation is an advanced state of human society possessing
Indus Valley Civilization What is Civilisation and Culture The Word Civilisation has been derived from Latin Word Civilis, which means citizens. Civilisation is an advanced state of human society possessing
Difference between Architecture and Sculpture. Architecture refers to the design and construction of buildings
 Art and Culture 1.1 Introduction Difference between Architecture and Sculpture Classification of Indian Architecture Indus Valley Civilization and their archaeological findings BY CIVIL JOINT The Word
Art and Culture 1.1 Introduction Difference between Architecture and Sculpture Classification of Indian Architecture Indus Valley Civilization and their archaeological findings BY CIVIL JOINT The Word
Downloaded from
 Key concepts in nutshells Period:- I. Early Harappan culture - Before 2600 BCE II. Mature Harappan culture-2600bce to 1900 BCE III. Later Harappan culture-after 1900 BCE - 1500 AD Extent of Harappan civilization:-
Key concepts in nutshells Period:- I. Early Harappan culture - Before 2600 BCE II. Mature Harappan culture-2600bce to 1900 BCE III. Later Harappan culture-after 1900 BCE - 1500 AD Extent of Harappan civilization:-
Sumerian Achievements
 Sumerian Achievements The Invention of Writing The Sumerians made one of the greatest cultural advances in history. They developed cuneiform (kyoo-neeuh-fohrm writing. But Sumerians did not have pencils,
Sumerian Achievements The Invention of Writing The Sumerians made one of the greatest cultural advances in history. They developed cuneiform (kyoo-neeuh-fohrm writing. But Sumerians did not have pencils,
HISTORY. Subject : History (For under graduate student) Lecture No. & Title : Lecture 4 Religious Beliefs, Practices & Script
 HISTORY Subject : History (For under graduate student) Paper No. : Paper-I History of India Unit, Topic & Title : Unit- 4 Topic- 2 Indus Civilization Lecture No. & Title : Lecture 4 Religious Beliefs,
HISTORY Subject : History (For under graduate student) Paper No. : Paper-I History of India Unit, Topic & Title : Unit- 4 Topic- 2 Indus Civilization Lecture No. & Title : Lecture 4 Religious Beliefs,
Sunday, February 12, 17. The Shang Dynasty
 The Shang Dynasty The Shang Dynasty The Shang Dynasty is one of the earliest dynasties in China This dynasty was centered in the Huang He (Yellow River) Valley and ruled from 1700-1122 B.C. For many years,
The Shang Dynasty The Shang Dynasty The Shang Dynasty is one of the earliest dynasties in China This dynasty was centered in the Huang He (Yellow River) Valley and ruled from 1700-1122 B.C. For many years,
Indus Valley Civilization
 Indus Valley Civilization Life in the Indus Valley by Joyce and David Mollet Today, the Indus Valley is a barren desert, broken only by the winding River Indus. A long time ago, when the land was first
Indus Valley Civilization Life in the Indus Valley by Joyce and David Mollet Today, the Indus Valley is a barren desert, broken only by the winding River Indus. A long time ago, when the land was first
Xian Tombs of the Qin Dynasty
 Xian Tombs of the Qin Dynasty By History.com, adapted by Newsela staff In 221 B.C., Qin Shi Huang became emperor of China, and started the Qin Dynasty. At this time, the area had just emerged from over
Xian Tombs of the Qin Dynasty By History.com, adapted by Newsela staff In 221 B.C., Qin Shi Huang became emperor of China, and started the Qin Dynasty. At this time, the area had just emerged from over
Indus-Saraswati Valley Civilization Arts and Culture
 Indus-Saraswati Valley Civilization Arts and Culture Srabonti Bandyopadhyay 1 Discoveries Creativity and the arts subsumed everyday life Technologically advanced techniques used No direct evidence but
Indus-Saraswati Valley Civilization Arts and Culture Srabonti Bandyopadhyay 1 Discoveries Creativity and the arts subsumed everyday life Technologically advanced techniques used No direct evidence but
HISTORY. Subject : History (For under graduate student) Topic No. & Title : Unit- 4 Indus Civilization Topic- c Chalcolithic Cultures of India
 HISTORY Subject : History (For under graduate student) Paper No. : Paper-I History of India Topic No. & Title : Unit- 4 Indus Civilization Topic- c Chalcolithic Cultures of India Lecture No. & Title :
HISTORY Subject : History (For under graduate student) Paper No. : Paper-I History of India Topic No. & Title : Unit- 4 Indus Civilization Topic- c Chalcolithic Cultures of India Lecture No. & Title :
An early pot made by the Adena Culture (800 B.C. - A.D. 100)
 Archaeologists identify the time period of man living in North America from about 1000 B.C. until about 700 A.D. as the Woodland Period. It is during this time that a new culture appeared and made important
Archaeologists identify the time period of man living in North America from about 1000 B.C. until about 700 A.D. as the Woodland Period. It is during this time that a new culture appeared and made important
THE HARAPPAN GENIUS. Bronze Chariot, Daimabad
 THE HARAPPAN GENIUS Bronze Chariot, Daimabad The early years of the 20 TH Century witnessed the discovery of remains of the Indus civilization simultaneously at Harappa & Mohenjodaro, revealing to the
THE HARAPPAN GENIUS Bronze Chariot, Daimabad The early years of the 20 TH Century witnessed the discovery of remains of the Indus civilization simultaneously at Harappa & Mohenjodaro, revealing to the
1. Introduction. 2. A Shang Capital City
 1. Introduction In ancient times, most of China s early farmers settled on the North China Plain, near the Huang He (Yellow River). In this chapter, you will explore one of China s earliest dynasties,
1. Introduction In ancient times, most of China s early farmers settled on the North China Plain, near the Huang He (Yellow River). In this chapter, you will explore one of China s earliest dynasties,
Ancient History for APSC
 EXAMPAGAL.COM Ancient History for APSC State civil services Pre/Mains Exampagal.com Contents India - Geographical Features and their Impact on History Pre-Historic India and the Harappan Culture The Vedic
EXAMPAGAL.COM Ancient History for APSC State civil services Pre/Mains Exampagal.com Contents India - Geographical Features and their Impact on History Pre-Historic India and the Harappan Culture The Vedic
BRICKS, BEADS AND BONES
 BRICKS, BEADS AND BONES Q. Would you agree that the drainage system of the Harappan cities indicates town-planning? Give reasons for your answer. Ans. i. We completely agree with the fact that all the
BRICKS, BEADS AND BONES Q. Would you agree that the drainage system of the Harappan cities indicates town-planning? Give reasons for your answer. Ans. i. We completely agree with the fact that all the
The Shang Dynasty CHAPTER Introduction. 4 A chariot buried in a Shang ruler's tomb was to serve the king in the afterlife.
 4 A chariot buried in a Shang ruler's tomb was to serve the king in the afterlife. CHAPTER I The Shang Dynasty 20.1 Introduction In Chapter 19, you explored five geographic regions of China. You learned
4 A chariot buried in a Shang ruler's tomb was to serve the king in the afterlife. CHAPTER I The Shang Dynasty 20.1 Introduction In Chapter 19, you explored five geographic regions of China. You learned
Moray Archaeology For All Project
 School children learning how to identify finds. (Above) A flint tool found at Clarkly Hill. Copyright: Leanne Demay Moray Archaeology For All Project ational Museums Scotland have been excavating in Moray
School children learning how to identify finds. (Above) A flint tool found at Clarkly Hill. Copyright: Leanne Demay Moray Archaeology For All Project ational Museums Scotland have been excavating in Moray
Ancient Mesopotamia and the Sumerians (Room 56)
 Ancient Mesopotamia and the Sumerians (Room 56) The Sumerians are thought to have formed the first human civilization in world history. They lived in southern Mesopotamia, between the Tigris and Euphrates
Ancient Mesopotamia and the Sumerians (Room 56) The Sumerians are thought to have formed the first human civilization in world history. They lived in southern Mesopotamia, between the Tigris and Euphrates
January 13 th, 2019 Sample Current Affairs
 January 13 th, 2019 Sample Current Affairs 1. Harappa grave of ancient 'couple' reveals secrets of Marriage What are the key takeaways of the excavation? Was marriage legally accepted in Harappan society?
January 13 th, 2019 Sample Current Affairs 1. Harappa grave of ancient 'couple' reveals secrets of Marriage What are the key takeaways of the excavation? Was marriage legally accepted in Harappan society?
Foods of Mesopotamia/Sumer: YOUR TURN! Draw a picture in each box. barley onions apples (for bread/beer) sheep cucumbers figs
 Civilization of Sumer FOOD SUPPLY: The people of Sumer created the first civilization, advancing their way of life over time. The first step towards creating a civilization was when the Sumerians established
Civilization of Sumer FOOD SUPPLY: The people of Sumer created the first civilization, advancing their way of life over time. The first step towards creating a civilization was when the Sumerians established
Excavations at Shikarpur, Gujarat
 Excavations at Shikarpur, Gujarat 2008-2009 The Department of Archaeology and Ancient History, the M. S. University of Baroda continued excavations at Shikarpur in the second field season in 2008-09. In
Excavations at Shikarpur, Gujarat 2008-2009 The Department of Archaeology and Ancient History, the M. S. University of Baroda continued excavations at Shikarpur in the second field season in 2008-09. In
Art History: Introduction 10 Form 5 Function 5 Decoration 5 Method 5
 Art History: Introduction 10 Form 5 Function 5 Decoration 5 Method 5 Pre-Christian Ireland Intro to stone age art in Ireland Stone Age The first human settlers came to Ireland around 7000BC during the
Art History: Introduction 10 Form 5 Function 5 Decoration 5 Method 5 Pre-Christian Ireland Intro to stone age art in Ireland Stone Age The first human settlers came to Ireland around 7000BC during the
Archaeological Material From Spa Ghyll Farm, Aldfield
 Archaeological Material From Spa Ghyll Farm, Aldfield Introduction Following discussions with Linda Smith the Rural Archaeologist for North Yorkshire County Council, Robert Morgan of 3D Archaeological
Archaeological Material From Spa Ghyll Farm, Aldfield Introduction Following discussions with Linda Smith the Rural Archaeologist for North Yorkshire County Council, Robert Morgan of 3D Archaeological
Signatures of Human Settlements before 1500 BC in the Indian Sub-continent: Inputs from Archaeology
 Signatures of Human Settlements before 1500 BC in the Indian Sub-continent: Inputs from Archaeology Kulbhushan Mishra Indian Archaeological Society, New Delhi mishra90@gmail.com Vimal Tiwari Archaeological
Signatures of Human Settlements before 1500 BC in the Indian Sub-continent: Inputs from Archaeology Kulbhushan Mishra Indian Archaeological Society, New Delhi mishra90@gmail.com Vimal Tiwari Archaeological
Year 4- The Indus Valley
 Year 4- The Indus Valley Enquiry Question What is the evidence that the ancient civilization of the Indus Valley was a well-developed society? Learning Challenges Where and when did the ancient civilization
Year 4- The Indus Valley Enquiry Question What is the evidence that the ancient civilization of the Indus Valley was a well-developed society? Learning Challenges Where and when did the ancient civilization
Bricks, Beads and Bones The Harappan Civilisation
 1 THEME ONE Bricks, Beads and Bones The Harappan Civilisation The Harappan seal (Fig.1.1) is possibly the most distinctive artefact of the Harappan or Indus valley civilisation. Made of a stone called
1 THEME ONE Bricks, Beads and Bones The Harappan Civilisation The Harappan seal (Fig.1.1) is possibly the most distinctive artefact of the Harappan or Indus valley civilisation. Made of a stone called
Chapter 2 The First River-Valley Civilizations, B.C.E.
 Chapter 2 The First River-Valley Civilizations, 3500 1500 B.C.E. Gilgamesh Strangling a Lion This eighth-century B.C.E. sculpture of a king, possibly Gilgamesh, from the palace of the Assyrian king Sargon
Chapter 2 The First River-Valley Civilizations, 3500 1500 B.C.E. Gilgamesh Strangling a Lion This eighth-century B.C.E. sculpture of a king, possibly Gilgamesh, from the palace of the Assyrian king Sargon
01. Consider the following pairs. Which of the above pairs is/are correct? 02. Consider the following statements.
 0 Consider the following pairs. Harappan Sites Location Dholavira Gujarat Rakhigarhi Punjab 3. Ropar Haryana 4. Alamgirpur UP Which of the above pairs is/are correct? c. 1 and 4 only and 4 Rakhigarhi -
0 Consider the following pairs. Harappan Sites Location Dholavira Gujarat Rakhigarhi Punjab 3. Ropar Haryana 4. Alamgirpur UP Which of the above pairs is/are correct? c. 1 and 4 only and 4 Rakhigarhi -
Chinese Terracotta Warriors 210 BC
 Chinese Terracotta Warriors 210 BC Ideas of things to bring to class with you: Elements of Art Board Terracotta Warrior presentation CD Take Home Sheets (please make copies a day or two in advance) Clay
Chinese Terracotta Warriors 210 BC Ideas of things to bring to class with you: Elements of Art Board Terracotta Warrior presentation CD Take Home Sheets (please make copies a day or two in advance) Clay
The Jawan Chamber Tomb Adapted from a report by F.S. Vidal, Dammam, December 1953
 Figure 1 - The Jawan tomb as photographed from helicopter by Sgt. W. Seto, USAF, in May 1952 The Jawan Chamber Tomb Adapted from a report by F.S. Vidal, Dammam, December 1953 I. Description of work and
Figure 1 - The Jawan tomb as photographed from helicopter by Sgt. W. Seto, USAF, in May 1952 The Jawan Chamber Tomb Adapted from a report by F.S. Vidal, Dammam, December 1953 I. Description of work and
An Ancient Mystery UNIT 6 WEEK 4. Read the article An Ancient Mystery before answering Numbers 1 through 5.
 Read the article An Ancient Mystery before answering Numbers 1 through 5. UNIT 6 WEEK 4 An Ancient Mystery Thousands of years ago, pharaohs, or kings, ruled the kingdom of ancient Egypt. The pharaohs were
Read the article An Ancient Mystery before answering Numbers 1 through 5. UNIT 6 WEEK 4 An Ancient Mystery Thousands of years ago, pharaohs, or kings, ruled the kingdom of ancient Egypt. The pharaohs were
LE CATILLON II HOARD. jerseyheritage.org Association of Jersey Charities, No. 161
 LE CATILLON II HOARD CELTIC TRIBES This is a picture of the tribal structure of the Celtic Society CELTIC TRIBES Can you see three different people in the picture and suggest what they do? Can you describe
LE CATILLON II HOARD CELTIC TRIBES This is a picture of the tribal structure of the Celtic Society CELTIC TRIBES Can you see three different people in the picture and suggest what they do? Can you describe
Indus Valley Civilization - Study Materials
 INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION: The Indus Valley Civilisation was one of the first great civilisations having a writing system, urban centres and a diversified social and economic system. It appeared nearly
INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION: The Indus Valley Civilisation was one of the first great civilisations having a writing system, urban centres and a diversified social and economic system. It appeared nearly
Photographs. Unless otherwise acknowledged, all photographs are the property of Pearson Education, Inc.
 Photographs Every effort has been made to secure permission and provide appropriate credit for photographic material. The publisher deeply regrets any omission and pledges to correct errors called to its
Photographs Every effort has been made to secure permission and provide appropriate credit for photographic material. The publisher deeply regrets any omission and pledges to correct errors called to its
The Lost World of Old Europe The Danube Valley, BC
 INSTITUTE FOR THE STUDY OF THE ANCIENT WORLD School Group Information Packet The Lost World of Old Europe The Danube Valley, 5000-3500 BC November 11, 2009 April 25, 2010 Group of Anthropomorphic Figurines
INSTITUTE FOR THE STUDY OF THE ANCIENT WORLD School Group Information Packet The Lost World of Old Europe The Danube Valley, 5000-3500 BC November 11, 2009 April 25, 2010 Group of Anthropomorphic Figurines
Ancient Ireland. Mesolithic Neolithic Bronze Age Iron Age (Celts) Early Christian Ireland
 Ancient Ireland Mesolithic Neolithic Bronze Age Iron Age (Celts) Early Christian Ireland Stone Age Ireland The Mesolithic Period Middle Stone Age. 7000BC. First settlers. Ice Age sea levels lower as water
Ancient Ireland Mesolithic Neolithic Bronze Age Iron Age (Celts) Early Christian Ireland Stone Age Ireland The Mesolithic Period Middle Stone Age. 7000BC. First settlers. Ice Age sea levels lower as water
SCOTLAND. Belfast IRISH SEA. Dublin THE REPUBLIC OF IRELAND ENGLAND ENGLISH CHANNEL. Before and After
 ALL ABOUT BRITAIN This book tells the story of the people who have lived in the British Isles, and is packed with fascinating facts and f un tales. The British Isles is a group of islands that consists
ALL ABOUT BRITAIN This book tells the story of the people who have lived in the British Isles, and is packed with fascinating facts and f un tales. The British Isles is a group of islands that consists
UNIT 6 MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS
 UNIT 6 MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS Structure Objectives Introduction From Villages to Towns.and Cities Harappan Civilization : Sources Geographical Spread Important Centres 6.5.1 Harappa 6.5.2 Mohenjodaro
UNIT 6 MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS Structure Objectives Introduction From Villages to Towns.and Cities Harappan Civilization : Sources Geographical Spread Important Centres 6.5.1 Harappa 6.5.2 Mohenjodaro
Sandals were made out of deerskin. They were decorated with pompoms and bits of other hides.
 Mayan Sports The most well known sport in Mesoamerica is Pok-ta-tok. It s a ball game one played in a large open area called a court on teams of 2-7 players. Players would have used a small 5-pound solid
Mayan Sports The most well known sport in Mesoamerica is Pok-ta-tok. It s a ball game one played in a large open area called a court on teams of 2-7 players. Players would have used a small 5-pound solid
Viking Loans Box. Thor s Hammer
 Thor s Hammer Thor is the Viking god of storms and strength. He made thunder by flying across the sky in his chariot and is the most powerful Viking god. Thor is the protector of the other gods and uses
Thor s Hammer Thor is the Viking god of storms and strength. He made thunder by flying across the sky in his chariot and is the most powerful Viking god. Thor is the protector of the other gods and uses
Tomb Raider: A Mantle of the Expert for ancient Egypt Prepare your area as well as you can to look like the inside of a tomb. Make it as dark as
 Tomb Raider: A Mantle of the Expert for ancient Egypt Prepare your area as well as you can to look like the inside of a tomb. Make it as dark as possible, rearrange furniture and change its look with heavy
Tomb Raider: A Mantle of the Expert for ancient Egypt Prepare your area as well as you can to look like the inside of a tomb. Make it as dark as possible, rearrange furniture and change its look with heavy
ARCH202 History of Architecture Spring
 University of Nizwa College of Engineering & Architecture Dept. of Architecture & Interior Design ARCH202 History of Architecture Spring 2013-2014 Dr. Janon Kadhim Associate Professor of Architecture ARCH
University of Nizwa College of Engineering & Architecture Dept. of Architecture & Interior Design ARCH202 History of Architecture Spring 2013-2014 Dr. Janon Kadhim Associate Professor of Architecture ARCH
Overview: From Neolithic to Bronze Age, BC
 Overview: From Neolithic to Bronze Age, 8000-800 BC By Dr Francis Pryor Last updated 2011-02-28 The British Isles have been populated by human beings for hundreds of thousands of years, but it was the
Overview: From Neolithic to Bronze Age, 8000-800 BC By Dr Francis Pryor Last updated 2011-02-28 The British Isles have been populated by human beings for hundreds of thousands of years, but it was the
Cambridge Archaeology Field Group. Fieldwalking on the Childerley Estate, Cambridgeshire. Autumn 2014 to Spring Third interim report
 Cambridge Archaeology Field Group Fieldwalking on the Childerley Estate, Cambridgeshire Autumn 2014 to Spring 2015 Third interim report Summary Field walking on the Childerley estate of Martin Jenkins
Cambridge Archaeology Field Group Fieldwalking on the Childerley Estate, Cambridgeshire Autumn 2014 to Spring 2015 Third interim report Summary Field walking on the Childerley estate of Martin Jenkins
Arsitektur & Seni SEJARAH ARSITEKTUR. Marble (granite) figure
 Marble (granite) figure More than 4,000 years ago the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers began to teem with life--first the Sumerian, then the Babylonian, Assyrian, Chaldean, and Persian empires.
Marble (granite) figure More than 4,000 years ago the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers began to teem with life--first the Sumerian, then the Babylonian, Assyrian, Chaldean, and Persian empires.
Native Americans On the the North American Content. Map of Hopi Land. Hopi 9/12/2015. Native American Indians 1
 Native Americans On the the North American Content Map of Hopi Land The Hopi Indians lived in the southwest dessert are of Arizona Hopi Homes were made of adobe (clay and straw) Each home housed one family
Native Americans On the the North American Content Map of Hopi Land The Hopi Indians lived in the southwest dessert are of Arizona Hopi Homes were made of adobe (clay and straw) Each home housed one family
STONES OF STENNESS HISTORIC ENVIRONMENT SCOTLAND STATEMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE
 Property in Care (PIC) ID: PIC321 Designations: Scheduled Monument (SM90285); Taken into State care: 1906 (Guardianship) Last reviewed: 2003 HISTORIC ENVIRONMENT SCOTLAND STATEMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE STONES
Property in Care (PIC) ID: PIC321 Designations: Scheduled Monument (SM90285); Taken into State care: 1906 (Guardianship) Last reviewed: 2003 HISTORIC ENVIRONMENT SCOTLAND STATEMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE STONES
For Creative Minds. Mummy Country Continent. Mummy Map
 For Creative Minds This section may be photocopied or printed from our website by the owner of this book for educational, non-commercial use. Cross-curricular teaching activities for use at home or in
For Creative Minds This section may be photocopied or printed from our website by the owner of this book for educational, non-commercial use. Cross-curricular teaching activities for use at home or in
Each object here must have served a purpose. Archaeologists must do their best to explain what that purpose was.
 Archaeologists have to use many different forms of reasoning to decipher the what and how about artifacts they discover. I mean seriously, what in the world are these things? Each object here must have
Archaeologists have to use many different forms of reasoning to decipher the what and how about artifacts they discover. I mean seriously, what in the world are these things? Each object here must have
The origin of man is believed to have started some 3 million years ago in southern Africa.
 The origin of man is believed to have started some 3 million years ago in southern Africa. Thousands of years ago Human migratory patterns can be traced back almost 200,000 years by using bones, tools
The origin of man is believed to have started some 3 million years ago in southern Africa. Thousands of years ago Human migratory patterns can be traced back almost 200,000 years by using bones, tools
PART 2 TEACHERS NOTES GO ROMAN THEME 3: OFF DUTY LET S INVESTIGATE NOTES AND OBJECT CHECKLIST
 PART 2 TEACHERS NOTES GO ROMAN THEME 3: LET S INVESTIGATE NOTES AND OBJECT CHECKLIST GO ROMAN THEME 3: When on duty, the soldiers were occupied with training, patrolling the Wall and carrying out maintenance
PART 2 TEACHERS NOTES GO ROMAN THEME 3: LET S INVESTIGATE NOTES AND OBJECT CHECKLIST GO ROMAN THEME 3: When on duty, the soldiers were occupied with training, patrolling the Wall and carrying out maintenance
The Euphrates Valley Expedition
 The Euphrates Valley Expedition HANS G. GUTERBOCK, Director MAURITS VAN LOON, Field Director For the third consecutive year we have spent almost three months digging at Korucutepe, the site assigned to
The Euphrates Valley Expedition HANS G. GUTERBOCK, Director MAURITS VAN LOON, Field Director For the third consecutive year we have spent almost three months digging at Korucutepe, the site assigned to
Primary Sources: Carter's Discovery of King Tutankhamun's Tomb
 Primary Sources: Carter's Discovery of King Tutankhamun's Tomb By Original transcription from the Griffith Institute, University of Oxford, adapted by Newsela staff on 08.08.16 Word Count 1,029 Level 1120L
Primary Sources: Carter's Discovery of King Tutankhamun's Tomb By Original transcription from the Griffith Institute, University of Oxford, adapted by Newsela staff on 08.08.16 Word Count 1,029 Level 1120L
Find out more about jeans
 INFO. SHEET Find out more about jeans We all wear jeans but how do we decide which ones to buy? Is it the cost, the style, or the shop they come from which is most important? Making jeans is big business
INFO. SHEET Find out more about jeans We all wear jeans but how do we decide which ones to buy? Is it the cost, the style, or the shop they come from which is most important? Making jeans is big business
T so far, by any other ruins in southwestern New Mexico. However, as
 TWO MIMBRES RIVER RUINS By EDITHA L. WATSON HE ruins along the Mimbres river offer material for study unequaled, T so far, by any other ruins in southwestern New Mexico. However, as these sites are being
TWO MIMBRES RIVER RUINS By EDITHA L. WATSON HE ruins along the Mimbres river offer material for study unequaled, T so far, by any other ruins in southwestern New Mexico. However, as these sites are being
Cambridge Archaeology Field Group. Fieldwalking on the Childerley Estate Cambridgeshire
 Cambridge Archaeology Field Group Fieldwalking on the Childerley Estate Cambridgeshire 2009 to 2014 Summary Fieldwalking on the Childerley estate of Martin Jenkins and Family has revealed, up to March
Cambridge Archaeology Field Group Fieldwalking on the Childerley Estate Cambridgeshire 2009 to 2014 Summary Fieldwalking on the Childerley estate of Martin Jenkins and Family has revealed, up to March
Digging for Sangam glory
 Know Meet Work Talk Cover Watch Read Takeaway Play Explore Hang Shoot Digging for Sangam glory Sibi Arasu 1 of 5 9/24/16, 12:23 AM The big scoop: The Archaeological Survey of India s excavation site in
Know Meet Work Talk Cover Watch Read Takeaway Play Explore Hang Shoot Digging for Sangam glory Sibi Arasu 1 of 5 9/24/16, 12:23 AM The big scoop: The Archaeological Survey of India s excavation site in
Latest archaeological finds at Must Farm provide a vivid picture of everyday life in the Bronze Age 14 July 2016
 Latest archaeological finds at Must Farm provide a vivid picture of everyday life in the Bronze Age 14 July 2016 Simplified schematic representation of a typical house at the Must farm settlement. The
Latest archaeological finds at Must Farm provide a vivid picture of everyday life in the Bronze Age 14 July 2016 Simplified schematic representation of a typical house at the Must farm settlement. The
History Around 800 BC, Etruscans settle in Etruria, north of the Palatine. Historians believe first that they came from Lydia in Asia Minor.
 Founding of Rome In 1200 BC, after the fall of Troy, the gods ordered Aeneas to lead his people to the promised land. Aeneas's group joined forces with Latins in Italy. Groups with iron weapons invaded
Founding of Rome In 1200 BC, after the fall of Troy, the gods ordered Aeneas to lead his people to the promised land. Aeneas's group joined forces with Latins in Italy. Groups with iron weapons invaded
Unit 6: New Caledonia: Lapita Pottery. Frederic Angleveil and Gabriel Poedi
 Unit 6: New Caledonia: Lapita Pottery Frederic Angleveil and Gabriel Poedi Facts Capital Main islands Highest point Language Government Noumea Grande Terre, 3 Loyalty Islands and numerous reefs and atolls
Unit 6: New Caledonia: Lapita Pottery Frederic Angleveil and Gabriel Poedi Facts Capital Main islands Highest point Language Government Noumea Grande Terre, 3 Loyalty Islands and numerous reefs and atolls
BLACK HISTORY MONTH - Week 1 #BlackHistoryMatters
 BLACK HISTORY MONTH - Week 1 #BlackHistoryMatters classroomconnection.ca WEEK 1: AFRICAN CIVILIZATIONS Africa is the cradle of humankind and Nubia, an early African society, is the oldest civilization
BLACK HISTORY MONTH - Week 1 #BlackHistoryMatters classroomconnection.ca WEEK 1: AFRICAN CIVILIZATIONS Africa is the cradle of humankind and Nubia, an early African society, is the oldest civilization
FORGOTTEN CITI ES ON THE INDUS
 FORGOTTEN CT ES ON THE NDUS Early Civilization in Pakistan from the 8th to the 2nd Millennium BC Edited by Michael Jansen, Maire Mulloy and Gunter Urban VERLAG PHLPP VON ZABERN. MANZ. GERMANY --.---_.._.....-
FORGOTTEN CT ES ON THE NDUS Early Civilization in Pakistan from the 8th to the 2nd Millennium BC Edited by Michael Jansen, Maire Mulloy and Gunter Urban VERLAG PHLPP VON ZABERN. MANZ. GERMANY --.---_.._.....-
NUBIAN EXPEDITION. oi.uchicago.edu. Keith C. Seele, Field Director
 NUBIAN EXPEDITION Keith C. Seele, Field Director Time for contemplation is seldom available in the field during an Oriental Institute season of excavation. But matters are scarcely better after the return
NUBIAN EXPEDITION Keith C. Seele, Field Director Time for contemplation is seldom available in the field during an Oriental Institute season of excavation. But matters are scarcely better after the return
Early African Art. By Anthony Sacco (Late African Art by Caroline DelVecchio)
 Early African Art By Anthony Sacco (Late African Art by Caroline DelVecchio) -Sub-Saharan = Africa with the exception of the Mediterranean Coast (Egypt, Morocco, etc.) -Mihrab = A niche that points to
Early African Art By Anthony Sacco (Late African Art by Caroline DelVecchio) -Sub-Saharan = Africa with the exception of the Mediterranean Coast (Egypt, Morocco, etc.) -Mihrab = A niche that points to
good for you be here again down at work have been good with his cat
 Fryʼs Phrases This list of 600 words compiled by Edward Fry contain the most used words in reading and writing. The words on the list make up almost half of the words met in any reading task. The words
Fryʼs Phrases This list of 600 words compiled by Edward Fry contain the most used words in reading and writing. The words on the list make up almost half of the words met in any reading task. The words
Murdering Microbeads. Year 5
 Murdering Microbeads Year 5 What did we do? Abstract We conducted an investigation to find out if selected facial scrubs contain plastic/polypropylene microbeads and if so, how much. Why did we do this?
Murdering Microbeads Year 5 What did we do? Abstract We conducted an investigation to find out if selected facial scrubs contain plastic/polypropylene microbeads and if so, how much. Why did we do this?
What Scientists Just Found Deep In The Ocean Is Seriously Unbelievable.
 What Scientists Just Found Deep In The Ocean Is Seriously Unbelievable. Off the coast of Egypt divers have discovered something that was thought to be lost a long time ago. It was said that the ancient
What Scientists Just Found Deep In The Ocean Is Seriously Unbelievable. Off the coast of Egypt divers have discovered something that was thought to be lost a long time ago. It was said that the ancient
Classroom Activity Ideas
 Classroom Activity Ideas We hope that a visit to the exhibition Constantine the Great will inspire you to try some of these follow-up classroom activities! These activities have been designed for Key Stage
Classroom Activity Ideas We hope that a visit to the exhibition Constantine the Great will inspire you to try some of these follow-up classroom activities! These activities have been designed for Key Stage
PREHISTORIC ARTEFACT BOX
 PREHISTORIC ARTEFACT BOX PREHISTORIC ARTEFACT BOX: COMPLETE BOX 1 Antler Retoucheur 11 Leather Cup 2 Flint Retoucheur 12 Flint Scrapers [1 large & 4 x small] in pouch 3 Hammer Stone 13 Flint Arrowheads
PREHISTORIC ARTEFACT BOX PREHISTORIC ARTEFACT BOX: COMPLETE BOX 1 Antler Retoucheur 11 Leather Cup 2 Flint Retoucheur 12 Flint Scrapers [1 large & 4 x small] in pouch 3 Hammer Stone 13 Flint Arrowheads
FOUR CYLINDER SEALS FROM KITION
 FOUR CYLINDER SEALS FROM KITION by V. E. G. KENNA and V. KARAGEORGHIS (a) KITION Kition, near modern Larnaca on the south coast of Cyprus, discovered as recently as 1959, seems to have been an important
FOUR CYLINDER SEALS FROM KITION by V. E. G. KENNA and V. KARAGEORGHIS (a) KITION Kition, near modern Larnaca on the south coast of Cyprus, discovered as recently as 1959, seems to have been an important
Wisconsin Sites Page 61. Wisconsin Sites
 Wisconsin Sites Page 61 Silver Mound-A Quarry Site Wisconsin Sites Silver Mound in Jackson County is a good example of a quarry site where people gathered the stones to make their tools. Although the name
Wisconsin Sites Page 61 Silver Mound-A Quarry Site Wisconsin Sites Silver Mound in Jackson County is a good example of a quarry site where people gathered the stones to make their tools. Although the name
Berkshire West Berkshire Tidmarsh E of the River Pang, on footpath running W-E from Sulham Hill to Sulham Lane, N of Oaklands Farm.
 5. Annex COMPONENTS OF DEFENCE AREA 7 Details of the defence works shown on Map 2 are given below. The listing is arranged in sequence of the unique database record numbers that are also given on the map.
5. Annex COMPONENTS OF DEFENCE AREA 7 Details of the defence works shown on Map 2 are given below. The listing is arranged in sequence of the unique database record numbers that are also given on the map.
UNCOVERING THE PAST CHAPTER 1
 Uncovering the past 00 Page 1 Monday, August 5, 2002 8:10 AM CHAPTER 1 UNCOVERING THE PAST When archaeologists uncover evidence of the past, they are finding objects that were made to last, or everyday
Uncovering the past 00 Page 1 Monday, August 5, 2002 8:10 AM CHAPTER 1 UNCOVERING THE PAST When archaeologists uncover evidence of the past, they are finding objects that were made to last, or everyday
World History 9 th Grade Emergence of Complex Society in East Asia Unit 4.2 Lesson 1 Lesson 1: Historical Context
 Lesson 1: Historical Context This unit addresses all Three Essential Questions, Humans and the Environment, Humans and Other Humans, Humans and Ideas. First, by their nature the earliest complex societies
Lesson 1: Historical Context This unit addresses all Three Essential Questions, Humans and the Environment, Humans and Other Humans, Humans and Ideas. First, by their nature the earliest complex societies
Ancient Chinese Chariots
 Reading Practice Ancient Chinese Chariots A The Shang Dynasty or Yin Dynasty, according to traditional historiography, ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium. Archaeological work at
Reading Practice Ancient Chinese Chariots A The Shang Dynasty or Yin Dynasty, according to traditional historiography, ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium. Archaeological work at
Chapter 2. Remains. Fig.17 Map of Krang Kor site
 Chapter 2. Remains Section 1. Overview of the Survey Area The survey began in January 2010 by exploring the site of the burial rootings based on information of the rooted burials that was brought to the
Chapter 2. Remains Section 1. Overview of the Survey Area The survey began in January 2010 by exploring the site of the burial rootings based on information of the rooted burials that was brought to the
Artifacts. Antler Tools
 Artifacts Artifacts are the things that people made and used. They give a view into the past and a glimpse of the ingenuity of the people who lived at a site. Artifacts from the Tchefuncte site give special
Artifacts Artifacts are the things that people made and used. They give a view into the past and a glimpse of the ingenuity of the people who lived at a site. Artifacts from the Tchefuncte site give special
THE HOHOKAM. Origins. Prehistoric Irrigation
 THE HOHOKAM PrintFeedback Share & BookmarkPress Enter to show all options, press Tab go to next option Font Size:+- Origins Where did Hohokam culture come from? To the first scientists who asked this question,
THE HOHOKAM PrintFeedback Share & BookmarkPress Enter to show all options, press Tab go to next option Font Size:+- Origins Where did Hohokam culture come from? To the first scientists who asked this question,
1. Presumed Location of French Soundings Looking NW from the banks of the river.
 SG02? SGS SG01? SG4 1. Presumed Location of French Soundings Looking NW from the banks of the river. The presumed location of SG02 corresponds to a hump known locally as the Sheikh's tomb. Note also (1)
SG02? SGS SG01? SG4 1. Presumed Location of French Soundings Looking NW from the banks of the river. The presumed location of SG02 corresponds to a hump known locally as the Sheikh's tomb. Note also (1)
h i s t om b an d h i s t r e a su r e s Worksheet CArter ArChAeoLoGY
 1 Worksheet CARTER ARCHAEOLOGY 2 1. Howard Carter s discovery Text A The Valley of the Kings The Valley of the Kings is on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the ancient city of Thebes. Thebes is called
1 Worksheet CARTER ARCHAEOLOGY 2 1. Howard Carter s discovery Text A The Valley of the Kings The Valley of the Kings is on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the ancient city of Thebes. Thebes is called
Cetamura Results
 Cetamura 2000 2006 Results A major project during the years 2000-2006 was the excavation to bedrock of two large and deep units located on an escarpment between Zone I and Zone II (fig. 1 and fig. 2);
Cetamura 2000 2006 Results A major project during the years 2000-2006 was the excavation to bedrock of two large and deep units located on an escarpment between Zone I and Zone II (fig. 1 and fig. 2);
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 16 Egypt through Naqada II Copyright Bruce Owen 2009
 Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 16 Egypt through Naqada II Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Egypt: The setting The Nile Flows NORTH, into the Mediterranean Sea (up on the map) so the UPPER Nile
Emergence of Civilizations / Anthro 341: Notes 16 Egypt through Naqada II Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Egypt: The setting The Nile Flows NORTH, into the Mediterranean Sea (up on the map) so the UPPER Nile
British Museum's Afghan exhibition extended due to popular demand
 City Tourism British Museum's Afghan exhibition extended due to popular demand ITM correspondent The British Museum's exhibition Afghanistan: Crossroads of the Ancient World has been extended until 17
City Tourism British Museum's Afghan exhibition extended due to popular demand ITM correspondent The British Museum's exhibition Afghanistan: Crossroads of the Ancient World has been extended until 17
Experiential Activity: Ancient Artifacts
 Experiential Activity: Ancient Artifacts Dig Site: Ancient Mesopotamia Artifact 1--Mesopotamia ARTIFACT 1 (Mesopotamia)--Details (close ups) from artifact: Artifact 2--Mesopotamia Artifact 3--Mesopotamia
Experiential Activity: Ancient Artifacts Dig Site: Ancient Mesopotamia Artifact 1--Mesopotamia ARTIFACT 1 (Mesopotamia)--Details (close ups) from artifact: Artifact 2--Mesopotamia Artifact 3--Mesopotamia
Colonial Cape Fear: Object Resource List
 Colonial Cape Fear: Object Resource List Clothing Tricorn-style Hat Three point hat worn by men. Shirt Cotton shirt worn by men. Boys wore similar shirts. Coat Wool coat with linen lining worn by men.
Colonial Cape Fear: Object Resource List Clothing Tricorn-style Hat Three point hat worn by men. Shirt Cotton shirt worn by men. Boys wore similar shirts. Coat Wool coat with linen lining worn by men.
Nubia. Sphinx of Taharqo Kawa, Sudan 680 BC. Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2
 Sphinx of Taharqo Kawa, Sudan 680 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities During your visit Gallery
Sphinx of Taharqo Kawa, Sudan 680 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities During your visit Gallery
Decorative Styles. Amanda Talaski.
 Decorative Styles Amanda Talaski atalaski@umich.edu Both of these vessels are featured, or about to be featured, at the Kelsey Museum. The first vessel is the third object featured in the Jackier Collection.
Decorative Styles Amanda Talaski atalaski@umich.edu Both of these vessels are featured, or about to be featured, at the Kelsey Museum. The first vessel is the third object featured in the Jackier Collection.
The ancient Egyptians believed that mummification would guarantee the soul passage into the next life. In no other civilization have such elaborate
 Video The ancient Egyptians believed that mummification would guarantee the soul passage into the next life. In no other civilization have such elaborate preparations for the afterlife been made in the
Video The ancient Egyptians believed that mummification would guarantee the soul passage into the next life. In no other civilization have such elaborate preparations for the afterlife been made in the
Anglo Saxon Introduce Me
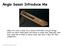 Anglo Saxon Introduce Me Hello, I m a lyre or harp. I m a musical instrument. I ve got strings which you pluck. When poets tell stories or songs they often play their harp. Kings like to listen to stories
Anglo Saxon Introduce Me Hello, I m a lyre or harp. I m a musical instrument. I ve got strings which you pluck. When poets tell stories or songs they often play their harp. Kings like to listen to stories
16 members of the Fieldwalking Group met York Community Archaeologist Jon Kenny at Lou Howard s farm, Rose Cottage Farm, at
 Terrington History Group Fieldwalking Group Field 1 Final report 21 October 2011 - fieldwalking 16 members of the Fieldwalking Group met York Community Archaeologist Jon Kenny at Lou Howard s farm, Rose
Terrington History Group Fieldwalking Group Field 1 Final report 21 October 2011 - fieldwalking 16 members of the Fieldwalking Group met York Community Archaeologist Jon Kenny at Lou Howard s farm, Rose
Melvin and Morris Explore Roatan, Honduras!
 Melvin and Morris Explore Roatan, Honduras! Morris and I have never seen a rainforest before, so we can t wait for our first glimpse of Roatan! Mom said we needed to have a good breakfast because we are
Melvin and Morris Explore Roatan, Honduras! Morris and I have never seen a rainforest before, so we can t wait for our first glimpse of Roatan! Mom said we needed to have a good breakfast because we are
Tell Shiyukh Tahtani (North Syria)
 Tell Shiyukh Tahtani (North Syria) Report of the 2010 excavation season conducted by the University of Palermo Euphrates Expedition by Gioacchino Falsone and Paola Sconzo In the summer 2010 the University
Tell Shiyukh Tahtani (North Syria) Report of the 2010 excavation season conducted by the University of Palermo Euphrates Expedition by Gioacchino Falsone and Paola Sconzo In the summer 2010 the University
included Harappa, and it is still called the Harappan Culture today in honour of that city, Mohenjo-daro, and Lothal, amongst others.
 Hello everyone, and welcome to Brains Matter s 24 th show for the 18 th of April, 2007. On today s show, I ll be talking about one of the oldest acknowledged civilisation in the world - the Indus Valley
Hello everyone, and welcome to Brains Matter s 24 th show for the 18 th of April, 2007. On today s show, I ll be talking about one of the oldest acknowledged civilisation in the world - the Indus Valley
INTRODUCTION Design develop the home decor articles inspired by the Royal Rajasthani jewelry. jewelry
 INTRODUCTION To relive monotony and add interesting look to his surroundings, to provide variety as well, man has tried to use various types of articles method and techniques of decoration. Till date he
INTRODUCTION To relive monotony and add interesting look to his surroundings, to provide variety as well, man has tried to use various types of articles method and techniques of decoration. Till date he
1 INTRODUCTION 1. Show the children the Great Hall Finds.
 This second activity in the How do archaeologists know these are royal sites? section follows on from the first, but can also be used as a stand-alone activity. This activity takes the children through
This second activity in the How do archaeologists know these are royal sites? section follows on from the first, but can also be used as a stand-alone activity. This activity takes the children through
